This article is written by Yamini Nijhawan, pursuing a Diploma in Advanced Contract Drafting, Negotiation and Dispute Resolution from Lawsikho.com.
Table of Contents
History of Limited Liability Partnership in India
To adopt Limited Liability Partnership in India few recommendations and suggestions were made by J.J. Irani Committee, The Bhatt Committee in 1972, Naik Committee in 1992, Expert Committee on Development of Small Sector Enterprises headed by Sh. Abid Hussain in 1997, Study Group on Development of Small Sector Enterprises (SSEs) headed by Dr S.P. Gupta in 2001and the Naresh Chandra Committee-II.
The Cabinet approved the Bill on December 7, 2006, which was then presented before Rajya Sabha on December 15, 2006. The Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Bill, 2008 received the approval of the Cabinet on 1st May 2008. Both Houses of Parliament passed the bill without any changes.
The Bill received the assent of the President on 7th January 2009. In India, The Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 was published in the official Gazette of India on January 9, 2009, and has been notified with effect from 31 March 2009. The LLP Act, 2008 thereby makes provision for the formation and regulation of limited liability partnerships and matters connected with it.
In India, The Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 was published in the official Gazette of India on January 9, 2009, and has been notified with effect from 31 March 2009. The LLP Act, 2008 thereby makes provision for the formation and regulation of limited liability partnerships and matters connected with it.
Meaning of Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
LLP is a Limited Liability Partnership is a corporate business vehicle that provides the benefits of limited liability of a company to its members and also allows to manage their internal management on the basis of mutually arrived agreement as in case of a partnership firm. Partners have lower liabilities to any debt which may arise in future in running the business. It contains elements of both ‘a corporate structure’ as well as ‘a partnership firm structure’ and is called a hybrid between a company and a partnership. The Partners are required to contribute towards the LLP as specified in the LLP Agreement. Their share can be in any form i.e. tangible or intangible, movable or immovable property, monies and cash.
In terms of liability under Limited Liability Partnership the Company is liable for losses or debts if arise in running the business where the individual members of the LLP shall not be liable for such losses or debts.
Example
XYZ LLP has 2 partners J and K, XYZ takes a loan of Rs.20 lakhs and is unable to repay the loan. Its capital is Rs. 10 lakhs where J is supposed to contribute Rs. 6 lakhs and K Rs. 4 lakhs but both the partners contribute s. 5 lakhs as J contributed Rs. 3 lakhs and K contributed Rs. 2 lakhs. In such a case LLP will be liable for up to the amount of Capital i.e. Rs. 10 lakhs and J and K will be liable for Rs. 5 lakhs as per their share of contribution. The Creditors cannot recover more amounts, if such amount is insufficient to clear the debts of the LLP.
Governance of Law
- By Limited Liabilities Partnership Act, 2008
- By Limited Liabilities Partnership Rules 2008
- By Registrar of Companies
- By the LLP agreement
Features of LLP
- Liability of Partners– The liability of Partners is limited to their contribution of share in the business. A partner is liable for his own wrongful acts. One Partner is not responsible for the acts of others due to negligence or misconduct.
- Legal entity- LLP is a body incorporated and a legal entity separate from its partners having perpetual succession as per Section 3 of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
- Limit of Partners – A minimum of two partners are required to form an LLP as per Section 6(1) of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008. There is no maximum limit on the number of partners.
- Audit of Accounts – LLP shall maintain annual accounts where audit of the accounts is required only if the contribution exceeds Rs. 25 lakh or annual turnover exceeds Rs. 40 lakh. A statement of accounts and solvency shall be filed by every LLP with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) every year.
- Admission or Retirement of Partner- LLP can continue its existence irrespective of changes in partners.
- Designated Partners– LLP shall have two individuals as designated partners and one of them shall be resident of India.

Process of Registration of Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
The process for registration is given below:
- Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
- Apply for Director Identification Number (DIN)
- Name Approval
- Incorporation of LLP
- File LLP Agreement
- To register LLP the first step is that the Designated Partners will apply for Digital signature as all the documents are filed online which are required to be signed digitally.
- The next step is to obtain Directors Identification number of all the directors in the LLP.
- Two proposed names for LLP can be filed after login to MCA official website for name approval of the LLP which will be processed by Central Registration Certificate.
