This article is written by Swathi Vajjhala, pursuing a Diploma in Business Laws for In-House Counsels from LawSikho.
Table of Contents
Introduction
With the advent of the internet, smartphones, and other apps, digital data has escalated. According to the National Security Agency, the internet processes 1,826 petabytes (PB) of data every day. In 2018, the amount of data generated daily was 2.5 trillion bytes. Previously, the International Data Corporation (IDC) estimated that the amount of data generated would double every two years. In the past two years, however, 90% of data was generated worldwide. Besides, Google now processes more than 40,000 searches per second or 3.5 billion searches per day. Facebook users upload 300 million photos, 510,000 comments, and 293,000 status updates every day. With all these figures at hand, we can imagine a humongous amount of data is generated every day.
So, the question which comes to our mind is what is Big Data? According to Investopedia, Big Data is a large amount of information collected from various social media websites, questionnaires, product purchases given voluntarily. This information is stored in computer databases and analysed using software designed to handle large, complex amounts of information and arriving at a conclusion at an increasing speed.
Big data has significantly impacted many sectors of world economics like health care, manufacturing, and retail. It is rebuilding the world and has left no industry untouched with its enormous advantages, and the banking industry is no such exception. Like Cloud, Internet of Things, Machine Learning, and Open Banking, Big Data is one of the financial industry’s buzz words. When a customer first steps into a bank, he/she brings many potentials like the potential of becoming a loyal customer, making suitable investments, a short-term relationship, or even the potential to fraud. Banks need to focus on their customers at a 360-degree angle to visualize their behavioural patterns, repayment habits, and financial needs.
Banks have to deal with millions of potential people every day, and for all of this, they need data, lots of it. With potential customers coming in, banks have to deal with lots of potential data. There is no data shortage in the banking sector. Big Data has emerged as a saviour for the banking industry.
With the help of Big Data, financial service companies have changed the way they do business. Big data minimizes the risk of fraud detection, compliance, and portfolio management. This risk reduction, combined with the optimization of the winning strategy, can provide financial services companies with a significant competitive advantage. Big data has enabled new strategies for companies that interact with the public markets to go beyond simple improvements. If the financial systems and products become more complex and complicated, this can create a way for fraudsters to do fraud. To save themselves from fraud and risk, financial firms have to switch to big data quickly to identify and prevent evolving and complex fraud schemes.
Private companies and governments recognize the enormous potential of using this knowledge to generate real value to consumers and increase productivity over time. Government departments use big data to assess systemic risk in major financial markets to implement protective measures against threats such as bubbles and recessions. At the same time, companies embrace preventive measures to avoid penalties that could endanger their viability and core business. This ubiquitous change has forced financial firms to evolve or perish. Extensive data could pass over companies and economies, but data science is the real game-changer.
In India, the Government is focusing on digitizing India by connecting all people with government departments through broadband services irrespective of urban or rural. Demonetization and Covid have unfolded a new era that accelerated digitalization, paving the way for e-banking and e-commerce companies in India. With lots of data involved in this whole process, Big Data can be a game-changer.
Types of Big Data
Structured Data
Any data that can be stored, accessed, and processed in a format is considered ‘structured’ data. Computer science has become more active in developing techniques for working with and deriving value from such data over the period. However, today we see problems with the size of this data as it grows exponentially; typical sizes are in the range of zettabytes.
Unstructured Data
Any data with an unknown shape or structure is classified as ‘unstructured data’. Unstructured data is enormous and poses a variety of challenges processing to derive a value from it. A case in point for unstructured data is a heterogeneous data source containing simple text files, images, videos, etc. Organizations these days have a wealth of data with them; however, unfortunately, they do not know how to make sense of it because it is in its raw form or unstructured format.
Semi Structured Data
Semi-structured data can contain data of either type. We can see semi-structured data as structured in their form, but they are in relational DBMS with, e.g., a table description. Semi-structured data is an example of data contained in an XML file.
Characteristics of Big Data
Due to its nature, a large amount of data is generated through its customers in the banking industry. This data is usually in the form of unstructured and semi-structured data. If this data is analyzed, banks can provide a better solution to their customers’ needs and ultimately making customers happy. Therefore, big data will help banks analyze their customers’ needs through its characters like:
Volume
The name big data itself has to do with a massive scale. The sample size plays a significant role in evaluating the value from the results. It also depends on the volume of data, whether specific data can be viewed as big data or not. ‘Size’ is also an attribute to consider when dealing with big data.
Variety
Variety refers to both structured and unstructured, heterogeneous sources and the nature of the data. Earlier, spreadsheets and databases were the only sources of data that take into account most applications. In analytical applications, data in the form of emails, photos, videos, monitoring devices, PDFs, audio, etc are also taken into account. The abundance of Unstructured data increases storage, processing, and data analysis problems.
