This article is written by Nibha Yadav, pursuing a Diploma in M&A, Institutional Finance, and Investment Laws (PE and VC transactions) from LawSikho.com.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Venture capital financing is a type of private equity funding which investors provide to startup companies or small businesses; they believe it has the potential for long-term growth and capital. People who fund startup companies or small businesses are popularly known as venture capitalists. Such venture capitalists can be investors with high net worth, pension funds, financial firms, or even insurance companies. Venture funding is at an earlier stage of the funding when the startups are in their initial phase whereas private equity is comparatively at a later stage of funding when the companies have relatively established themselves in the market. Venture capitalists invest their resources into high-risk ventures in expectations of high returns. They are driven by the principle of high-risk high returns. Since the funding is at a very initial stage of the business. Venture capitalists not only invest their valuable money in the companies but also their managerial abilities. One of the biggest advantages of VC funding is that the investors can heavily negotiate the price of the companies they are buying since they are in their startup phase and when the business blooms they can sell the company at a much higher rate.
In this article, we shall be discussing the entire process of structuring a venture capital right from entry to its exit strategy along with the different criteria that a VC firm must satisfy before investing in the investee company; the essential rights they must negotiate and the pros and cons of a venture capital financing.
How does venture capital work?
Today, venture capital’s niche exists because of the capital markets; startups have the innovation, idea but they don’t have reliable assets to offer to the investors, for this reason, it is hard for them to raise funds from banks or financial institutions. Investment banks and public equities are constrained by the regulatory compliances and the conventional operating methods meant for securing public funds and therefore they are reluctant to invest in companies who cannot offer assets to secure debts. There is no hard-and-fast rule as to the functioning of VC but since it involves high risk it is generally advisable to invest in ventures which offer extraordinary returns within a desired framework of time with an easy exit option. There are certain fundamental criteria that venture capitalists shall consider before investing in a startup; it is colloquially known as Venture Capital Speculation Criteria. These speculation criteria assist the investors in structuring a better venture capital deal and they are as following:
i) To have sufficient returns at acceptable risks
Venture capitalists expect at least a 25% – 35% return per year over the lifetime of the investment. A capitalist should be aware that each phase of the development will require speculation; it will unravel the uncertainty, risk involved, and the duration of the investment. There are various methods to profit in a venture like through an IPO, mergers, and acquisitions.
ii) Investment profile vis-a-vis organisation’s profile
Venture capitalists do not invest in good people or good ideas but in reality, they invest in good industries which are more competitively forgiving than the market as a whole. Recently, the capital flow has shifted towards the technology, engineering sector owing to the creation of ample intellectual property which has the capability to hinder the rival’s development. Even if an entrepreneur has talent or a charismatic personality, it is difficult for him to get VC funding if his business is in a low-growth market segment. Capital in a way is allocated to industries where most companies are likely to look good in the near future.
iii) Decoding the logic of the deal
There are many factors that affect the deal structure but whatever the specifics may be the logic of the deal is always the same i.e. to give the investors in VC funds both downside protection and a favourable position for additional investment if the company in the future starts blooming.
For example, if a VC fund invests $3 million in a startup for an exchange of 40% preferred equity ownership; these preferential rights give its investors downside protection. So the venture capitalists receive a preference in the event of liquidation or a merger over the common shareholders. Secondly, these investors also enjoy upside provisions, they can invest in the VC at a predetermined price if the startup is doing well and thereby, raise their stakes in the startup.
iv) Determining attractive returns for the VC
Typically, venture capitalists expect ten times the return of the investment over a period of five years. The expected returns combined with the preferential rights result in an annual compound interest rate of around 58%. Though this is a very high-cost capital return, it is necessary in order to deliver average fund returns above 20%. For example, if the VC raises $100 million and if there are four to five partners then these partners are assured an average salary of $200,000 to $400,000 annually along with the operating expenses. But how are venture capital investors benefited from this structure? For that, the real upside lies in the appreciation of the VC’s portfolio. If the value of the portfolio increases investors generally get a 70 – 80% share of the gains while the partners take the remaining 20-30%. This can be further explained by the following chart known as Pay for Performance.
