This article is written by Shreya S.K Pandey, a student of Law College Dehradun Faculty of Uttaranchal University. In this article, she discusses the debit note, credit note and the E-way bill, features of debit and credit notes and how the registration of E-way bill is done under Goods and Services Tax (GST) and how to unregister person will enroll in E-way Bill System.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Goods and Services Tax (GST) was introduced as the “One Nation One Tax” scheme in India. Many tax schemes were substituted after the introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST). It accumulated all the indirect taxes which were existing in India. Under, Chapter VII (Tax Invoice, Credit and Debit Notes), Section 34 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017, Credit and Debit Notes are discussed. But this provision does not clearly talk about the particulars which are required in the debit note and the credit note. It is left up to Government that the credit notes and debit notes will include those particulars which the Government will prescribe. Under Chapter VI (Tax Invoice, Credit and Debit Notes) of Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Rule, 2017, Rule 53 deals with the particulars to be mentioned in the debit notes and the credit notes. Anyone issuing the debit note and the credit note is under liability to mention these particulars strictly in the document. E-way bill is discussed under Rule 138 of Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Rule, 2017. The provision is vague as it does not clearly talk about the E-way bill.
Now, understand the whole concept of the Credit Note, Debit Note, and E-way Bill briefly in the following contents.
Debit Notes
Debit Note is an instrument or document which is given by the buyer or purchaser of the goods and services to the seller. The debit note is issued by the purchaser against the seller to inform him that the goods or services have been returned and now the seller is debited against the purchaser to the sum of goods and supplies return.
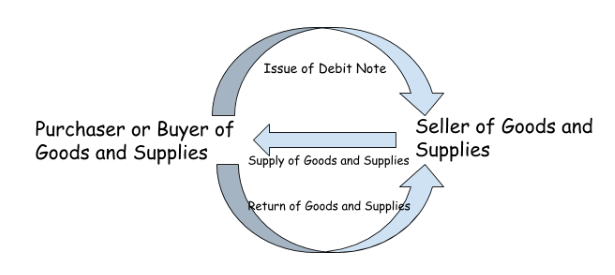
If the purchaser has paid for the goods and supplies at the time of transfer then the amount which is to be debited shall be adjusted in the further purchase of goods and services from that seller. When the purchaser had not paid the amount for the goods and services which he bought, then in such condition the amount to be debited shall be deducted from the actual amount which is required to be given to the seller.
Debit Note Example
A corporation “XYZ” purchase goods of Rs. 2,00,000 from another corporation say “ABC”. But, the corporation “XYZ” came to know that goods worth Rs. 50,000 are damaged. They inform about this to the corporation “ABC” during the delivery of goods.
Corporation “XYZ” issued a debit note of Rs. 50,000. Now, they have to give Rs. 1,50,000 to corporation “ABC”.
Now, consider a situation where the corporation “XYZ” has already made the payment to the corporation “ABC”. And, after making the payment, they came to know that the goods worth Rs. 50,000 are damaged. In this situation, the corporation “XYZ” will issue a debit note worth Rs. 50,000 to the corporation “ABC”. Whenever the corporation “XYZ” will buy goods in the future from the corporation “ABC” the amount will be reduced from the payment.
Important Features of Debit Note
- The reason for sending the debit note is to notify the seller about the debit made in his account along with mentioning the reason behind it.
- When goods are returned, the “purchase return book” is renewed according to this.
Purchase Return Book:- When goods are returned due to any reason i.e. false in quantity, bad quality, etc., this return of purchase has to be maintained in a record and that record is purchase return book. If returning of goods is frequent then in such case it is maintained or recorded in the journal.
- The debit note is made like an invoice or bill and it represents the positive amount.
- Purchaser or buyer use debit note while returning the goods purchased on credit.
Important point

- Debit shall include the particulars which are prescribed by the Government after making rules.
- The details which are required to announce in the debit note are:-
- Return for the month when the debit notes are issued or received by the person.
- Return for the consecutive month.
- The declaration must be done in a specified time period. It must not be later than:-
- September at the successful end of the financial year when the supply was done.
- The date on which annual return was filed.
Debit Note Entry
Book of Purchaser or Buyer
When a buyer or purchaser returns goods or services these are known as purchase return. When these goods are returned to the seller then,
- Current liability decreases as payables against credit purchase reduce.
- As the credit purchase degrade, there is a decrease in expense.
|
Account of Creditor |
Debit |
|
Purchaser Return Account |
Credit |
Seller’s Book
When buyers return goods, they are received back by the seller. Goods that are received back by the seller are known as sales return. When the goods are received by the seller, there is a certain effect of this is upon seller-
- As credit sales degrade, there is a decrease in revenue.
- Current assets decrease as receivables against credit sales reduce.
|
Sales Return Account |
Debit |
|
Account of Debtor |
Credit |
Debit Entry
Debit note in GST
According to Section 2(38) of the Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, a debit note is a record or document which is delivered or issued under Section 34(3) by a registered person.
Section 34(3) of the Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, states that when a Tax Bill or Invoice has been delivered due to the supply of goods and services and it is found that-
- The value of goods and services which is mentioned in the bill or invoice is less than the substantive value of goods and services.
- The Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate is debited at a low rate in respect of the actual rate which is applicable for those goods and services,
The person who has furnished the goods and services i.e registered person will deliver or issue a debit note to the receiver of those goods and services. A debit note increases the liability of the supplier upon the tax.
Section 34(4) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, deals with the situation when the debit note is issued during the return of the goods and services.
When a registered person issues a debit note for any goods and services, he has to mention the details of such a debit note in the “return for the month” when such debit notes have been delivered or issued and after this the liability of the tax will be adjusted.
The debit note may be issued in two situations:-
- When the value of the tax on the goods and services are changed after the bill or invoice is issued.
- When the tax upon the goods and services is changed after the bill or invoice is issued.