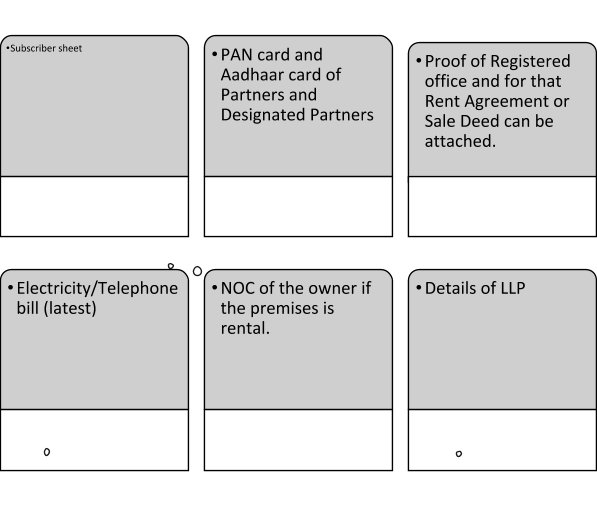
- For Incorporation of LLP following documents shall be annexed:
Members in Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
In every LLP there shall be two Designated Members as per Section 7 of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 who shall be the individuals where one individual shall be a resident of India. LLPs are created between the members who act as partners and manage the activities by pooling resources to lower down the costs of LLP by increasing its capacity for growth. The liabilities of Partners are limited as they may lose the assets in partnership but not their personal assets.
No Partner is liable on account of the independent or unauthorized actions of other partners, individual partners are shielded from joint liability created by other partner’s due to wrong decisions or misconduct.
Difference Between Partnership and LLP
|
S.No |
Basis |
Partnership |
LLP |
|
1. |
Governing Law |
Partnership Act, 1932 |
Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 |
|
2. |
Registration |
The Registration of Partnership is not compulsory. However, the unregistered Partnership firm cannot be sued. |
The Registration of LLP is compulsory with the Registrar of Companies (ROC). |
|
3. |
Liability |
Every Partner is liable, jointly for the acts of other partners alone or for all the acts of the firm in course of partnership. |
Under LLP the liability of partners are limited as per their share of contribution. |
|
4. |
Legal entity |
Partnership firm has no separate legal entity. |
The LLP has a separate legal entity. |
|
5. |
Enforcement |
Partnership Act provisions are different in various states as the enforcement of the act is at State level |
The enforcement of LLP Act is made by the Central Government which is applicable to all States. |
|
6. |
ITR |
No returns are to be filed with the Registrar of Firms |
The annual statement of accounts and annual return has to be filed with ROC. |
|
7. |
Can Minor become Partner |
Minor can become partner in Partnership |
In LLP minors cannot become partners. |
General Clauses in LLP Agreement
- Duration of LLP
- Contribution by Partners total contribution by each partner in LLP, additional capital contribution if any by the Partner
- Rights and Duties of Partner
- Voting rights of each partner
- Capital Contribution and Profit sharing ratio in case of Admission of new Partner
- Retirement of Partner
- Death of any Partner
- Borrowings of LLP
- Salary or Remuneration of Partners
- Term of the Agreement
Essential Clauses In LLP Agreement
- Competitive Clause
- Vesting Clause
- Interest on Capital and loan taken by Partners or the limit of loan
- Liability of LLP for the acts of Partners
- Addendum/Amendment in LLP Agreement
Conversion of Partnership Firm into LLP
Partnership firm that is willing to get converted in to Limited Liability Partnership can easily convert by applying Form 17 i.e. Application and Statement for the conversion of a firm in to LLP along with Form 2 i.e. Incorporation document and Subscriber’s statement.
Conversion of Private/Unlisted Public Company into LLP
Any Private or Public Unlisted company that is willing to get converted in Limited Liability Partnership can be converted by applying through Form 18 i.e. Application and Statement for the conversion of Private Company/unlisted Public Company into LLP. Form 18 needs to be filed along with Form 2 i.e. Incorporation document and Subscriber’s document.
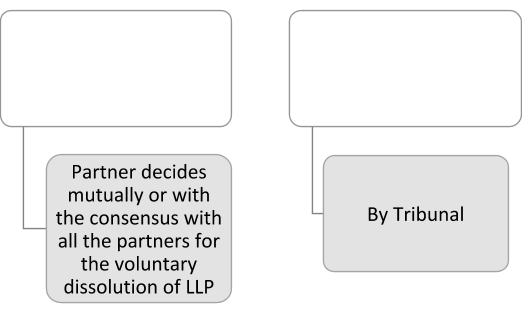
Dissolution or Winding Up of LLP
Conclusion
The concept of LLP is a combination of Partnership which is beneficial for both small and medium size firms. Each partner is responsible for his own deeds or negligence. As also it is termed as an “alternative corporate business vehicle” as the functioning is same as any other general partnership but it comes with a special provision of the limited liability rule.
References
- http://www.mca.gov.in/MinistryV2/llpact.html
- http://www.mca.gov.in/LLP/pdf/HowToIncorporateLLP.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Limited_Liability_Partnership_Act,_2008
- Resolu/26112/153934?link:0:0:/v3/schools/352/courses/21604/ldrm/paid/153934/Basics_of_Limited_Liability_Partnerships_lenc.epdf
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skill.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack










 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


