This article is written by Surbhit Shrivastava who is pursuing a Diploma in Intellectual Property, Media and Entertainment Laws from LawSikho.
Table of Contents
Introduction
With the price of Bitcoin hitting an all-time high of $60,000, investment in cryptocurrencies is the new craze today, and the world market in general has become increasingly interested in cryptocurrencies. Elon Musk’s Tesla Inc. reportedly invested US$ 1.6 billion in Bitcoin, which is enough to estimate its potential, since Musk is considered a visionary in the tech community. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets which are based on blockchain technology. Many people who are new to the concept of blockchain tend to use ‘Bitcoin’ and ‘Blockchain’ interchangeably, however, this is not the case.
One cannot deny the role Bitcoin has played to popularize blockchain, but Bitcoin is one of the 4,000 cryptocurrencies that use blockchain technology. Some other notable cryptocurrencies are Ethereum, Ripple and Dogecoin. The blockchain used by different cryptocurrencies may or may not be the same, and some may be more advanced than others. For example, the Ethereum blockchain supports smart contracts and executes transactions much faster than the Bitcoin blockchain.
What is Blockchain?
Since you now know that all blockchains are not the same, you must be wondering “So what exactly is a blockchain?” The simplest way to understand blockchain is to imagine a number of blocks in a chain, each with its own unique identity. Think of a ‘block’ as data stored in a box. Now, the special thing about blockchain is that it is decentralized, i.e. no single entity has ‘control’ over the blockchain. Each and every ‘node’ in the chain contains a ledger of all transactions and therefore every entity in the blockchain has a record of all the things happening on that blockchain.
The blockchain runs on a set of protocols set by the managers of the blockchain, and each member in the blockchain has access to all transactions made in that blockchain, thereby maintaining transparency. However, to ensure privacy, the names of the users are encrypted, which means that although everyone can see what transaction has been made, they cannot determine the parties that entered into that specific transaction.
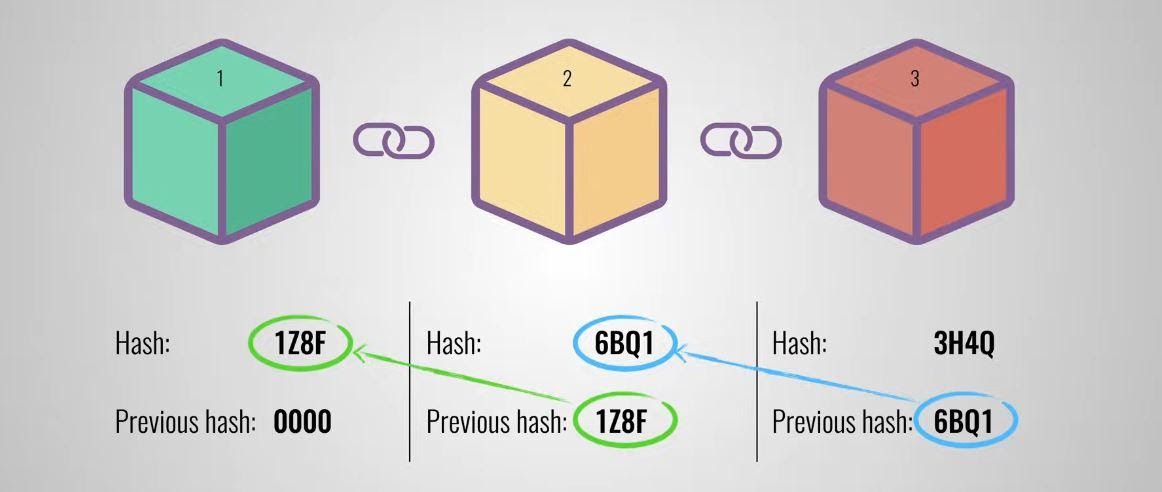
A block consists of data of multiple transactions. Once a block is added to the chain, it is impossible to modify its contents. Each block is linked to the previous block using a ‘hash’ which is basically a number assigned to that block, which helps determine its ‘position’ in the chain. It can be understood with the help of the following diagram:
Source: Simply Explained, How does a Blockchain work on YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSo_EIwHSd4
This is to ensure that the block once created cannot be tampered with. If even a single digit in the data contained in block 1 in the above diagram changes, its hash changes and it would no longer be identified by block 2, and this block would further not be identified by block 3, and so on and so forth. If a hacker wants to modify a block, he will have to modify all the subsequent blocks, and that is simply not possible (The Bitcoin blockchain alone had around 500,000 blocks in 2017). This is what makes blockchains extremely secure.
