This article is written by Srishti Kaushal, a first-year student of Rajiv Gandhi National University of Law, Punjab, pursuing B.A. LLB. (Hons.). In this article, she discussed the difference between the presidential and parliamentary forms of government, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Table of Contents
Introduction
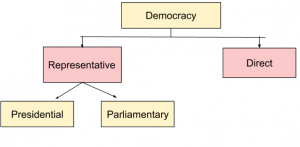
More than 50% of the world today has a democratic government, which allows for popular participation through the electoral process. These democratic governments can be representative or direct.
In a direct democracy, political power is placed in the hands of all individuals in the state who come together to make a decision. In a representative democracy, on the other hand, individuals that are elected through an electoral process act as intermediaries between the people of the state and the policy decisions. Basically, a person elected by the people takes decisions on their behalf.
Now a representative democracy can be divided into Parliamentary and Presidential democracy. In this article, we will discuss the features, advantages and disadvantages of both of these types of representative governments, and the difference between them.
Presidential form of government
A Presidential system is also called a congressional system. It refers to a system of governance in which the President is the Chief Executive and is elected directly by the people. The head of the government thus exists separately from the legislature. It is a form of government where the three branches (legislature, executive and judiciary) exist separately and cannot dismiss or dissolve the other branch. While the legislature makes the laws, the President enforces them and it is the courts that are responsible for exercising judicial duties.
The origin of the Presidential form of government can be traced back to medieval England, France and Scotland, where the executive authority lay with the Monarch or Crown (King/Queen) and not the estates of the realm (Parliament). This influenced the constitutional makers of the United States of America, who created the office of President, for which direct elections were to be held. Let’s have a look at the countries where the Presidential system is followed today.
|
Area |
Countries |
| Central and South America | The United States of America; Argentina; Bolivia; Brazil; Chile; Colombia; Costa Rica; Dominican Republic; Ecuador; El Salvador; Guatemala; Honduras; Mexico; Nicaragua; Panama; Paraguay; Peru; Uruguay; Venezuela. |
| Africa | Angola; Benin; Burundi; Cameroon; Central African Republic; Chad; Comoros; Republic of Congo; Gabon; Gambia; Ghana; Guinea; Kenya; Liberia; Malawi; Mozambique; Nigeria; Sierra Leone; Seychelles; Sudan; South Sudan; Tanzania; Togo; Zambia; Zimbabwe. |
| Asia | Indonesia; Maldives; Palau; Philippines; South Korea. |
| The Middle East and Central Asia | Afghanistan; Iran; Belarus; Cyprus; Kazakhstan; Tajikistan; Turkmenistan; Uzbekistan; Yemen. |
To understand this system better, let’s look at its features, advantages and disadvantages.
Features
The Presidential system of democratic governance has the following features:
- President does not have nominal powers. He is both the head of the executive and the head of the state. As the head of the executive, he has a ceremonial position. As the head of the government, he acts as the chief real executive. Thus, the Presidential system is characterised by a single executive concept.
- President is directly elected by the people or the electoral college.
- The President cannot be removed, except through an impeachment procedure for a grave unconstitutional act.
- The President governs with the help of a small body of people. This is his cabinet. The cabinet is only an advisory body which consists of non-elected departmental secretaries, who are selected by the president. It is responsible to the President, and the departmental secretaries can be removed by him.
- The President and his cabinet are not answerable to the legislature, nor are they members of the legislature.
- The concept of Separation of powers is clearly visible in the Presidential system. The three branches are completely separated and members of one branch cannot be the members of the other branch.
- The President can veto the acts of the legislature. He/She can also grant pardon.
Advantages
Now let’s look at the advantages of having a Presidential system:
- In most Presidential systems, the President is elected directly by the people. This creates more legitimacy than that of a leader who has been appointed indirectly.
- Since in a Presidential system the branches of the government work separately, it becomes easier to maintain the system checks and balances.
- The President, under this system, is usually less constrained and can take decisions more independently. Thus, this system allows for quick decision making. This becomes very beneficial at the time of crisis.
- A Presidential government is more stable. This is because the term of the President is fixed and is not subject to majority support in the legislative. Hence, he/she does not need to worry about losing the government.
- Since it is the President who chooses his cabinet and the executive need not be legislators, the President is able to choose experts in various fields to head relevant departments in his government. This ensures that only the people who are capable and knowledgeable form part of the government.
