What is UGC NET? Complete guide covering eligibility, exam pattern, Paper I and II syllabus, JRF vs Assistant Professor difference, application process, and career benefits. This article is written by Neeli Neelay Shah, Senior Legal Content Writer at LawSikho.
Table of Contents
If you have completed your Master’s degree and want to teach at a university or pursue PhD with government funding, UGC NET is the examination you need to clear. This national-level test, conducted twice yearly, determines whether you can become an Assistant Professor at Indian colleges and universities or receive a monthly stipend while conducting doctoral research.
Understanding the UGC NET and Its Purpose
UGC NET, or the University Grants Commission National Eligibility Test, serves as India’s standardized gateway to academic careers. The examination validates your teaching aptitude and subject expertise through a rigorous assessment, qualifying successful candidates for faculty positions or research fellowships. Think of it as the academic equivalent of clearing a bar exam for lawyers or a medical licensing test for doctors; it establishes minimum competency standards for those entering higher education as teachers or researchers.
Conducted by National Testing Agency (NTA)
The National Testing Agency took over UGC NET administration from CBSE in December 2018, bringing standardized computer-based testing and improved examination infrastructure. NTA conducts the exam twice annually in June and December sessions, publishing all official notifications, application forms, admit cards, and results on their official portal. The agency has made the examination more accessible by establishing test centers across hundreds of cities, allowing candidates from smaller towns to appear without traveling to metros.
Gateway to Teaching in Universities and Colleges
Clearing UGC NET with Assistant Professor eligibility allows you to apply for permanent teaching positions across central universities, state universities, deemed universities, and affiliated colleges throughout India. The Bar Council of India and similar regulatory bodies mandate UGC NET qualification for faculty appointments in their respective disciplines. Without this qualification, even candidates with exceptional subject knowledge cannot apply for most government college teaching positions, making UGC NET the essential credential for academic career entry.
Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) for PhD Scholars
Beyond teaching eligibility, UGC NET awards Junior Research Fellowship to top performers, providing financial support for doctoral research. JRF holders receive monthly stipend of ₹37,000 during the first two years, increasing to ₹42,000 from the third year as Senior Research Fellow. This fellowship funds your entire PhD journey for up to five years, eliminating financial barriers to advanced research. Many premier institutions also give admission preference to JRF holders, making this qualification doubly valuable for research-oriented candidates.
UGC NET Eligibility Criteria
Before investing months in preparation, confirm that you meet UGC NET’s eligibility requirements. These criteria ensure candidates possess the academic foundation necessary for teaching and research roles, and they vary slightly based on your category and target qualification.
Nationality and Other Requirements
Only Indian nationals can appear for the UGC NET Exam. You must possess valid identity documentation such as Aadhaar, passport, or voter ID for verification during application and examination. Additionally, your Master’s degree subject must correspond to an available Paper II subject; if your qualification does not match any of the 85 subjects offered, you cannot appear for the examination regardless of other eligibility criteria.
Educational Qualifications and Percentage Requirements
You need a Master’s degree or equivalent from a UGC-recognized university in a subject corresponding to one of the 85 Paper II subjects offered. General and General-EWS category candidates require minimum 55% marks in their postgraduate degree, while SC, ST, OBC-NCL, PwD, and third gender candidates need only 50% (a 5% relaxation). If you are in your final year of Master’s, you can apply with “Appearing” status but must complete the degree with required percentage within two years of appearing.
Under NEP 2020 provisions, candidates completing Four-Year Undergraduate Programmes (FYUP) with 75% marks can also apply for UGC NET directly without a Master’s degree, provided their programme includes research components from a recognized university. This relatively new pathway acknowledges the enhanced academic rigor of four-year programmes under the new education policy framework.
Age Limit for JRF and Assistant Professor
Here is where eligibility differs based on your goal. For Assistant Professor eligibility alone, there is no upper age limit whatsoever. Whether you are 30, 40, or 50, you can appear for the UGC NET exam and qualify for teaching positions.
However, if you want Junior Research Fellowship with its monthly stipend, you must be 30 years or younger as on the notification date. Reserved category candidates get relaxations: 5 years for OBC-NCL, SC, ST, PwD, and women (making it 35 years), and 3 years for LLM holders and up to 5 years for candidates with prescribed research experience.
UGC NET Exam Pattern
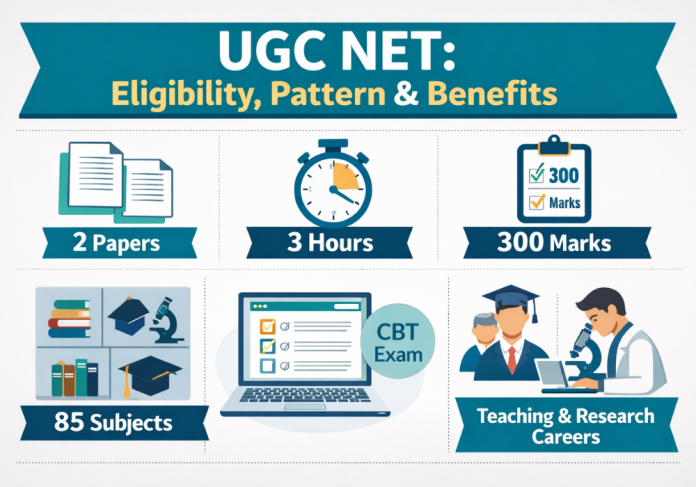
Understanding the examination structure helps you allocate preparation time effectively. The UGC NET Exam follows a standardized exam pattern testing both general aptitude and subject-specific knowledge through two papers attempted in a single three-hour session.