When supplier may issue a debit note
- When bill or invoice of tax has been issued by the supplier and then the actual value of the tax on the goods and services exceeds the tax amount which is specified in the invoice or tax.
- When the number of goods and services which are received by the receiver or recipient and which is supplied by the supplier goes beyond the quantity which is specified in the bill or invoice.
Debit Note vs. Invoice
Many a time it was observed that there is some confusion relating to the debit note and invoice. Confusion arises due to the reason that debit note is also issued for a proof of transaction when the delivery was done. Debit notes and the invoices are two different documents. If, in case, the seller of goods and services prefer to adjust the amount which he had sent previously then he may use the debit note alternately.
|
Sr. No. |
Debit Note |
Invoice |
|
1. |
Debit Notes are a kind of memorandum. |
The invoice shows the list of the goods and services which are purchased and the total amount required to be paid for those goods and services. |
|
2. |
A debit note is issued by the purchaser of goods and services to the seller. |
An invoice is issued by the seller of goods and services to the buyer. |
|
3. |
The debit note signifies a formal request. |
Invoice gives proof that the transaction has occurred between a seller and a buyer. |
|
4. |
Debit notes are treated as a notification for the due payments. |
The invoice shows the poll of the total amount which has been already paid. |
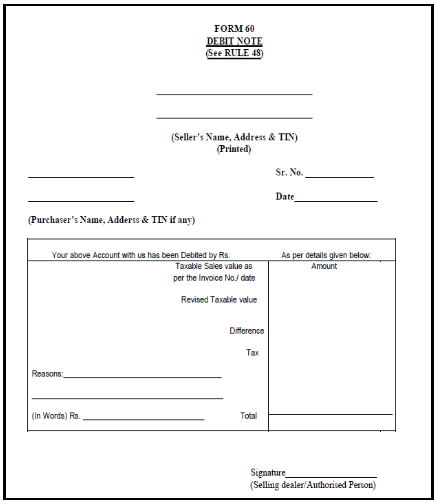
Debit Note Format
Debit notes are memorandum which is used by the purchaser. They are a kind of promissory note which is issued by the purchaser or the buyer of goods and services informing the seller that he is under liability to issue a credit note. It a type of commercial document or a formal document that is used by the business sector.
Format 1 of the Debit Note

Format 2 of the Debit Note
Format 3 of the Debit Note
Format 4 of the Debit Note
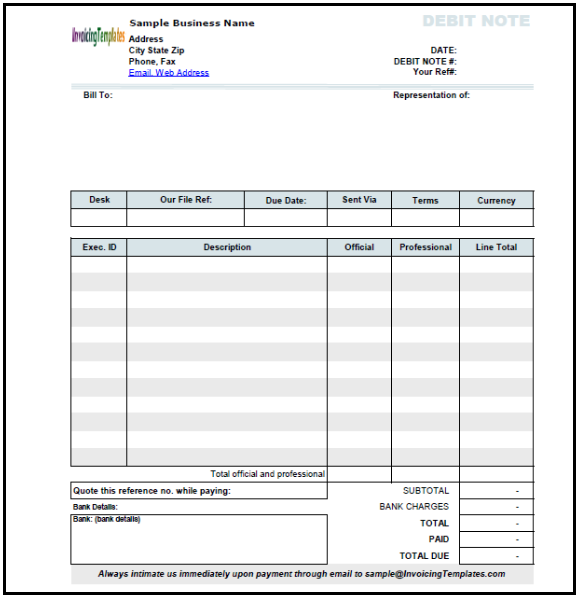
Format 5 of the Debit Note
The debit note shall contain specified contents. There is no proper defined format of the debit note, but still, there are some important content or details which are required to be mentioned in it. The debit note must give the particulars about the money which is required to be debited from the seller’s account. Purchaser or buyer shall specify the reason for issuing the debit note.
Though there is no prescribed format for the debit note, it is necessary to specify some details in it. Rule 53 of Central Goods and Services Tax Rule, 2017, deals with the particulars which are required to be mentioned in the debit notes, these particulars are:-
-
- The word “Debit Note” must be marked or indicated noticeably wherever it is applicable.
- Supplier’s name, Goods and Services Tax (GST) Identification Number and address must be mentioned in the invoice.
- Document’s nature
- Consecutive Serial Numbers are unique numbers for every financial year.
- Issuing date of the document.
- Recipient’s name, Goods and Services Tax (GST) Identification Number or Unique Identification Number and Address (if it is registered).
- When the recipient or receiver is an unregistered person then particulars to be mentioned were a name, delivery address, recipient’s address including the State’s name and its code.
- Serial number and date of the bill of supply and the corresponding tax bill or invoice.
- Tax Rate, the amount of the tax which is credited or debited to the recipient and receiver or value of taxable supply of goods and services.
- Digital signature or signature of the supplier or representative authorized by him.
There is no time limit for the issuance of the debit notes.
What is Credit Note?
Credit Note is an instrument or document which is given by the seller of the goods and services to its buyer or purchaser. Through the credit notes, the vendor of goods and services notify or inform its customer that credit of amount has been made in his account. Due to the return of goods and services by the purchaser, the amount has been credited in his account.
When the goods and services are returned by the purchaser or the buyer, he will issue a debit note to the seller. The debit note signifies that the seller is in liability to pay the specified amount to the purchaser. When the seller will credit the amount in the account of the purchaser, he will issue a credit issue notifying that the amount has been credited to his account.
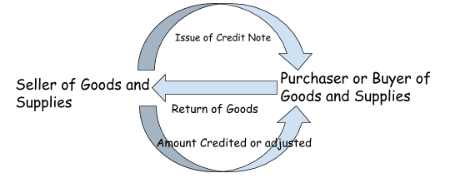
The amount may be adjusted in the next transaction. When the buyer will repurchase the goods and services from that particular buyer or purchaser then the amount may be adjusted in that particular transaction. The purchaser will be allowed to pay the less amount of the goods and services, he will not pay to the extent of the amount of the goods and services returned during the last transaction.