- Once the election is complete and the President gains power, the whole nation accepts him/her. Political rivalries are forgotten and people look at problems from a national view, rather than a party view.
Disadvantages
There are certain disadvantages which come with the Presidential System. Let’s understand what these are:
- The Presidential form of governance is autocratic as it places a lot of power in the hands of one person, i.e., the President. Also, the President is out of the control of the legislature.
- The complete separation between the legislature and executive may lead to conflicts and a deadlock between the executive and the legislature. The legislature may refuse to accept the policies of the executive; while the executive may not agree to the Acts passed by the legislature, and the President may even veto them.
- This system gives the President the power to choose the people of his choice for his cabinet to form the government. The President may misuse this power and choose his relatives, business partners etc, which might affect the political working of the state.
- It leads to less accountability in the government and may also result in the legislature and the executive playing the blame game in time of crisis.
Parliamentary form of government
A Parliamentary form of democracy is also known as the Cabinet form of government or the ‘Responsible Government’. It refers to a system of governance in which the citizens elect representatives to the legislative Parliament. This Parliament is responsible to make the decisions and laws for the state. It is also directly answerable to the people.
As a result of the elections, the party with the greatest representation forms the government. Its leader becomes the Prime Minister and performs various executive functions along with the members of Parliament appointed by the Prime Minister to the cabinet.
The parties who lose the elections form the minority and serve as opposition in the Parliament. These parties challenge the decisions of the party in power. The Prime Minister may be removed from power in case the members of Parliament lose confidence in him.
Attempts to create a system of Parliamentary democracy were seen in the European Revolution of 1848 but these did not lead to any consolidated system. Parliamentary democracy came to be in 1918 and developed throughout the twentieth century.
Let’s look at the countries which have a Parliamentary democracy.
|
Area |
Countries |
| North and South America | Antigua and Barbuda; The Bahamas; Barbados; Belize; Canada; Dominica; Grenada; Jamaica; Saint Kitts and Nevis; Saint Lucia; Saint Vincent and Grenadines; Trinidad and Tobago; Suriname. |
| Asia | Bangladesh; Bhutan; Cambodia; India; Iraq; Israel; Japan; Kuwait; Kyrgyzstan; Lebanon; Malaysia; Myanmar; Nepal; Pakistan; Singapore; Thailand. |
| Europe | Albania; Andorra; Armenia; Austria; Belgium; Bulgaria; Croatia; Czech Republic; Denmark; Estonia; Finland; Germany; Greece; Hungary; Iceland; Ireland; Italy; Kosovo; Latvia; Luxembourg; Malta; Moldova; Montenegro; Netherlands; North Macedonia; Norway; San Marino; Serbia; Slovakia; Slovenia; Spain; Sweden; Switzerland; United Kingdom. |
| Oceania | Australia; New Zealand; Papua New Guinea; Samoa; Vanuatu. |
Now let’s look at the features, advantages and disadvantages of Parliamentary form of government to understand it better.

Features
- The head of state and the head of government are different under the Parliamentary form of government. The head of the state is usually the President or monarch. He/she has only ceremonial powers. The head of the government is generally the Prime Minister and he/she is vested with real power.
- It can be either bicameral (with two houses) or unicameral (with one house). A bicameral system usually consists of a directly elected lower house, which in turn elects the upper house.
- The powers of government are not completely separated. The lines between the legislature and the executive are blurred as executive forms part of the legislature.
- This system is also characterised with the majority party rule. But no government can be a hundred percent majority, and the Parliament also consists of the opposition.
- The council of ministers, in this system, are collectively responsible to the Parliament. The lower house of Parliament can even dismiss the ruling government by passing a no confidence motion in the house.
- Most of the time, in this form of government the cabinet proceedings are kept secret and are not meant to be divulged to the public.
Advantages
Adopting a Parliamentary system of governance has certain advantages. Let’s look at these in detail:
- There is better coordination between the legislature and the executive. This is because executive is part of the legislature and most members of the lower house support the government . Thus, in Parliamentary system, there is lesser tendency of disputes and conflicts, which makes it comparatively easier to pass legislation and implement it.
- This type of government is more flexible as, if required, the Prime Minister can be changed. For instance, in the UK during the Second World War, Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain was replaced by Winston Churchill.
- A Parliamentary democracy allows representation of diverse groups. This system gives opportunities to various diverse ethical, racial, linguistic and ideological groups to share their views and enable making of better and suitable laws and policies.