UGC NET Paper I: Teaching and Research Aptitude: 50 Questions for 100 Marks
Paper I evaluates your aptitude for academic careers through 50 multiple-choice questions worth 2 marks each. The questions span 10 units covering teaching methodology, research concepts, logical reasoning, data interpretation, communication skills, ICT awareness, environmental science, and higher education system knowledge. Every candidate, regardless of their chosen subject, faces the same Paper I questions in their examination shift.
UGC NET
Paper II: Subject-Specific Knowledge Test: 100 Questions for 200 Marks
Paper II tests your in-depth knowledge of your chosen subject through 100 multiple-choice questions carrying 2 marks each. The questions cover your subject’s complete postgraduate-level syllabus, typically divided into 8-10 units. The difficulty level is higher than Paper I, assuming you have thorough command over concepts studied during your Master’s programme.
Choosing Your Subject from 85+ Options
NTA offers 85 subjects for UGC NET Paper II, covering humanities, sciences, social sciences, languages, commerce, law, and interdisciplinary fields. Your choice must correspond to your Master’s degree specialization; an English Literature postgraduate should select English, not Journalism or Linguistics. Review the complete subject list and syllabus on the NTA website before applying, as you cannot change subjects after application submission except during the brief correction window.
Exam Mode and Duration of the UGC NET
UGC NET is conducted exclusively in Computer-Based Test (CBT) mode across designated examination centers nationwide. You attempt both papers consecutively in a single 180-minute (3-hour) session without any break between papers. The computer interface allows navigation between questions, marking questions for review, and changing answers before final submission. If you have never taken a computer-based exam, practice with NTA’s mock test available on their website to familiarize yourself with the interface.
Marking Scheme and Qualifying Marks
Each correct answer earns +2 marks with no negative marking for incorrect or unattempted questions. This candidate-friendly scheme means you should attempt every question; guessing cannot hurt your score but might add valuable marks. To qualify for Assistant Professor eligibility, meet the aggregate 40%/35% threshold in both papers. For JRF, you must additionally score in the top 6% of all qualified candidates in your subject, with actual cut-off marks varying by session and subject based on candidate performance.
UGC NET Syllabus
The syllabus defines your preparation scope. Understanding what topics to study and their relative importance helps you prioritize effectively rather than spreading effort thinly across everything.
UGC NET Paper I Syllabus
Paper I syllabus comprises 10 units: Teaching Aptitude, Research Aptitude, Reading Comprehension, Communication, Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude, Logical Reasoning, Data Interpretation, Information and Communication Technology (ICT), People Development and Environment, and Higher Education System. Each unit theoretically contributes 5 questions, though actual distribution varies by examination shift.
High-Weightage Units to Focus On for Paper I
Analysis of previous year papers reveals that Teaching Aptitude and Research Aptitude together contribute approximately 10-12 questions (20-24 marks), making them your scoring foundation. Logical Reasoning and Mathematical Reasoning reward consistent practice and together add another 10-12 questions. ICT has emerged as high-scoring due to its finite testable content; memorising common abbreviations (HTTP, HTML, URL, LAN, WAN) and government digital initiatives like SWAYAM Prabha and Digital India. Lower-weightage units like Environment and Higher Education can be covered through current affairs reading and targeted memorization of key facts.
UGC NET Paper II Subject-Specific Syllabus
Paper II syllabus varies completely based on your chosen subject. Each of the 85 subjects has a dedicated syllabus typically divided into 8-10 units covering core areas of that discipline at postgraduate level. The depth expects thorough conceptual clarity, not surface-level awareness; questions test application and analysis, not mere definition recall.
Subject-Wise Syllabus for Most Common Subjects
Popular subjects have well-defined syllabi reflecting standard Master’s curricula. Law Paper II covers Jurisprudence, Constitutional Law, Torts, Crimes, Contracts, Family Law, Property Law, Administrative Law, Company Law, and International Law. English Literature includes British Literature (period-wise), American Literature, Indian Writing in English, Literary Criticism and Theory, and Linguistics. Commerce covers Accounting, Management, Marketing, Finance, HR, and Business Environment. Political Science spans Political Theory, Indian Politics, Comparative Politics, International Relations, and Public Administration.
Access Your Subject Syllabus for Paper II UGC NET
Download your subject’s official syllabus PDF from the UGC NET official website. These documents are available in both English and Hindi and provide detailed topic breakdowns under each unit. Print your syllabus immediately and use it as your preparation roadmap, checking off topics as you cover them. Cross-reference syllabus units with your Master’s coursework to identify gaps needing additional study.