A credit note is also issued when the goods and services issued or delivered are less, this is to inform the purchaser that he is not required to make the payment. The month in which the credit note was issued, It must be specified in the GST return of that month.
Example:- A corporation “XYZ” purchase goods of Rs. 2,00,000 from another corporation say “ABC”. But, the corporation “XYZ” came to know that goods worth Rs. 50,000 are damaged. They inform about this to the corporation “ABC” during the delivery of goods.
Corporation “ABC” issued a credit note of Rs. 50,000. Now, the corporation “XYZ” has to give Rs. 1,50,000 to corporation “ABC”.
Now, consider a situation where the corporation “XYZ” has already made the payment to the corporation “ABC”. And, after making the payment, they came to know that the goods worth Rs. 50,000 are damaged. In such a situation, whenever the corporation “XYZ” will buy goods in the future from the corporation “ABC” the amount will be reduced from the payment.
Important Features of Credit Note
- It is issued by the seller of the goods or services to inform or notify the buyer or purchaser that the amount has been credited in his account along with the reason behind it.
- When an amount is credited to the account of the purchaser due to the reason that the goods and services have been returned, the “sales return book” will be renewed accordingly.
Sales Return Book:- When goods and services have been returned by the purchaser to the seller or vendor, he records the return of sale in a book which is known as “Sales Return Book” or “Returns Inwards”. When the buyer or purchaser returns the goods due to the bad quality, defective quantity, etc. If returning of goods is frequent then in such case it is maintained or recorded in the journal.
- A credit note is issued by the seller when the goods sent are impaired or damaged, insufficient and faulty at the purchaser’s end.
- A credit note shows a negative amount.
Credit Note entry
Book of Purchaser or Buyer
When a buyer or purchaser returns goods or services these are known as purchase return. When these goods are returned to the seller then,
- There shall be a decrease in the liability to pay the particular creditor.
- There shall be a decrease in the payment or expenditure which is incurred earlier to buy particular goods.
|
Account of Creditor |
Debit |
|
Purchaser return account |
Credit |
Seller’s Book
When buyers return goods, they are received back by the seller. Goods that are received back by the seller are known as sales return. When the goods are received by the seller, there is a certain effect of this is upon seller-
- There is a decrease in revenue which is earlier reserved as a sale.
- There shall be a decrease in the assets because now the debtor will not make the payment.
|
An account of Sale Return |
Debit |
|
An account of debtor’s |
Credit |
Credit Note in GST
According to Section 2(37) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, a credit note is a record or document which is delivered or issued under Section 34(1) by a registered person.
Under Section 34(1) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, when the bill relating to the tax has been delivered or issued and if :
- The tax which is charged in the bill exceeds the tax which is to be charged in that supply.
- When goods and services have been returned by the receiver or the recipient due to the reason that the goods and services are faulty.
Then the seller will issue a credit note to the receiver or recipient. The credit note will contain all the details or particulars which are prescribed in Rule 53.
Section 34(2) of Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, states that, when a registered person delivers or issues a credit note relating to the goods and services which has been supplied, then he must announce the particulars or details of that credit note in the return for month when such specified credit note has been issued.
Debit notes may be issued at any time as there is no restriction or boundation of time for issuing the debit note. But in case of the credit note, there is time boundation i.e.
- Before the date of filing the annual return, the credit note shall be declared.
- A credit note shall be declared by the September 30, in a sequence to the year in which they have been issued.
Example of the time restriction in credit note:-
|
Condition 1 |
Condition 2 |
|
|
Supply year |
2018 |
2018 |
|
Filing of annual returns |
30/11/2019 |
15/9/2019 |
|
September 30 of the next or in sequence year |
30/9/2019 |
30/9/2019 |
|
Previous of the succeeding states. |
30/9/2019 |
15/9/2019 |
When credit notes may be issued:-
- The value of tax which is mentioned in the bill or invoice is higher than the actual amount of tax.
- When the receiver of goods and services return them back to the supplier.
When the liability of the receiver or recipient of the goods and services to pay the amount of tax reduces, he issues the debit note to the supplier. In proportional to the debit note, the credit note is issued by the supplier.
Credit Note Format in GST
A credit note is a document or record which is allotted by the vendor or trader when the goods are returned by the purchaser or buyer. The government site for Goods and Services Tax (GST) provides a format for the credit note.
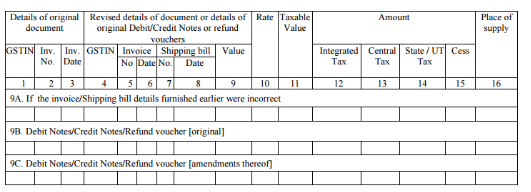
This is a credit note under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) which a vendor or seller will issue to a purchaser in case of return of goods by him.
Rule 53 of Central Goods and Services Tax Rule, 2017, deals with the particulars which are required to be mentioned in the credit notes, these particulars are:-
-
- The word “Credit Note” must be marked or indicated noticeably wherever it is applicable.
- Supplier’s name, Goods and Services Tax (GST) Identification Number and address must be mentioned in the invoice.
- Document’s nature
- Consecutive Serial Numbers are unique numbers for every financial year.
- Issuing date of the document.
- Recipient’s name, Goods and Services Tax (GST) Identification Number or Unique Identification Number and Address (if it is registered).
- When the recipient or receiver is an unregistered person then particulars to be mentioned were a name, delivery address, recipient’s address including the State’s name and its code.
- Serial number and date of the bill of supply and the corresponding tax bill or invoice.
- Tax Rate, the amount of the tax which is credited or debited to the recipient and receiver or value of taxable supply of goods and services.
