This article is written by Raj Jaiswal pursuing Diploma in Business Laws for In-House Counsels from LawSikho.
Table of Contents
Introduction
India is one of the largest fastest-growing economies in the world with an average growth rate of 7%. With a population size of 1.3 billion, it is one of the most lucrative markets in consumer products.
The food and beverage industry is one of the fast-growing in India due to the increase in purchasing power of the people and the urbanization of small cities which has increased the demand for processed foods and beverages in the last few years.
In the recent past, India has witnessed a sharp growth in the Food and Beverage (F&B) Industry. Increasing commodity branding, increase in the opening up of the retail sector, entry of multinationals in the F&B industry, increase in local products and the low cost of technology are the factors of such sharp growth of the food & beverage industry. Besides, a large part of the industry also consists of the import and export of food and beverages.
Therefore, India has enacted various rules and regulations in harmony with the international laws and standards, which every industry in the area of Food & beverages needs to comply with.
In this article, we will discuss the legal requirements related to food and beverages that PepsiCo needs to comply with. Let us first begin with the introduction of the company ‘PepsiCo’ and its business.
About PepsiCo Incorporation
PepsiCo Inc. is a multinational company, headquartered in Harrison, New York. It was formed with the merger of two companies i.e., Pepsi-Cola and Fruit-Lay in 1965. Thereafter, in 1998 PepsiCo acquired Tropicana and had a merger with Quaker Oats in 2001, which added more food and beverage brands to its portfolio. Since then PepsiCo has expanded its portfolio to a broader range of food and beverages brands.
PepsiCo Inc. entered India in 1989 and established as PepsiCo India Pvt. Ltd. and has grown to become one of the largest MNC food and beverage businesses and one of the major players in the Indian subcontinent.
It entered India as a food and agro-based products company. The liberalization of the Indian economy in 1923 helped PepsiCo expand its business in India. Currently, it has headquarters in Gurugram, Haryana. PepsiCo India’s diverse portfolio in food and beverages includes iconic brands like Pepsi, Kurkure, Lays, Quaker, Tropicana 100, and Gatorade.
Legal compliances that PepsiCo needs to run its food and beverage business
As stated earlier, the food and beverages business in India is one of the most lucrative and trending businesses with exponential growth, and PepsiCo is one of the largest players in it. But in order to run a food and beverage business, it is imperative for PepsiCo to follow a set of guidelines and to comply with the legal aspects in order to carry out its food and beverages business. Failure to comply may land up PepsiCo with unnecessary legal hindrances. Let us see what mandatory compliances need to be followed.
-
Food license
The first and foremost prerequisite for PepsiCo to start a food and beverage business in India is to obtain a food license from the FSSAI. FSSAI stands for the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India. It is obtained for the purpose of manufacturing, preparing, distribution, and transportation of food and beverages.
FSSAI is a body established in the year 2008, and its procedure is regulated by Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSSA) and Regulations, 2011 and Rules, 2011. The FSSAI license is of 3 types based on the annual turnover of the company:
- FSSAI Registration: For businesses with an annual turnover of Rs. 12 lakhs.
- FSSAI State License: For businesses with an annual turnover of Rs. 12 lakhs to 20 crores.
- FSSAI Central Licence: For businesses with an annual turnover above Rs. 20 crores.
Here, PepsiCo has to apply for the central license as its business has an annual turnover of more than Rs 20 crores.
FSSAI registration/license can be obtained either offline or online. Once the registration process gets completed, an FSSAI license number is issued to the food business operator. This license number is to be displayed on all the food and beverage products of the company.
-
Packaging and labelling
PepsiCo needs to comply with certain packaging and labelling regulations in order for the smooth running of its food and beverages business. The packaging and labelling requirements for packaged food and other commodities in India have governed under the Food Safety and Standards (Packaging and Labelling) Regulations, 2011, the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, the Legal Metrology Act, 2009 and the Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities) Rules, 2011.
Non-compliance with the prescribed requirements and the regulations will trigger a monetary penalty which may extend to one lakh rupees or imprisonment for a term which may extend to one year or with both to PepsiCo.
-
Fire department No Objection Certificate (NOC)
To run its business in the food and beverages industry, PepsiCo has to apply for a No Objection Certificate (NOC) for its building/unit from the fire department of the concerned area. PepsiCo has to make an application to the concerned fire department along with the necessary documents such as the model of the building, building plans, and certificate from the architect. Apart from this PepsiCo also has to fill out a questionnaire related to compliance with fire safety rules and regulations. After the verification of the application and the documents, officials of the fire department will carry out certain inspections of the building of PepsiCo.
The main purpose of this is to protect its employees and workers from fire hazards. Therefore, a No Objection Certificate is required from the fire department for the food and beverages business.
To get a No Objection Certificate (NOC) From Fire Department, the company has to register its premises for NOC from the State Fire Department before the construction of the building starts. Applications for registration can be made online on the state government website. After getting all the safety equipment installed in place, the company can invite the Chief Fire Officer (CFO) for inspection and get the NOC.
-
Environmental clearance
The main objective for getting an environmental clearance is to reduce the environmental damages which are caused by these industries.
The food and beverage industry is also considered a polluting industry as it contributes to environmental pollution by way of smoke emissions from the making process of foods and beverages and also from the washing of food waste. Therefore, in order to establish and operate its food and beverage business, PepsiCo needs to obtain environmental clearance from the concerned State Pollution Control Board (PCB). To obtain an environmental clearance PepsiCo has to apply on the website of the concerned State Pollution Control Board (PCB). Further, categories of the establishment are provided by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) depending on the scale and type of industry and operations of the businesses.
