In this article, Divya pursuing Diploma in Entrepreneurship Administration and Business Laws from NUJS, Kolkata, discusses Things you should know about Qualified Institutional Placement.
Introduction
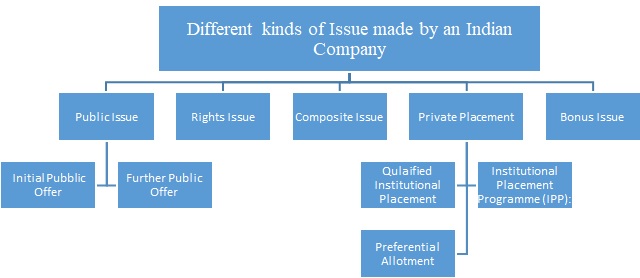
The table above provides the manner in which every Indian Company issues securities. The concept of QIP comes from Private Placement where a Company registered under the Companies Act, 2013 issues to certain Qualified Institutional Buyers. However, this issue can be only made by the companies that have been listed with the Securities and Exchange Board of India. Only they are authorized to make such issue term Qualified Institutional Buyers has been defined under Securities And Exchange Board Of India (Issue Of Capital And Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2009
“Qualified institutional buyer” means:
- A mutual fund, venture capital fund[, Alternative Investment Fund]9 and foreign venture capital investor registered with the Board;
- A 10[foreign portfolio investor other than Category III foreign portfolio investor], registered with the Board;
- A public financial institution as defined in section 4A of the Companies Act, 1956;
- A scheduled commercial bank;
- A multilateral and bilateral development financial institution;
- A state industrial development corporation;
- An insurance company registered with the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority;
- A provident fund with minimum corpus of twenty five crore rupees;
- A pension fund with minimum corpus of twenty five crore rupees;
- National Investment Fund;
- Insurance funds set up and managed by army, navy or air force of the Union of India;]
Conditions relating to Private Placement have been defined under Chapter VII of the Securities And Exchange Board Of India (Issue Of Capital And Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2009.
- A special resolution which approves the Qualified Institutional Placement mjust be passed by the Shareholders in their respective company.
- The shares that have to be issued to the Qualified Institutional Buyers must belong to the same class and must be listed by a recognized National Stock Exchange.
- Their listing must have been done at least one year prior. This is mandatory as only if the condition is fulfilled can a company pass the special resolution as is required and mandated by the provisions of Companies Act, 2013 and 1956.
- Special provisions have been mentioned in regard to a transferee company that might have undergone Merger or Amalgamation or any such related transaction that might have a similar effect otherwise. This shall be in reference to Section 391 -394 of the Companies Act, 1956.
Appointment of Merchant Banker
Guidelines also make it necessary that a merchant banker shall be appointed who will be registered with the Board and shall exercise due-diligence.
- The merchant banker shall, issue a Due Diligence Certificate mentions that all the requirements under Chapter VIII of the ICDR have been complied with.[1]
- Issue of Placement Document: This document shall contain all the necessary information that the buyer must be aware of so that they make an informed choice. In furtherance of this objective, SEBI passed the Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements, Amendment Regulations, 2012, with effect from 30th January 2012. The information to be disclosed is mentioned in the Schedule XVIII which was introduced as Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements, Amendment Regulations, 2012, with effect from 30th January 2012 and is in para Materia to the Disclosures Mentioned in Part G of Schedule VIII.
- The copies of the document shall be circulated only to selected investors after proper numbering.
- For obtaining approval from the Securities Exchange Board the Placement document shall be submitted and shown along with the due-diligence certificate for obtaining due permission from the Stock Exchange.
- This document shall also be then published on the website with a specific mention in regard to the offer, and its validity which does not extend to the general public or any other category of Investors, other than those specified.
- Schedule XVIII: This shall contain information relating to The Financial Statements of the Company, a summary of the offer and the eligible securities along with the Risk factors that might be associated.