- Digital signature or signature of the supplier or representative authorized by him.
Important Point
- A credit note and debit note shall contain a bill or invoice number.
- The bill or invoice number mentioned in the credit note or the debit note must be of the original supply.
- Particulars or the details of the credit notes and debit notes shall be declared in FORM GSTR-1. And these details shall be taken into account with the particulars of the original bill number, Goods and Services Tax (GST) Identification Number and the date.
- The particular or details of the Credit note and debit note shall be in FORM GSTR-1.0n. When details will be filled it will auto-populated into the FORM GSTR-2A for the receiver. The receiver of the supply may accept it or either reject it or modify those particulars or details and then file FORM GSTR-2.
- There is a time restriction on the issuance of the credit note but there is no time boundation for the issuance of the debit note.
Difference between Credit Note and Debit Note
|
Sr. No. |
Grounds for Comparison |
Debit Note |
Credit Note |
|
1. |
Meaning |
Debit Note is a document or an instrument that is issued by the purchaser of goods and services to inform the seller that his account has been debited for the amount to the extent to which the goods and services have been returned. |
Credit Note is a document or an instrument issued by the seller of goods and services to inform the buyer or purchaser that the amount to the extent of the goods returned has been credited in his account. |
|
2. |
Uses |
Blue ink is used to write the Debit Note. |
Red ink is used to write the debit note |
|
3. |
It represents |
It represents a positive amount |
Represents a negative amount |
|
4. |
Book to be updated |
When a debit note is issued, then a Purchase Return Book is renewed. |
When a credit note is issued, then a Sales Return Book is renewed. |
|
5. |
Consequence |
Account receivables are minimized |
Account payables are minimized. |
|
6. |
Substitution |
Credit Note |
Debit Note |
E-way Bill
E-way Bill is an instrument or document which is created electronically. The generation of the E-way bill is necessary because of the movement or motion of goods and products which are worth more than Rs. 50,000. When any goods or products are moved from one place to another, but within India except Delhi, E-way bill is required. When the goods value more than Rs.1 Lakh and the movement of goods or product is within Delhi then the generation or creation of E-way bill is required.
The document or instrument of E-way Bill is produced online for the conveyance of goods and services. It is immaterial whether the conveyance is intra-state or inter-state. If an E-way bill is produced in one state then it shall be acceptable in every Union Territory or the State of India.
E-way bill was introduced but the Central Board of Excise and Customs in Goods and Services Tax (GST). It enables the transportation of goods and services up to Rs. 50,000. When the Goods and Services Tax (GST) was enforced in India, the E-way bill was also launched. But, the E-way bill was never launched in an authorized way as there is some technical problem on the portal of its online registration due to which it is on grasp.
The generation, cancellation or extension of an E-way bill may be done through its website or by SMS and through Site to Site Integration. Supplier or recipients get a distinctive E-way bill number or EBN when they generate the E-way bill.
GST E-way Bill Rules
Rule 138 (Chapter XVI) of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Rule, 2017. Deals with the E-way Rules.
The rule specifies that the government is in charge of mention which document a person will carry while he is transporting the goods and services or while the goods are in transit storage. The government will specify the document by the notification until a system of E-way bill is approved or developed by the council.
The provision of E-way rule under Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Rule, 2017, is vague or ambiguous. The rule does not directly talk about the E-way bill. It says that “Till such time as an E-way bill system is developed and approved by the council”. The person who is conveying the goods and services will carry a document when goods are in movement, which is specified by the Government for such purpose. But, those documents are not directly stated as an E-way bill. The government is empowered to specify those documents, by notification, till the E-way bill system will be developed by the authority and it will get approval from the Council.
E-way bill system
For generating the E-way bill, there are some prior conditions, they are:
- A person who is required to generate the E-way bill must register on the portal of the E-way bill.
- Any bill or invoice relating to the collection of goods which is to be sent must be with the person generating the E-way bill.
- When the conveyance of the goods or services is by road then the ID of the transporter and the vehicle number is required to be with the person generating the E-way bill.
- When the conveyance of the goods or services is by air, ship or rail then the transport document number, ID of transport and date on the document must be with person generating E-way bill.
E-way bill generation
Section 68 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, deals with the inspection of the goods which are in movement.
There is a requirement by the Government that the person who is transporting or conveying the goods may carry or hold a document with himself if the value of goods exceeds a certain limit.
The document which a person is carrying with himself for conveying the goods will be approved in a manner that is prescribed by the Government.
When the proper officer obstructs any transportation of goods and services, he will ask or claim the person who is transporting the goods to present the document which was prescribed in the Section and the person is duty-bound to present the documents and the devices and he will also allow the proper officer to inspect the goods.
Applicability of E-way Bill under Goods and Services Tax (GST)
For the conveyance of goods from a state to another state, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) will be applicable. E-way bill was first introduced by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highway and it was introduced for only 14 days on a trial basis. It was enforced or applicable from April 1, 2018. The E-way bill was first announced in stages which was started from April 15, 2018, up to June 16, 2018. The system of E–way bill was applicable when the stages roll-out was completed.
Before the introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST), there was a “Way Bill” system. Waybill was applicable during the regime of Value Added Tax (VAT) for the transportation of goods and services. This bill was not generated online rather the document was created physically for the transportation or conveyance of the goods and services. Now, after the amendment and introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) the Way Bill in Value Added Tax (VAT) was substituted with an E-way bill which is a document or record electronically generated.
Who shall generate E-way bills?
E-way bill in Goods and Services Tax (GST) shall be generated by:-
- A registered person under Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- Where there is a conveyance of goods and services under GST by a registered person, then in such case E-way bill shall be generated by the registered person or the recipient (receiver) of the consignment.
- E-way bill may be generated by the transporter when the goods are transferred to the transporter by the registered person for its conveyance or the movement.