Difference between JRF vs Assistant Professor
Understanding this distinction helps you set appropriate preparation goals. Both qualifications come from the same examination but serve different purposes and have different requirements.
Key Difference at a Glance
The differences between JRF and Assistant Professor eligibility span age requirements, selection criteria, purpose, and financial benefits. Understanding these helps you decide where to focus your preparation efforts.
Age Limit
Assistant Professor eligibility has no upper age limit; you can appear at any age and qualify for teaching positions. JRF requires you to be 30 years or younger (with category-wise relaxations. If you are above 30, you can still qualify for Assistant Professor but not for JRF fellowship.
Selection
JRF requires scoring in the top 6% of qualified candidates in your subject. The actual cut-off varies by subject and session; popular subjects like Commerce and Economics typically have higher cut-offs due to more candidates. Assistant Professor eligibility requires only meeting minimum qualifying marks: 40% in each paper for General category, 35% for reserved categories.
Purpose
JRF supports research careers by funding your PhD journey with monthly stipends and annual research grants. Assistant Professor eligibility supports teaching careers by making you eligible for faculty positions in universities and colleges. JRF holders can do both; they can pursue PhD with funding AND apply for teaching positions simultaneously at some institutions.
Financial Benefit
JRF provides immediate financial benefits: ₹37,000 monthly for years 1-2, ₹42,000 monthly for years 3-5, plus annual contingency grants (₹10,000 for humanities, ₹12,000 for sciences) and House Rent Allowance if hostel accommodation is unavailable. The total value over five years exceeds ₹25 lakhs. Assistant Professor positions offer long-term employment with 7th Pay Commission salaries starting at ₹57,700 basic pay (₹75,000-₹1,00,000 total with allowances in central universities).
Qualifying for both JRF and Assistant Professor
Yes, and ideally you should aim for this. If you score in the top 6%, you automatically receive both JRF and Assistant Professor eligibility. You can then choose to pursue PhD using the fellowship, apply for teaching positions, or explore institutions allowing both simultaneously. Scoring just above the minimum threshold limits your options to teaching-only eligibility. The strategic implication: prepare to maximize your score rather than merely clearing cut-offs.
Application Process for UGC NET
The application process is entirely online through the NTA portal. Understanding each step helps you complete registration without errors that could delay your examination.
Online Registration and Form Filling
Visit ugcnet.nta.ac.in and click on the application link when the notification is active. Register using your email and mobile number to generate login credentials. Then fill the detailed application form with personal details, academic qualifications, category information, and examination preferences including your Paper II subject and preferred exam cities. Upload a passport-size photograph (10-200 KB, JPEG, white background) and signature (4-30 KB, JPEG, black/blue ink on white paper) meeting specified dimensions. Double-check all entries before submission, as most fields cannot be edited afterward.
Application Fee
Application fees vary by category: ₹1,150 for General/EWS, ₹600 for OBC-NCL, and ₹325 for SC/ST/PwD/Transgender candidates. Pay through Net Banking, Credit Card, Debit Card, or UPI using the integrated payment gateway. After successful payment, download and save the confirmation page as proof. If payment fails but amount is deducted, wait 72 hours for automatic refund before re-attempting.
Career Benefits After Qualifying UGC NET
UGC NET qualification transforms your career prospects in academia and opens doors to opportunities beyond traditional teaching roles.
Assistant Professor Salary and JRF Stipend
NET-qualified Assistant Professors receive 7th Pay Commission Level 10 pay scale with basic pay starting at ₹57,700 monthly, reaching up to ₹1,82,400 at maximum. With Dearness Allowance (currently 55%), House Rent Allowance (8-24% based on city), and other benefits, in-hand salary ranges from ₹75,000 to ₹1,00,000 in central universities. State universities and private institutions offer varying packages, typically ₹45,000-₹70,000 in-hand. JRF holders receive ₹37,000 monthly for two years as Junior Research Fellow, increasing to ₹42,000 as Senior Research Fellow for years 3-5.
Career Opportunities in Academia and Beyond
Beyond traditional faculty positions, UGC NET qualification opens diverse career pathways. EdTech companies actively recruit UGC NET-qualified subject experts for content development, online teaching, and curriculum design roles with competitive salaries sometimes exceeding academic packages.
Research institutions like ICSSR, ICHR, and various think tanks hire UGC NET-qualified researchers for analyst positions. Coaching institutes for competitive examinations value UGC NET-qualified (especially JRF) faculty for their demonstrated expertise. Publishing houses, educational consultancies, and government bodies working on education policy also recognize UGC NET qualification as a credible academic credential.
Conclusion
UGC NET serves as India’s gateway to academic careers, qualifying successful candidates for Assistant Professor positions and Junior Research Fellowship. The examination tests both teaching aptitude through Paper I (50 questions, 100 marks) and subject expertise through Paper II (100 questions, 200 marks) in a single three-hour computer-based session. With eligibility requiring a Master’s degree (55%/50% marks) and no age limit for teaching eligibility (30 years for JRF with relaxations), the examination welcomes candidates across career stages.
For detailed information on this topic, visit here.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack








 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