Velocity
Velocity or speed refers to the rate at which data is generated. How quickly the data is formed and prepared, fulfilling the requirements determines the true potential of the data. Velocity represents how fast data flows from sources such as business processes, program logs, networks, Social media platforms, sensors, mobile devices, etc. The flow of information is enormous and continuous.
Veracity
Veracity refers to the uncertainty and inconsistency that the data can often show, which can hinder the process of handling and managing the data effectively.
Benefits of Big Data Processing
The ability to process big data brings several advantages, such as:
Companies or businesses can use external information/intelligence while making decisions. For example, access to social data from websites like Facebook, Twitter is helping companies to optimize their business strategies.
Businesses can improve customer services with the help of Big Data. Traditional customer feedback systems are replaced by new systems developed using big data technologies. In these new systems, big data and natural language processing technologies are used to read and evaluate consumer responses.
Early identification of a risk for the product/service and better operational efficiency. Big data technologies create a staging area or landing zone for new data before deciding which data to move into the data warehouse. Besides, such integration of big data technologies and data warehouses helps a company to outsource data that is rarely accessed.
Indian Banking Sector
After independence, the banking industry in India has extraordinarily expanded. Several financial mismanagement and scandals in the 1960s and 1970s forced the government to nationalize most banks. After 1991, private banks emerged stronger and more robust.
According to RBI, there are currently 12 public banks, 22 private banks, and 46 foreign banks that are licensed to conduct banking in India. There are 61 national rural banks and over 90,000 also cooperative banks. India’s banking sector has a network valued at Rs 81 trillion ($ 1.31 trillion). According to the research results from KPMG-CII, the Indian banking industry is expected to become the fifth largest banking sector in the world by 2020 and the third-largest by 2025.
Technology has been a critical enabler for transformation and innovation of the world. It has made markets more innovative, structured, and service-oriented. It even paved the way for the growth of the digital economy. Every sector of the world’s industry is going through digital transformation, be it agriculture, health, education, and even financial institutions. Financial institutions are using the technology for simple money transfer to a complex trading system, making financial services more accessible, cheap, efficient, and innovative. This rapid evolution of digital technology is taking the world by storm and posing challenges to the regulatory authorities in a country like India. Technology helped the banking industry with online banking, mobile banking, and remote banking, reducing dependency on physical branches and reaching a broader customer base using virtual bank resources.
India, with a population of 1.3 billion, is transforming and innovating in the field of Fintech. With the large population and mostly young, digital penetration is high, making India an exciting global space for Fintech.
Application of Big Data to Indian Banking System
To tackle the problems faced by banks, a company named Aspires systems has created PropelStream.
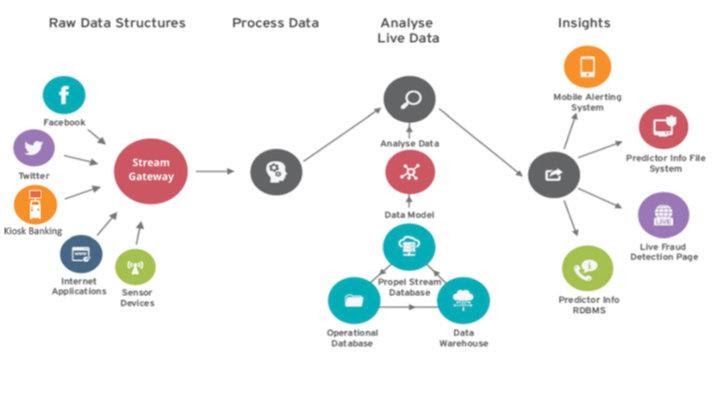
Source: Aspires Systems
Propelstream, is a real-time streaming analytics solution built to create and capture value from disparate sources of data. It collects real-time data from all the available sources like router switches, banks, internet apps, and social channels like Facebook and Twitter. Predictive messages are then sent to receivers via channels like mobile, file systems, and fraud detection pages. It also helps to accumulate data and on the accumulated data it can give reliable market predictions like stock exchanges, inflation etc.
Challenges faced by Banks
Risk Management
Establishing a comprehensive risk management system is of paramount importance for banking organizations. If they lack comprehensive risk management, they will suffer from enormous loss of revenue. Organizations need to keep innovating new things to stay alive in the competitive world and increase their profits as much as they can. Big data analysis helps companies identify threats in real-time and, of course, protect the consumer from possible fraud. A bank may encounter numerous kinds of risks like credit, event, business, market, customer, and operational risks. All these risks combined will lead to liquidity risk. Therefore, it is essential for a bank to establish a comprehensive risk management system.
Fraud Detection
The rapidly progressing digital world offers us a wide range of opportunities and advantages, but at the same time, we can see an increase in fraud cases. Personal data is more vulnerable than ever to cyberattacks, which is the most significant obstruction a banking organization faces. Using big data analytics and specific machine learning algorithms now enables companies to identify fraud before deployment. It does this by identifying general user trends spending, anticipating irregular user behaviour, etc.
