In this article, Palak Gurjar pursuing Diploma in Entrepreneurship Administration and Business Laws from NUJS, Kolkata, discusses Import duty on luxury cars such as Mercedes, BMW, Audi, Bentley, Jaguar, Rolls Royce and others.
Introduction
Customs duty which is also known as import duty has been in use since time immemorial. Some of the famous scholars like Smith asserts that the practice of taxing commerce is as old as commerce itself. The scope of customs duties has evolved in scope over time so much so that people started dividing custom duties into two types. One is Specific custom duties and the other is ad valorem duty.
Historically, countries apply custom duty for two main reasons. The first was to help fill the state coffers and to protect the domestic industries. It is in between 19th century and 20th century most state has made then own laws related to customs duty which is the main source of revenue to the government. Tax during medieval time was so much so that people started suffering.
History of customs duty
The concept of customs duty was first introduced in India in 1786 which erstwhile went through several changes. Lately several Acts like Sea Custom At 1894, Indian Stamp Act 1894, Air custom have been covered under the India Aircraft Act of 1911 and Land Customs Act 1924 was passed by the government of India. Eventually, all these Acts were consolidated and customized in one Act known as Custom Act 1962.
After the Act of 1962 various changes had been incorporated and the custom rates started declining since 1991. The peak customs rate during 1991 is 150% which drastically fall down to 40% in 1997-98. This rate again reached its peak with the imposition of a surcharge. Country like India, has been victim of various upward and downfall of the economy. The government never stopped and the renowned economist like Manmohan Singh and Raghuram Rajan helped the economy to come to the state of equilibrium
New Economic Policy 1991 and Import Duty
With the introduction of the New economic policy in India in the year 1991 which brought globalization and liberalization required that the trade knows no boundaries. It opened the gates to the global market. During that time exporting and importing is the only way to lift economy because every country has is endowed with some or the other advantage in resources and skills but not all. Therefore, to get access to the resources that are readily available in others country it is important to make those goods available through imports.
Import duty
Overview
Import duty is the concept that came into existence since time immemorial. It basically is duty or the tax that is levied by the government of any country and are due when any private individual or a commercial entity imparts anything within the geographical and its valuation method is CIF(Cost, Insurance and freight ).
Duty Rates and Sales Taxes
Duty can be ad valorem (as a percentage of value) or specific (rupees per unit). Duty rates fluctuation rate is very high if vary between 0% to 150% with 11.9% as an average. Goods like laptops and electronics products are never subject to duty. Till date there is no sales tax on the imported goods. All under the new Act all the goods are subject to tax regardless of their value.
History of imported goods in India
The 1st wheel alleged to have been used for transport about 4000 years ago but it was in 18th century that the 1st horseless carriage actually rolled on the road. In the India in 1897 that the Indian resident from Kolkata brought 1st car in India, subsequently in 1898 four cars were imported in Bombay one of them was owned by Jamshed Ji Tata. Generally, the import duty on all the luxury imported in India is 125% which obviously not a small cape of rate. Some few years back it was 60% which in 2014 jumped to 100%. Buyers of Lamborghini, Ferrari, Rolls Royce and Audi in India then switches to win – win situation for both the buyers and sellers where the buyer purchase second hand car from the seller. The selling price of the car might not be high in its home country but it gets costlier when it is imported because import duty on cars is calculated on CST (Cost, Insurance and Freight) which apparently makes is costly. Buyer prefers purchasing from seller because these cars are rarely driven especially in India where you have got such a pathetic road and are available in immaculate condition and prices that are much cheaper than the brand new one. A business man in Delhi had a budget of 2 crores and he wouldn’t mind spending 50 lakhs and ergo, he purchased a second hand Lamborghini Gallardo for 2.5 crore which otherwise a new brand Gallardo would have costed him 1 crore more.
Lamborghini
The government has raised the import duty to 167 on the luxury car which is getting Lamborghini the Italian car in trouble and the company expects its sales to be lower than the last year. It was comfortable for the big market players like Lamborghini, Audi, Rolls Royce if the government ease the import duty on the car and cap import duty at 2011 levels when it was 60% .
Rolls Royce
Rolls Royce a subsidiary of BMW has hoped to increase the sale by 70% in India but the increased import duty charges and weakness in the rupee are having an effect on price. In March, the customs duty on fully built cars coming into India whose price is US $40000 increased to 75% from 60%. Additional taxes and charges will gear up the total import casts to 140 % as against 110%.
Why so much of tax?
The reason behind the imposition of tax on the luxury car by the government is obviously to discourage the import of luxury car and encourage domestic manufacturer to build the car in the country itself which will eventually create more jobs and valuable transfer of technology takes places. It will give a good boost to the local economy. The main problem with Indian Taxation system is dealt according to Robin Hood policy takes from rich and give to the poor.