- An unregistered person under Goods and Services Tax (GST)
- When there is a conveyance or transportation of goods or consignment by the unregistered person then in such case the generation of E-way bill shall be done by the unregistered person only and not by anyone else.
- when there is a conveyance of goods and services by an unregistered person to a registered person in such case it shall be treated as a conveyance by the registered person, therefore, it is the liability of the registered person to generate the E-way bill.
E-way Bill Registration
Through the online portal of Goods and Services Tax (GST) i.e. gst.gov.in the E-way bill was generated. It may also be generated by SMS by giving a registered number. Goods and Services Tax (GST) online portal also has the option to change the vehicle number from the E-way Bill which has been generated already, Cancellation of E-way bill, E-way bill print, etc
Things required for the generation of the E-way bill:-
- A person must have an account on the portal of the E-way bill.
- For the conveyance of goods from the road, there must be vehicle number and transport ID.
- For the conveyance of goods through the air, ship or rail, there must be Transport document number, transport identification and document shall specify the date.
- There must be an invoice or bill or challan of the specified goods and services for which an E-way bill is required to be generated.
Registration by registered person or taxpayer
The registered person or taxpayer will register on the Goods and Services Tax (GST) online portal in the following way:-
- Open the E-way bill portal through https://ewaybillgst.gov.in/
Note: If the online portal of Goods and Services Tax (GST) shows the “Login”, then, close it. Frontpage or home page of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) E-way Bill system will look like this:
2. You will find a registration column on the right-hand side of the E-way bill system portal. “Registration” will be easily visible in between the “Contact us” and “Log in”. Click on “Registration” and then “e-way Bill Registration” available under it.
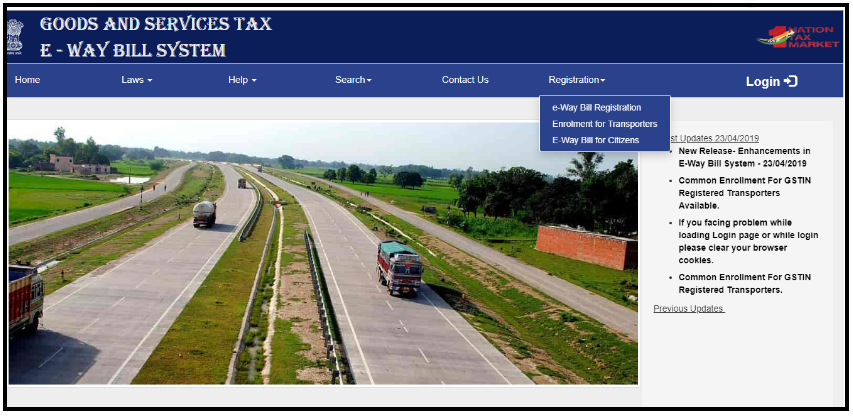
3. When you click on the “e-way Bill Registration” it will direct to this page
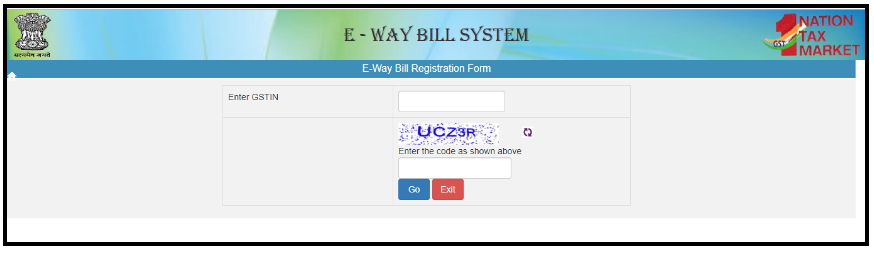
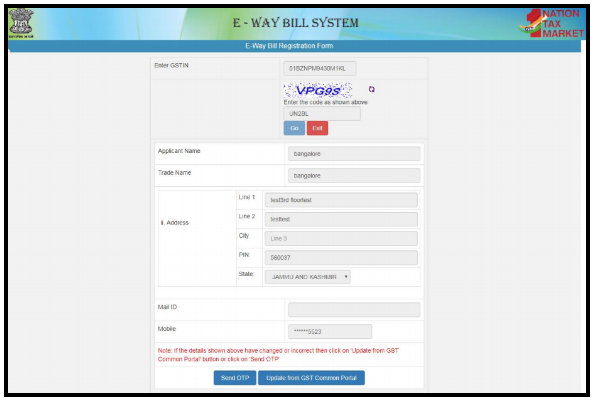
In this page, type your “Goods and Services Tax Identification Number” and the “captcha code”.
4. “One Time Password” or “OTP” will be generated after the submission of “Goods and Services Tax Identification Number” and now you have to verify that “One Time Password” or “OTP”
Check the auto-filled columns before clicking on the “Send OTP”. After receiving the “One Time Password”, which will be received in the registered mobile number, you have to verify it by clicking the button of the “Verify One Time Password”.
5. Now, the final step is to enter a “New Used ID”. You are also required to set a password.
Note: Do not share your password with anyone. It is to prevent your information which is linked with the portal or connected with the site.
If there will be an error in the details filled by you, the “E-way Bill System” portal will pop up a message to inform you.
E-way Bill Login
After registering in the E-way bill system through the https://ewaybillgst.gov.in/, now a person may generate the E-way bill for the purpose of conveying or transporting goods and services across India. For the purpose of generating the E-way bill online, you have to login through https://ewaybill.nic.in/. Follow these steps to generate an E-way Bill:-
A person who is required to generate the E-way bill must register in the portal of E-way bill i.e. from https://ewaybill.nic.in/
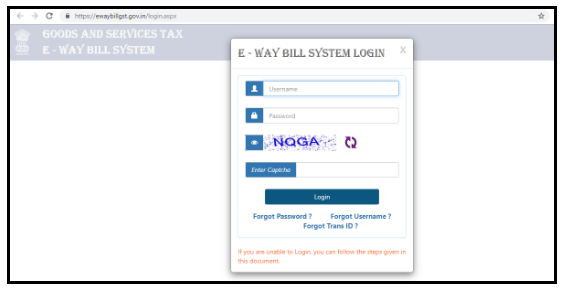
After login through the registered Id, a dashboard will be open on the portal of the E-way bill. The portal will display the information regarding the recent activity done in the portal. The portal will also display some more options at the left side of the screen.