- Adding to, it makes mentions to make disclosures regarding the project in which the money shall be invested, its break up cost and the break up. It also makes it necessary to have Audited Financial Statements prepared by An Independent Auditor. The ultimate objective is to ensure that the Investors make a real choice
Pricing of the QIP
It shall be based on the price which cannot be less than the average of the highest price of the equity shares and the lowest prices on the stock exchange in the week, two weeks prior to relevant date. The term relevant date has been defined under Regulation 81(c) of the ICDR Regulations.[2]
- The Qualified Institutional Placement is subject to certain conditions wherein it has been mentioned that:
- It is necessary that 10% of the Eligible Securities are allocated to any Mutual Fund and if no subscription is made by any Mutual Fund House it can be allotted to any other Qualified Institutional
Restrictions on Allotment
Certain restrictions have been imposed wherein it is mentioned that in any whatsoever, the Qualified Institutional Placement cannot be made to the Promoter or any of his relatives or to any manner who may be related to the promoter in any way. For the said purposes any person who by lending has acquired the status and capacity as that of Promoter is excluded from the purview of this Section. However, exceptions have been created where certain persons like those who have been persons who have been granted certain rights under the Shareholders Agreement or have voting rights or have certain veto powers or have certain rights in respect to nominate a director or a board
Minimum number of allottees
The number of QIBs to whom shares are allotted shall not be less than
- Two, in cases where the issue size is <= Rs.250 crores
- Five, where the issue size is >= Rs.250 crores[3]
Also once The applicants in qualified institutional placement have made their bid and the issue process has been closed they cannot withdraw their bids after the Closure.
- Timeline for the process: Regulation 88 of the ICDR regulations mentions that once a special resolution has been passed the allotment to the buyers has to be made within a time frame of 12 month which is effective from the date the Special resolution.
- These Regulations also pose a restriction wherein not before the expiry of six months from the date special resolution was passed the Company was authorized to further undergo Qualified Institutional Placement.
- A limit has been placed on the amount for which securities can be made in a financial year must be less than five times the net-worth of the company in the previous financial year. The investment through QIP cannot be made more than five times the net-worth as per the audited Balance Sheet in the preceding financial year.
- Tenure: The tenure of the convertible or exchangeable eligible securities issued through qualified institutions placement shall not exceed sixty months from the date of allotment.
Restriction on Selling: Restriction is placed in respect of the eligible securities which cannot be sold by the allottee for at least a period of one year from the date of allotment, except otherwise on a Stock Exchange.
Advantages
- Speedy process – This mode of qualified institutional placement is essentially the most expeditious method by which capital can be raised without undergoing any cumbersome process. Generally, by other methods, it takes a lot of time and money to undergo the documentation and approval.[4]
- Saves Cost: It saves ancillary expenses which otherwise are involved when securities rae issued by some any other mode. The Floatation Costs are minimised.
Advantages for the QIBs
Potential for buying large stakes in Market: Today this method has become a useful key and is being used by large Business Houses and Banks. In cases where a company cannot directly buy from the market a large stake as it might create market volatility, in this way issuing shares by increasing capital is one of the ways to attract investors.
Better bargains take place by means of QIP, as it gives the opportunity to raise and purchase as well at better-bargained costs.
Recent Updates on QIP
- SEBI has recently expressed its concern over the declining QIP and mentioned the following “As a markets regulator, one of Sebi’s mandates is market development. They have been concerned why QIP as a product has lost attraction with listed companies and to discuss the same, they had called investment banks for a meeting last week,” [5].
- As per the records of 2016, only four or five companies have undertaken QIP, which is a growing issue for the SEBI as the entire purpose for which it was enacted is not being fulfilled. This was essentially done with an aim to reduce External Commercial Borrowings on the lines of the American Depository System.
- SBI plans to issue its largest QIP, breaking its own record. It plans to raise its capital base launched at a price of Rs 287.58 per equity share. This might be followed by other Public Sector Banks who might take up a similar path so that they are able to implement the Basel III norms. This is supposed to be the Largest QIP that has been issued across the nation. [6]
References
[1] while seeking in-principle approval for listing of the eligible securities issued under qualified institutions placement, furnish to each stock exchange on which the same class of equity shares of the issuer are listed, a due diligence certificate stating that the eligible securities are being issued under qualified institutions placement and that the issuer complies with requirements of this Chapter.
[2] (c) “relevant date” means:
(i) in case of allotment of equity shares, the date of the meeting in which the board of directors of the issuer or the committee of directors duly authorised by the board of directors of the issuer decides to open the proposed issue;
(ii) in case of allotment of eligible convertible securities, either the date of the meeting in which the board of directors of the issuer or the committee of directors duly authorised by the board of directors of the issuer decides to open the issue of such convertible securities or the date on which the holders of such convertible securities become entitled to apply for the equity shares. Conditions for qualified institutions
[4] http://www.blog.sanasecurities.com/what-is-qualified-institutional-placement/
[5] Sebi seeks inputs from investment bankers to reverse slump in QIP
activity Fri, Aug 19 2016. 04 07 AM IST http://www.livemint.com/Money/XxD6KjvIbAB9DjA96yC9zM/Sebi-seeks-inputs-from-investment-bankers-to-reverse-slump-i.html
[6] http://www.businesstoday.in/sectors/banks/sbi-launches-largest-qip-will-more-companies-take-qip-route/story/253809.html (June6,2017.)
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack









 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