Conventional methods of IP Management
Intellectual Property Management refers to maintaining the IP portfolio of a company, and taking steps to ensure timely acquisition of IP rights, their exploitation and protection, and in the case of an infringement, enforcement of the rights. A company may have a variety of IP rights in its possession, some of which are accounted for and some which are not. An IP portfolio can be said to be the sum total of all IP rights which are accounted for and which are usually managed through an IP management software.
IP management software uses the power of technology for achieving its objectives, which makes it highly effective. A good IP management software would contain features such as patent tracking, marketplace monitoring and image protection. Such a software would scan hundreds of thousands of websites in a day, and would report whether any infringement case is made out. For example, the IP management software of a company like Rolex would scan shopping websites to determine whether any fake items are being sold marketed as a product of Rolex.
IP management is essential for all companies, but it has a serious drawback. The drawback is that IP rights are still granted by the government in the first place, which is governed by a process, and which usually involves paperwork and documentation. It is after this tedious process a company is granted IP ownership and only then can this information be fed into the IP management software. Basically, the software would just run the checks and present the instances of infringement, which would then have to be investigated. If a case is made out, the whole process will end with a lengthy legal battle.
Blockchain for IP management
Blockchain technology presents a case for IP management that seeks to bring a major change in how IP rights are registered, acquired, exploited, protected and enforced. Blockchain technology can play havoc with the conventional methods of IP management and force them to completely reconsider how they work, because blockchain technology will act as conclusive proof regarding the ownership of rights which will make the process faster and more economical.
Registration of IP Rights
First and foremost, blockchain technology can be used to do away with the paperwork and documentation for registration of IP Rights. The data otherwise put on paper, can be put on a blockchain and verified by government-controlled nodes which would act as the verifiers of the grant of IP rights. Once the block is added to the blockchain with a timestamp, all nodes on the blockchain will have the knowledge that a party is granted an IP right, courtesy of the distributed ledger system. This information is also verified by all the nodes, so one can be assured that the data in a block is authentic.
Exploitation of IP rights
The data on the block can include a short description of the actual IP Right, and interested parties can either contact the rights holder or fulfill conditions to enable the execution of a smart contract through which IP rights can be acquired or licensed. This process would take a few minutes, compared to the lengthy process of contract drafting, signing and execution. The block also acts as a proof of contract between two parties, which can prove to be useful in the case of a dispute later.
Protection of IP rights
Since a block on the blockchain is encrypted and secure from attacks, the description of IP rights are safe on the blockchain. Consider this example given by Shkor: A group of scientists working on a vaccine shares the formula with a corporation who then delays or even refuses the funding, and then proceeds to use the research or formula for their own uses. Blockchain can prevent such type of unauthorized exploitation by proving to all the nodes in that network that the sharing was done for grant of funding, and not for exploitation. Since a record of all transactions on the blockchain is present with all members of the chain, the blocks are time-stamped and cannot be tampered with, it will be difficult for the corporation to defend its case.
Enhanced protection of copyright
Since a copyright is protected by the virtue of its inception, a block on the blockchain can act as conclusive proof of inception of work since a block is time and date stamped. If copyright infringement of this work happens, the creator has a strong piece of evidence to prove his ownership over the copyright.
One benefit of selling art through mediums that use blockchain such as NFTs is that one can always trace the piece of art to its original creator, no matter how many times it has been transferred or licensed.
IP Portfolio on the blockchain
An entity can use blockchain to keep a record of all its IP holdings. For this, a centralized model of the blockchain is suggested, in which all nodes connect to one or more government-controlled nodes, which keep a record of all entities that hold their IP rights through the blockchain. If this system is followed, the regulatory authorities and interested parties can verify possession of rights without going through a lengthy process, since they can make use of the network to trace the owner. An IP portfolio on the blockchain would also prove to be relatively cheaper than one maintained by a software.