The list will show the “e-way bill” as the first option. Click on that option.
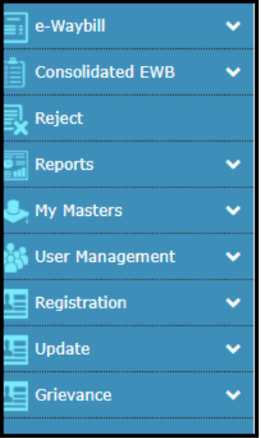
A further list will be open. If a person wants to generate a new E-way bill, then he has to click on the first option “Generate New”.
A screen will be open. The required details must be entered in the columns.
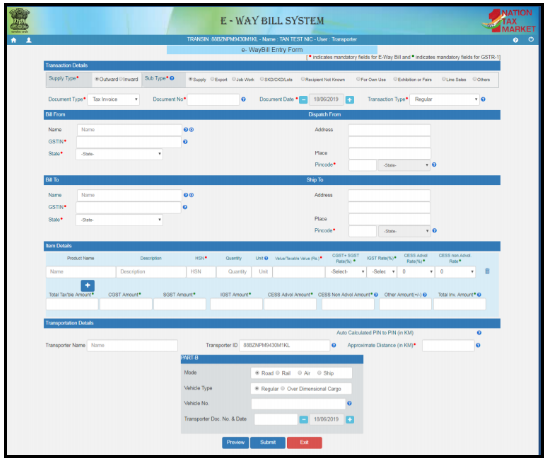
The above screen displays various options with various sub-options. This is an “E-way Entry Form”. The person is now required to fill it in detail. These are the sub-options which a person is required to fill.
Type of Transaction:- If a person is a supplier than the transaction will be “outward” and if a person is a receiver or recipient than the transaction will be “inward”.
Transaction’s Subtype:- Sub-Type relating to the transaction will be displayed according to the type of the transaction.
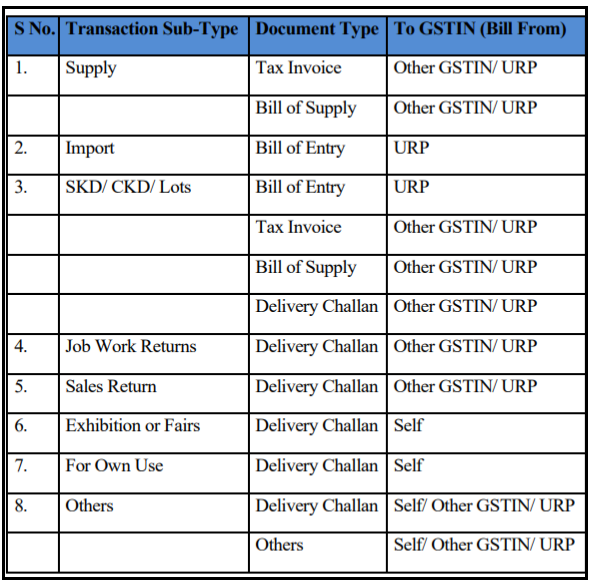
If outward:- If the transaction type of a person is outward then you have to enter the name, Goods, and Services Tax Number (GSTN), you may also enter the additional places of your business. These are the document types, transaction subtypes which you have to fill.
If inward: It the transaction type is inward then you have to fill in name, Goods, and Services Tax Number (GSTN), Address and state in the option.
Details of document: In the option “Details of Document” have to fill the details about your document. The type of your document, number of your document and the date of the document.
Note: The future date is not acceptable so a person generating the E-way bill is not allowed by the portal to enter any date in the future.
Details relating to “Bill To” and “Bill From”:- In the option “Details relating to Bill” shall be entered. The supplier’s detail and recipient’s detail will be filled. When the type of transaction will be selected, the details relating to “From/To” will be automatically filled in the column.
Note: The supplier or recipient have to fill “Unregistered Person” i.e. “URP” instead of “Goods and Services Tax Identification Number” i.e. “GSTIN” when the person generating the E-way bill is unregistered.
Details of item:- In the option “Details of item” you are required to enter all the details relating to the item. The items detail must be mentioned which are required to be transferred. It will ask to enter the “Product Name”, description, etc.
Details regarding transport:- Last option is “Details regarding transport” in which you will enter the details relating to the vehicle, transporter and mode of transportation must be filled in the next section.
Once all details have been entered, a person may check all the details which are entered by him through the “Preview”. After re-look from all the details submitted earlier, now a person may generate the E-way Bill Number by submitting the details.
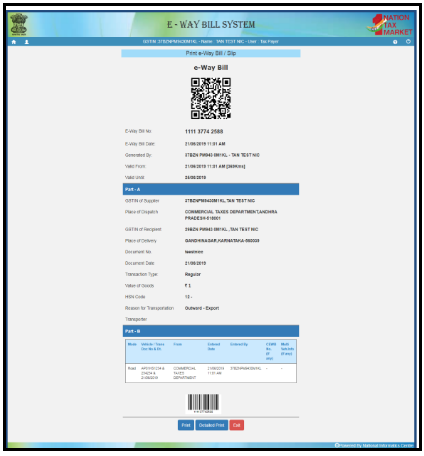
Reprinting of the E-way bill
If a person wants the E-way bill again, then he may reprint it. For the purpose of the reprint, these are the methods:-
- On the online portal of the E-way bill, a person will see the option E-way bill on the left-hand side of the portal. After clicking on the E-way bill, there is an option of “ Print EWB” below all the options. Click on the “Print EWB”
2. Now, the second step is to fill or enter the E-way bill number. You have to enter your: Unique or E-way Bill Number” and then click on ”GO”. if you are not sure about your E-way Bill number then click on “Exit” to leave the page.