As per statistica.com annual volume of mismanaged plastic waste created by PepsiCo as of 2019.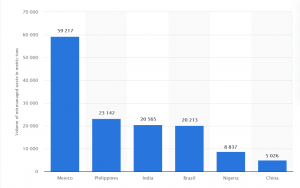
- Export Quality Certification
This certification is governed under the Export (Quality Control and Inspection) Amendment Act, 1984.
The main purpose of the Regulation of Exports and Imports Act is to facilitate export trade through quality control and inspection before the products are sold to international buyers.
Subject to the stipulations provided under the act, the Central Government is authorized to recognize and constitute agencies for quality control or assessment. The act further directs the Central Government for the establishment of the Export Inspection Council. The Export Inspection Council after conducting a necessary inquiry and after getting satisfied with the standard requirements of the goods possessed may issue a certificate in the prescribed manner.
Therefore, PepsiCo must comply with the regulations of the Export (Quality Control and Inspection) Amendment Act, 1984 in order to get the certification for its export of food and beverage products.
-
Voluntary standards
There are two organizations that deal with voluntary standardization and certification systems in the Food and Beverage Industry in India:
-
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
BIS was established by the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986. Its purpose is not to only serve the consumer’s interest but also to introduce quality products in the Indian markets.
-
Directorate of Marketing and Inspection (DMI)
It is for “AGMARK” Standards. This certification mark is given to the agricultural products in India, this mark certifies that the products conform to the set of standards that are approved by the Directorate of Marketing and Inspection.
PepsiCo must apply for the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) certification, as it is mandatory for certain products such as packaged drinking water, mineral water to have a BIS certification requirement under the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restriction on Sales) Regulations, 2011.
-
Trademark certification
Trademark certification is governed under the Trademarks Act, 1999. Trademark is a branch of Intellectual property rights. This license permits the entity to maintain the ownership right of its products and services.
Therefore, in order to create a brand image among customers, PepsiCo must obtain a trademark certification/registration of their intellectual property for their distinctive/unique identity. Trademark registration/certification will provide PepsiCo the ownership over their intellectual property created and will help deter the use of the branding by competitors. To obtain a trademark license one can make an application online on the Intellectual Property India portal by entering the required details with the required fee and documents. Subsequently, after the verification of the application and the documents, a trademark registration/certificate will be allotted to the applicant.
Here are some trademarks owned by PepsiCo:
- More smiles with every sip
- Rockstar unplugged
- Mountain dew game fuel
- Pepsi
- Mountain dew
- Aquafina
- Mountain dew frostbite
- PepsiCo more smiles with every sip and bite
Tax registrations in the food and beverage industry
Every business including the food and beverages industry has to comply with the several tax regulations of the country in which they are operating their business. It is one of the most important registrations in any business.
Here, PepsiCo, in order to run his food and beverage business has to comply with three types of taxes regime:
-
Income Tax
Every entity shall have a PAN (Permanent Account Number) and TAN (Tax Account Number) in the name of the business and in case of a Sole-Proprietorship, in the name of the individual in whose name the transactions are to be made in the business. The Income Tax Department issues PAN and TAN.
-
Goods and Service Tax (GST)
GST is mandatory for all businesses, be it a sole-proprietorship, limited liability partnership, partnership, company, or firm, irrespective of their scale, volume, or frequency. GST is payable only when the turnover of the entity is more than Rs. 20 Lakhs in a financial year. Also in some special categories, as categorized under the GST Act, 2017, it is payable when turnover is more than Rs. 10 Lakhs in a financial year. To pay GST a business has to register and obtain a GSTIN – a unique Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN).
-
Professional Tax
Professional Tax is levied by the State Government on the salary paid to every individual working in the entity. The tax rate tends to differ from state to state. States issue a registration certificate or an enrolment number, for the purpose of payment of the professional tax.
Labour law registrations
Labour laws play a major important role in the establishment of labour-relations and in protecting the rights of labour, their wages, their union, and moreover building a link between government and workers. It provides a peaceful industrial relation between labourers and organized workers.
Labour law registrations have great importance wherever they are applicable. It regulates the conditions of employment in commercial establishments like working hours, payment of wages, minimum wages, equal remuneration, payment of gratuity, payment of bonus, overtime pay, opening and closing hours, maternity leave, public holidays, etc.
Employees Provident Fund registration (EPF), Employees State Insurance registration (ESI), Contract Labour Registration are some important labour laws where registration is necessary, and PepsiCo must comply with them.
Conclusion
The food and beverage industry in India is growing rapidly and is one of the fastest-growing industries in India. In the recent past, it has become more considerable for the food and beverages industry to get all the mandatory food and beverages business requirements. These regulations have made it mandatory to maintain food quality and plenty of safety measures, so people can consume the food items safely. Hence, it is important for PepsiCo to obtain licenses through various authorities like the Food Corporation of India, FSSAI, and others who deal in the food and beverages industry, and to run its business PepsiCo also needs to comply with the tax and labour regulations of the country in which he is operating his business.
The government of India enacted various regulations and designed numerous licenses to protect the rights of the consumers to quality food. FSSAI is one of them. The basic function of the Food Safety and Standards Act (FSSA) is to ensure that there is a hygienic and healthy supply of food and beverages and products. Any compromise made by the company to comply with these regulations will not only attract legal penalties but can also lead to devastating consequences for a large number of people consuming the food and beverages of the said company.
Therefore, PepsiCo, in order to stay ahead in this competitive market, needs to adhere to a strong legal framework and compliance with the requisite registrations and licenses which can be a differentiating factor amongst competitors.
References
- https://icrier.org/pdf/Streamlining_Food_Safety_Compliance_Report.pdf
- https://food.chemlinked.com/foodpedia/food-regulation-india
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skills.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals, and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack












 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