With the immense benefits it brings, blockchain technology can radically change the way entities manage their IP portfolio. This would bring a major setback to the current IP management companies, who would find it hard to compete with a faster, more economical and a more promising technology. However, IP Management software can still prove to be useful for detection of infringement on the internet, but its role might get limited to that purpose in the future if blockchain is incorporated into the IP domain.
Every coin has two sides, and blockchain is no different. While the benefits it can offer are lucrative enough for businesses to give the technology a try, the governments are not very enthusiastic about it. Governments of many nations have regarded cryptocurrencies as mediums of money laundering and illegal trade. In fact, the Indian Government is planning to ban all privately operated cryptocurrencies. Even though it is a fact that cryptocurrencies are just one of the uses of blockchain, the negative image of cryptocurrencies has affected blockchain technology in general, and regulatory authorities are skeptical about it. This poses as a major hurdle before the technology can be adopted in a mainstream fashion.
Apart from the negative image, blockchain technology still has a lot of technical hurdles before it. Skilled computer programmers are needed to develop the blockchain network for regulating the registration of IP rights. While this is not impossible, it is certainly very difficult and since the technology is still novel, there are a lot of technical intricacies present which determine what can be possible on the network and what cannot be. It might take years to program, develop and stably run such a network. Also, the upkeep of a blockchain network needs a huge amount of computing power. Every node on the network needs this power, and it would require considerable capital investments.
Conclusion
The possibilities of use of blockchain technology for IP management are promising. The technology seeks to radicalize how IP rights are managed, and has the potential to damage the business of IP management software companies to a large extent. The technology can be used for keeping a registry of IP rights, providing proof of ownership and executing contracts without human intervention, all with minimal supervision and maintenance.
However, since the technology is still new, there are a lot of technical intricacies that need to be taken care of, especially the need for skilled computer programmers and the requirement of heavy computing power. The negative image of blockchain due to cryptocurrencies can also prove to be a major obstacle for the widespread use of this technology. Also, blockchain cannot completely replace the need for IP management software, since such software has a variety of other purposes which cannot technically be done on a blockchain.
Hence, blockchain and IP management software should not be seen as competitors. They should rather be put to work together, as this will ensure that the IP community reaps the maximum benefits of the conjunction of these two powerful and capable technologies.
References
- Luke Conway, The 10 Most Important Cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin, INVESTOPEDIA (Jan 19, 2021). https://www.investopedia.com/tech/most-important-cryptocurrencies-other-than-bitcoin/
- Damien Cosset, Blockchain: What is in a Block? DEV COMMUNITY (Dec 28, 2017). https://dev.to/damcosset/blockchain-what-is-in-a-block-48jo
- Priyadarshini Sinha, What is IP Management and What are the skills needed for IP Management? IPLEADERS BLOG (April 23, 2019). https://blog.ipleaders.in/ip-management-skills-needed-ip-management/
- Mirjana Stankovic, Is Intellectual Property Ready for Blockchain? MEDIUM.COM (Oct 2, 2019). https://medium.com/swlh/blockchaining-intellectual-property-can-blockchain-help-us-better-manage-ip-rights-afb3cb9299cd
- Alex Shkor, How Blockchain will disrupt IP Management, LAWYER MONTHLY (Mar 2, 2020). https://www.lawyer-monthly.com/2020/02/how-blockchain-will-disrupt-intellectual-property-management/
- Aftab Ahmed & Nupur Anand, India to propose cryptocurrency ban, penalizing miners, traders Reuters (Mar 15, 2021). https://www.reuters.com/article/uk-india-cryptocurrency-ban-idUSKBN2B60QP
- https://www.automation.com/en-us/articles/january-2021/the-future-of-blockchain-in-intellectual-property
- https://www.wipo.int/wipo_magazine/en/2018/01/article_0005.html
- https://spicyip.com/2021/04/non-fungible-tokens-nfts-and-copyright-law-a-nifty-dilemma.html
- https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=d96ed012-8789-4e87-bc1d-70ba76569c0f
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skill.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack











 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