The E-way bill which is going to be displayed may be used or print again.
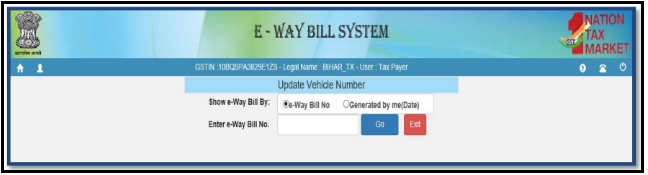
Generation of E-way bill (Part-B)
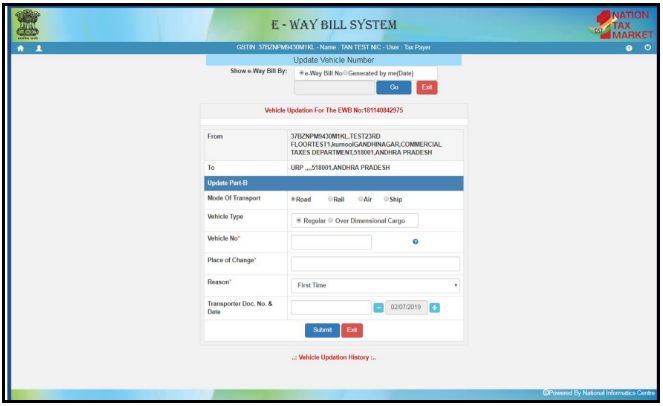
To fill or enter the information relating to the Part-B in the E-way bill, then the steps to be followed are:-
- On the left side of the E-way bill portal, click on the E-way bill. Then the further list will be open. Select the option “Update Part B/Vehicle”.
- Now. the portal will ask to enter either the date on which E-way bill was generated or E-way bill number. The portal will display or list the generated E-way bill.
3. The third step is to choose a proper E-way bill i.e. EWB. if the E-way bill requires the changes. It shall be done and the last step is to submit it by clicking on the submit option.
Unregistered Transporters
If a transporter is unregistered, then, he will not be able to register through the method which is discussed above. He has to enroll in the “E-way Bill System” by giving all the details relating to his business. When he filled the details, the “E-way Bill System” will generate a fifteen character transporter ID and user credentials for the unregistered transporter. For enrolling, he is required to have a business type, PAN details, and place of his business, etc. Now, methods for enrolling in the “E-way Bill “ portal is:-
Open the “E-way Bill System” portal.
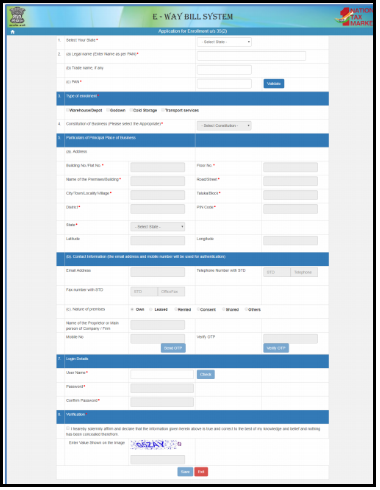
- Click on the option “Enrollment for transporters”. After selecting the option, this page will open:
- Unregister transporter is required to enter his legal name which is mentioned in his PAN. he had to select a state and enter his PAN number. Now, he had to validate it by clicking on the “Validate” button.
- Now the unregistered transporter has to select the constitution of business and the kind of the enrolment.
- Now, the unregistered transporter has to enter all the details relating to the business and contact.
- The next step is to upload the identification proof and address by opting for the “Upload” button.
- Now, unregistered transporter will be asked to set the username and password according to the rule and his convenience
- After all this, the user will give the declaration relating to the correctness of the information which is given by him by clicking the option “checkbox”.
- At last, the unregistered transporter will click on the “save” option. After saving this, the E-way Bill System will generate fifteen digits “Trans ID”. This will be shown to him. Now, unregistered transporter may give this Trans ID to any of his clients who will enable the transporter to enter the vehicle number for the purpose of the movement of goods.
E way Bill Format
E-way bill format is-
- There is an online filing of Part A of FORM GST INS-01. It is an online Goods and Services Tax (GST) portal which is filled by the Registered supplier.
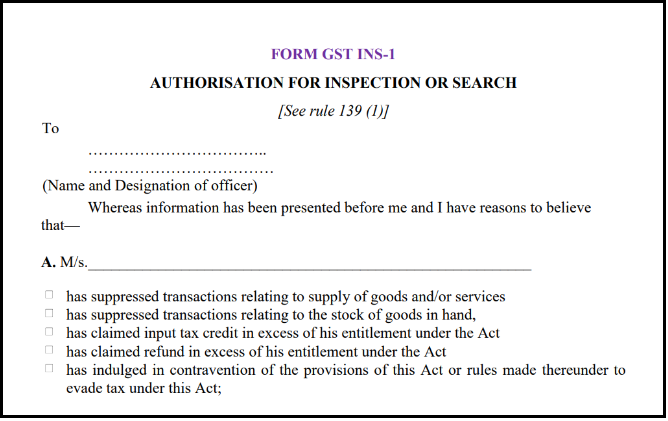
2. In the Goods and Services Tax (GST) portal the registered person or the receiver of goods and services will fill the Part B of FORM GST INS-01.
3. When goods and services are transferred by the registered person to the transporter than a registered person will fill the Part A and B of FORM GST INS-01.