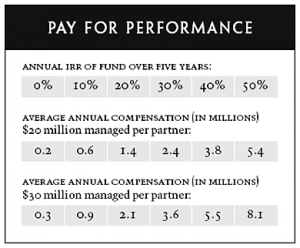
Let’s say for a typical VC portfolio, $20 million is managed by each partner, and there lies a 30% upside appreciation on the funds i.e. there is 30% profit on the VC’s total fund then the average annual compensation for the fund partners will be around $2.4 million; nearly all of this comes from the fund appreciation. From the perspective of a VC investor, this compensation is acceptable because the fund is giving attractive returns on investment and there lie incentives aligned with making the investments a success.
v) The upside for the entrepreneurs offered by a VC
Many entrepreneurs coming from universities, and corporations have revolutionary business ideas, innovation, and zeal to work but most importantly they lack the capital to fund such ideas and eventually convert them into successful businesses. This is where venture capital funds come into the picture. VCs not only invest their capital in new businesses but they also invest their invaluable managerial skills from designing market strategies to synergising the resources; they do it all. VCs look for the value an individual brings to the firm through skills like team management, willingness to take risks, ability to sell oneself, and the entrepreneurs who can offer such skills have an upper hand in negotiating a deal.
Entrepreneurs should make their own assessments just like VC firms which will enable them to find favourable funding for their startups. They should assess and determine the skills required, the funding needed, probability of success in a reasonable period of time, methods to raise additional funds, etc in order to find a suitable VC partner.
vi) Exit strategy
A venture capital funding is short-term funding with 3-7 years as the ideal time period; businesses offering attractive returns within the favourable time period along with an easy exit plan are generally picked by VC investors.
How is a venture capital investment structured?
Once a venture capitalist satisfies all the speculation criteria as discussed above, the next step is to effortlessly negotiate his rights in the proposed deal. Let’s take a look at the essential rights of an investor that should become a part of the stock purchase agreement along with the representations and warranties.
i) Essential rights of a venture capitalist
Once a VC investor is firm on investing money in a company, these are the rights they generally expect out of the transaction:
- Right to elect the majority of the directors to the company’s board – This will enable the investor to exercise substantial control over the management of the company vis-a-vis the day-to-day business of the company.
- Right to access various reports like the financial statements of the company, any other related information – This is one of the non-negotiable rights; it is of utmost importance for the investor to see how his investment is performing
- Right to have its stocks registered on recognised stock platforms – An easy exit plan is one of the criterias that an investor should fulfill before investing his money into the company. In case the company is not doing well the investors will have the choice to opt for an IPO and sell their shares at a fair market value
- Right to maintain its percentage share ownership in the investee company by participating in future stock offerings – This is where preferential rights, right of the first refusal becomes extremely important; when the company is issuing new shares or transferring its old shares the investors shall have an upper hand and should have the first-hand opportunity to opt for these shares over the common shareholders so that their ownership in the company is maintained on pro-rata basis.
ii) Negotiating and drafting a stock purchase agreement
Once the investors and the investee company have executed the term sheet the next step is to enter into a stock purchase agreement in order to reflect the terms and conditions of the transaction. A stock purchase agreement will typically contain these clauses however, there can be additions and subtractions to this agreement as per the requirements of the parties.
- Covenants of the investee company like Memorandum of Association, Articles of Association, etc.
- Conditions to the closing of the deal can include conditions precedent and conditions subsequent.
- Representations and warranties of the investee company.
- Exhibits and other allied agreements specifying the rights of the investor.
- Indemnification clause so as to reimburse the losses, damages, expenses incurred by the investor due to negligence of the investee company.