- Since, the executive is responsible to the Parliament, it has the power to keep a check upon the activities of the executive. Moreover, the members of the Parliament can move resolutions, discuss matters and ask questions of public interest to put pressure on the government. This enables responsible governance.
- Parliamentary system prevents autocracy. This is because the executive is responsible to the legislature, and it is possible to vote out the Prime Minister through a no confidence motion. Thus, power does not get concentrated in the hands of only one person.
- In case, the no confidence motion is passed, the leader of the state invites the opposition to form the government. Thereby, this system provides an alternate government.
Disadvantages
The Parliamentary system also has certain disadvantages. These are:
- Because of party fragmentation, the legislators cannot exercise their free will and vote as per their own understanding and opinions. Rather, they have to follow the party policy.
- The system might lead to legislators who intend to enter the executive only. They are largely unqualified to legislate, which can hamper the working of the government.
- Since the executive is formed of the members of the winning party, it is not the experts who head the departments.
- Since, in the Parliamentary system, tenure of the council of ministers is completely dependant upon their popularity, there is no fixed tenure. Because of this they often hesitates to take bold and long-term policy decisions.
- Such governments might prove to be unstable. This is because the government exists only as long as they maintain majority support in the house. Many a times, when coalition parties come into power, the government is short lived and disputes arise. Because of this, the executive puts all of its focus upon staying in power, rather than worrying about the welfare of people and state of affairs.
In India
In India, the system of democracy which exists is the Parliamentary Democracy. This model has been borrowed from the UK, but there are certain differences:
- While in the UK, the Prime Minister can only be from the lower house, in India, the Prime Minister can be from both Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha.
- While in the UK once a person is appointed as the speaker, he/she ceases to be a member of his/her party, in India, the speaker continues to be a member of his/her party but must make sure that he/she is impartial in the proceedings.
Difference between the Parliamentary and Presidential forms of the Government
| Basis | Parliamentary Form of Government | Presidential Form of Government |
| Meaning | It is a form of government where the legislature and executive are closely related to each other. It is a system in which the citizens elect representatives to the legislative Parliament. | It is a system of government in which the three organs of the government – the executive, judiciary, legislature work separately. In it, the President is the chief executive and is elected directly by the citizens. |
| Executive | There is dual executive as leader of the state and leader of the government are different. | There is a single executive as the leader of the state and the leader of the government is the same. |
| Ministers | The ministers belong to the ruling party and are Members of Parliament. No outsider is allowed to become a minister. | The ministers can be chosen from outside the legislature, and are usually industry experts. |
| Accountability | The Executive is accountable to the Legislature. | The Executive is not accountable to the Legislature. |
| Dissolution of lower house | The Prime Minister can dissolve the lower house. | The President cannot dissolve the lower house. |
| Tenure | The tenure of the Prime Minister depends upon the majority support in the Parliament, and is thus, not fixed. | The tenure of the President is fixed. |
| Separation of Powers | The principle of Separation of powers is not followed strictly. There is concentration and fusion of powers between the Legislative and the Executive. | The principle of Separation of powers is strictly followed. Powers are divided and the Legislature, the Executive and the Judiciary work separately. |
| Party Discipline | Party discipline is stronger and the system leans towards unified action, block voting and distinct party platforms. | Party discipline is comparatively less and failure to vote with one’s party does not threaten the government. |
| Autocracy | This type of government is less autocratic as immense power is not given to only one person. | This type of government is more autocratic as immense power is concentrated in the hands of the President. |
Conclusion
The system of governance in countries differs depending on whether a country has a Presidential or Parliamentary system. There are some countries who have adopted a mixture of both these types as well. These systems have multiple differences based on separation of powers, accountability, executives etc.
Both of these systems come with their own advantages and disadvantages. A country chooses the system which suits it the most. The Parliamentary system allows representative governance, which is suitable in a diverse country like India.
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/social-sciences/Parliamentary-democracy.
- https://byjus.com/free-ias-prep/Presidential-and-Parliamentary-form-of-government/.
- https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/Parliamentary-system-in-india-1437202137-1.
- https://www.lawteacher.net/free-law-essays/administrative-law/the-Presidential-and-Parliamentary-governance-forms-administrative-law-essay.php.
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skills.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals, and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
Follow us on Instagram and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more amazing legal content.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack











 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