4. If the consignor of the goods and services will not fill the FORM GST INS-01, then the transporter will fill the form.
5. When there is an unregistered supplier, the E-way bill will be generated by the transporter or the supplier for the conveyance of goods and services in FORM GST INS-01. The receiver of the goods and services will be treated as the supplier if he is a registered person.
6. When there is one transportation or conveyance of the multiple goods and services then the separate generation of E-way bills. It is the duty of the transporter to specify the serial number of every E-way bill in FORM GST INS-02 and there will be a combined generation of a bill in the portal.
7. The verification of the E-way bill may be done by the Commissioner or any of the authority empowered by him. He may verify the E-way bill at any time during the conveyance of the Goods. The report of the verification shall be documented by in Part A of FORM GST INS-03 by the proper officer, not beyond the 24 hours from the inspection.
8. The inspection report which is finalized must be recorded not beyond the three days from the inspection in Part B of FORM GST INS-03.
9. If a vehicle has been in custody exceeding the time limit of thirty minutes then the information will be uploaded in FORM GST INS-04. It will be followed when there is no compliance with the E-way bill rules.
E-way bill validity
The validity of the E-way bills depends upon the distance of the vehicle after which it expires. The day and time on which the E-way bill is generated, the validity of the E-way bill starts.
- When distance traveled by the vehicle is less than 100 Km then the E-way bill remains valid for the one day.
- When the distance traveled by the vehicle is between 100 Km to 300 Km then the E-way bill will remain valid for three days.
- When the distance traveled by the vehicle is between 300 Km to 500 Km then the E-way bill will remain valid for the five days.
- When the distance traveled by the vehicle is between 500 Km to 1000 Km then the E-way bill will remain valid for ten days.
- When the distance traveled by the vehicle is more than 1000 Km the E-way bill will remain valid for fifteen days.
The Commissioner of Good and Services Tax (GST) may extend the E-way bill validity for a definite good.
|
Sr. No. |
Type of Conveyance |
Distance in Kilometers, up to |
The validity of E-way Bill |
|
1. |
Cargo (Normal) |
100 Kilometers Each additional 100 Kilometers |
One Day One Additional Day |
|
2. |
Cargo (Over dimensional) |
20 Kilometers Each additional 20 Kilometers |
One Day One Additional Day |
If a taxpayer or holder wants he may extend the validity of the E-way bill. The time limit to extend the E-way bill is either four hours before or four hours after the expiry of its validity. In simple, the taxpayer has eight hours to extend the validity of the E-way bill and if he fails to extend its validity he will face the penal consequences.
Penalties for not carrying the E-way bill
When a transporter is caught conveying the goods or consignment without having the E-way Bills than he has to face the legal consequences. The penalty which will be imposed upon the transporters for not carrying the E-way bill is-
- Fine
If there is a conveyance or transportation of goods from one State to another without the E-way bill then the transporter will be held liable to pay Rs. 10,000 or the amount of tax evasion whichever will be high.
- Detention of Goods
Where it is observed that the taxpayer has not obliged with the policies which are specified than his goods and vehicle will be confined or detained. Such an act will be done without any prior notice. When the taxpayer who is liable to pay the tax pays the full amount of goods or either half, his vehicle or goods may be set free.
Conditions when E-way bill is not required
E-way bill is required for the conveyance of goods or consignment from one state to another. But there are certain goods or consignment for which E-way bills are not required, these goods are-
|
Sr. No. |
Description of Goods |
|
1. |
For any Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) which is supplied to the NDEC (Non-domestic Exempted Category Customers) and households. |
|
2. |
When Kerosene oil is sold under the Public Distribution System (PDS) |
|
3. |
When the Department of Post transports the Postal Baggage. |
|
4. |
Any precious or semi-precious stones and cultured pearls or natural pearls. Any metal which is precious and metal is covered with precious metal. |
|
5. |
Produce of goldsmith or silversmith, jewelry and further articles |
|
6. |
Any personal used or household belongings |
|
7. |
Currency |
|
8. |
Any goods which are conveyed is alcoholic for the consumption of humans, crude petroleum, petrol or motor spirit, high-speed diesel, aviation turbine fuel, natural gas. |
|
9. |
Any coral and worked (9601) or unworked (0508) coral. |
Exemption of E-way Bill area wise
- When goods or consignments are conveyed under the custom seal or custom direction.
- When the goods which are conveyed are shipped from the countries which are least developed such as Bhutan and Nepal.
- When there is a conveyance of the containers, which are vacant, from one country to another.
- The goods which are conveyed from the air cargo complex, airport, custom port, land customs station to a container freight station or inland container depot for the clearance by the custom.
Exemption of E-way Bill vehicle wise
- If there is a conveyance of goods and consignment through cycle, skateboard, rickshaw, push scooters or any other non-motorised transportation.
- When the goods are conveyed by the State Government, Central Government or other local authorities as a dealer or consignor through the trains or rails
Exemption of E-way Bill person wise
- When the goods and consignments are conveyed as a consignor or consignee from the Ministry of Defence or Ministry of Defence.
- When the goods are conveyed by the State Government, Central Government or other local authorities as a dealer or consignor through the trains or rails
Conclusion
Debit Notes/Credit Notes and E-way Bill are new documents of growing India. They are introduced after the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST). Debit notes are issued by the purchaser or buyer on the other hand credit not is the seller’s document. Whenever the goods are returned purchaser or buyer will mention it in the purchase return book. Seller after issuing the credit note will mention it in the sales return book. E-way Bill replaced the Way-Bill. Value Added Tax (VAT) system was followed in the Indian tax system before the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and waybill was part of it. With the introduction of the GST, the economic pattern of India has been changed. The whole purpose is to lead India to a developed region.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack










 Allow notifications
Allow notifications



Very informative and elaborate article.