GST and its impact
Presently luxury cars are price as under:-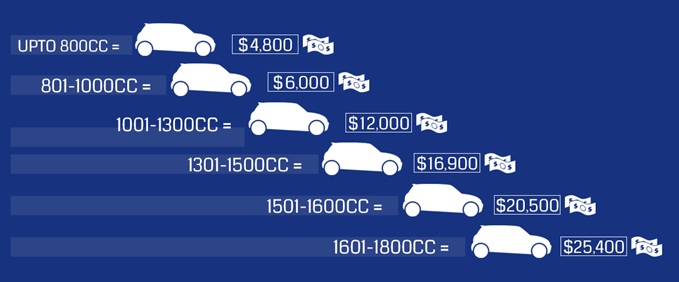
- Luxury –(less than 1500cc)Excise 22% +Cess 1.1%+VAT 14% =42.1%
- SUVs – (less than 1500 cc)Excise 30%+Cess 1.1%+VAT 14%=45.1%
Prior to GST, tax paid by the car manufacturer was 27.6%to 45% but after the GST it is between 17 to 18% and then it will be in the interest of the entire segment.
India is finally on the path of having a simplified taxation system and people are finally going to get rid of double taxation system. It is very important to understand the impact of GST on the car price.
- Small cars– Cars with under four-meter length powered by a petrol engine not greater than 1.2-litre or a diesel engine not greater than 1.5-litre by displacement.
- Mid-size cars– Cars over four-meter length powered by either a petrol or a diesel engine not greater than 1.5-litre displacement.
- Luxury cars– Cars over four-meter length powered by either petrol or a diesel engine that is greater than 1.5-litre displacement.
- SUVs– Cars over four-meter length and powered by either petrol or a diesel engine that is greater than 1.5-litre displacement.
Table – A
| Existing Taxes Levied | Proposed GST | ||||
| Base | Cess | Net | |||
| Small Cars | Petrol | 26% – 34% | 28% | 1% | 29% |
| Diesel | 27.5% – 35.5% | 28% | 3% | 31% | |
| Mid-size Cars | 40.5% – 48.5% | 28% | 15% | 43% | |
| Luxury Cars | 44.5% – 51.5% | 28% | 15% | 43% | |
| SUVs | 47.5% – 54.5% | 28% | 15% | 43% | |
Break-up of existing taxes mentioned in Table – A is as under in Table -B:
Table – B
| Excise | VAT | Infra Cess | Luxury Cess | Octroi (select states) | Green Cess (select states) | Total tax (incl. in ex-showroom price) | ||
| Small cars | Petrol | 12.5% | 12.5% – 14.5% | 1% | 1% for any car that costs over Rs 10 lakh | Around 4% in select states on all cars | 1% on Diesel vehicles with engine capacity exceeding 2000cc | ~26% – 34% |
| Diesel | 12.5% | 12.5% – 14.5% | 2.5% | ~27.5% – 35.5% | ||||
| Mid-size cars | 24% | 12.5% – 14.5% | 4% | ~ 40.5% – 48.5% | ||||
| Luxury cars | 27% | 12.5% – 14.5% | 4% | ~ 44.5% – 51.5% | ||||
| SUVs | 30% | 12.5% – 14.5% | 4% | ~ 47.5% – 54.5% |
Effect of GST on Car Import Duty
GST implementation will possess profit as well as loss for everyone. With the coming of the GST the government seeks to remove multiple indirect taxes imposed by the central and the state government. Also, the import duty on the luxury and sports car will drastically be reduced and now the imported cars can be purchased easily without paying heavy import duty. All the import duties on the entire luxury car with power 15000cc or more will be reduced by around 42%. With the coming of GST, it is domestic manufacturer like Tata who will have to face the stiff competition as the customs duty on imported cars is to large extent liberalized.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
https://t.me/joinchat/J_
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack









 Allow notifications
Allow notifications



There is an issue with this otherwise good blog. It states 15,000cc in the last paragraph, titled “Effect on..”. Kindly correct it to 1500cc. No car has a 15Litre engine. Lol.
Hello.. This blog is very helpful for getting a knowledge of how to trade globally. It is true that in the starting phase industrialist face difficulties when they trade globally. our organisation