- The price of the stock to be purchased and the number of shares to be sold.
iii) Representations and warranties
Representations and warranties are an indispensable part of any capital venture investment; herein the investee company is expected to represent its true financial and operational conditions, failing to do so can invoke the rights of the investor to seek remedies as laid out in the agreement. Some of the most common and most used representations and warranties include the following; such that:
- The company is incorporated and is in compliance with all the relevant laws of the land.
- The exact outstanding capitalisation of the investee company is represented.
- The company’s financial statements are prepared in accordance with the accepted accounting procedures and are true.
- The company has no liabilities other than the ones reflected in its most recent balance sheet.
- The intellectual property of the company does not infringe the rights of others.
- The company owns all the assets it claims to own, except the leasehold property as disclosed by the company, and that the assets are free of any lien, encumbrances except for the ones disclosed.
The representations and warranties clause can run into pages depending on the requirements of the investor.
Advantages and disadvantages of a VC fund
Advantages
- Business expertise – The biggest advantage of a VC fund is along with the capital investment, venture capitalists provide invaluable guidance and consultation from the expertise they have developed over the years. Decision-making is one of the key areas that can make or break a business idea; these investors can help the entrepreneurs in making critical decisions as the business grows.
- Connections – Venture capitalists are very well connected in the business community; being able to access these connections can make a tremendous difference to the company
- Additional resources – In the earlier stage of development, a young company may be incapable of taking care of legal, tax compliances. A VC firm can extend support in these critical areas and help the business grow. Faster growth with great success is two key benefits that a VC can offer.
- Buy up the competition – With the money that VC funds have to offer investee company can go broad and tackle multiple markets than their competitors. This also means one can undercut the competition for the time being and may also acquire or buy up the competition and make that part of the business plan.
- Being able to hire and attract great teams – In the initial stages of the business, startups may find it difficult to attract talent to come work with them as they have very little to offer. But VC-funded startups can give talented people the confidence to give their best and in turn, these people can count on getting paid for their work.
Disadvantages
- Losing control – It is likely that an investor would want to be involved in the management of the company. The size of their stake in the company will determine their involvement in the company; since the investors have an upper hand in such deals it is possible for an entrepreneur or the founding partners to have little to no control in the company.
- Minority ownership – Depending on the ownership stake of the VC firm in the investee company, which in most cases can be more than 50%, an entrepreneur or a founder could be giving up ownership of their own business.
- Getting a smaller piece of a big pie – With the ownership stakes and control over the company, venture capital may make the startup worth billions of dollars but this would also mean that the entrepreneurs will have little to nothing with them even if the company is valued at $100 million.
What are the other alternatives to venture capital funding?
Considering that every advantage of venture capital funding has a disadvantage, it becomes important to consider the other alternatives to venture funding. Bootstrapping, angel investors, self-funding, investment from friends and families are the other options entrepreneurs can opt for. It is essential to understand that just like venture capital each of these alternatives come with their own sets of advantages and disadvantages. In order to determine what type of funding an entrepreneur should go for; the following factors like the amount of funding required, desire for control, the ultimate goals and objectives, leverage in negotiations must be taken into consideration.
Conclusion
Venture capital fills the void between funding the innovation and the conventional sources of capital available for going concerns. Venture capital firm connects the other three main players of a venture capital industry consisting of the entrepreneurs who need funding for their businesses, investors who want high returns on their investment, and investment bankers who want companies to sell, and a VC firm makes money for itself by creating a suitable market for the other three. VC funding remains one of the most favourable sources of funding even after the risks and negatives that are attached to it; what’s important is to balance them against the advantages in your business.
References
- How Venture Capital works
- The structure of a venture capital investment
- Pros and Cons of venture capital
- How do venture capital and private equity deals work
- Advantages & Disadvantages of a venture capital
- Pros and cons of venture capital financing
Students of LawSikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skills.
https://t.me/joinchat/J_0YrBa4IBSHdpuTfQO_sA
Follow us on Instagram and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more amazing legal content.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack










 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