Bank fraud creates an imbalance in the economy, which often leads to a slowdown in the market. Because of such scams, the stock markets face major crashes, which significantly impact the economy. This leads to a slowdown in economic growth and often disappearance of foreign investment.
Customer Satisfaction
Customer Satisfaction is one of the challenges faced by banks. Banking companies need customers who hold on to them for a long time. So, they need to make customers happy by understanding their needs and offering them beneficial products.
According to a survey conducted by Capgemini, only 37% of the customers think that their bank understands their needs. This is because only a handful of banks like Bank of America, Deutsche Bank, and CitiBank have delved into big data.
To understand customer needs, Banks should take the help of Big data to analyze their customer’s data based on various factors and parameters that can address customers’ needs in a much effective way. For example – Is the client/customer just married? Offer them a home Loan. Do customers have children opting for higher education? Make an offer of student loans on tailor-made interests depending on the income of the customer. After successful completion of the loan payments, offer them another relevant one. Offer vacation trips on birthdays and anniversaries or special coupons to use credit cards when they are near a store.
Keep an eye on every communication with customers for sentiment analytics, like are customers satisfied with the bank’s services? Have they complained a lot lately? Customers usually use social media websites like Twitter, Facebook, or Linkedin to record their feelings against banking companies. As soon as these emotions are recorded, they can be divided into positive and negative, and they can be used to provide services to consumers by applying different filters. Know when a customer will leave the bank as we know that acquiring new customers costs more than retaining old ones. When the bank knows about its customer’s problem, attention must be paid to find a solution.
All this information will help banks come closer to customer’s life and understand customers and their needs in a much better way. India, being the fifth largest economy globally, its credit penetration as a ratio to GDP remains low. Therefore, it is high time for Indian banks to opt for Data Analytics with so much advantage. Big Data can help banks and understand customer needs making both parties victorious in a transaction.
Business Optimisation
Big data can be helpful in combination with machine learning. Banks can analyze internal processes and take measures to optimize them. In this way, banks can significantly reduce operating costs.
Regulating Big Data
With the exponential growth and widespread adoption of the benefits of big data, great attention needs to be paid to the various challenges and risks associated with collecting and using big data. If these risks are not adequately addressed, the risks can outweigh the benefits of big data and severely hamper public support for wider cross-industry use of big data. Despite this understanding, the countries have been slow to regulate big data. This article addresses, among other things, the wide range of significant data concerns such as the quality of data sources, antitrust issues, and consumer protection. Only the most significant challenge is dealt with – the subject of data protection.
Most of the world’s significant jurisdictions do not currently have laws that specifically regulate big data.
United States
There is no uniform data protection law. Instead, any business or organization that wishes to conduct big data activities must comply with several different regulations, including industry-specific data protection laws that govern the data required for their business operations, contractual requirements, and other industry and/or region-specific regulations that apply to these companies.
In the United States, the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has federal powers to enforce data protection regulations. However, due to their federal structure, actual enforceability is dubious. Most of the regulations predominantly reside with the state, adding to the confusion as different state regulations are sometimes incompatible and hinder the functioning of companies across state borders.
European Union
In 2018, the European Union (EU) replaced the previous EU data protection directive with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The GDPR sets out several basic standards that companies need to follow while handling the data of EU citizens. Companies must take the consent of data subjects to process their information. GDPR has provisions for the secure cross-border transfer of data, mandatory requirements for companies to appoint a data protection officer to monitor compliance with the GDPR.
The GDPR is recognized as the most comprehensive data protection law in the world today due to many factors. The most important of these is that the GDPR applies to organizations operating in the EU and overseas, protecting the data of its citizens.
India
India currently lacks comprehensive, dedicated, and specific data protection legislation and, more particularly, regulations related to big data. However, the Information Technology Act, 2000 has been amended to include the Information Technology Rules, 2011 to protect personal data.
In 2012, the Indian government introduced the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019. A joint parliamentary committee is currently reviewing the PDP bill. Even after it comes into force, the law is likely to be implemented gradually, and there is currently no information on the timetable for implementation. Upon entry into force, India’s first law will protect personal data and repeal the relevant amended sections and rules of the Information Technology Act, 2011. While the bill fails to contain any specific provisions related to big data, similar to the GDPR, its implementation in India will have far-reaching implications, which are also expected to regulate big data activities.
Conclusion
The age of big data is just around the corner. Organizations need to understand what big data is like and how to use it as it has the calibre to unlock various market potentials. The advantages and benefits are significant for companies to disregard. Combining different data sets, such as company data, public data, and social data, would provide even more information.
However, financial services companies are still lagging when implementing big data analytics tools representing untapped value creation potential for the banking industry. This must be assessed from the point of view of IT (information technology) or the LoB (Line of Business). The impact of big data on society will be prominent and phenomenal, but how society affects big data remains to be seen.
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skill.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack











 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


