In this article, Ranjit Krishnan Ramanath who is currently pursuing M.A. IN BUSINESS LAWS, from NUJS, Kolkata, discusses Assignment and Licensing of Trademarks in India
Abstract of the research undertaken
The trademark assignment in the handling to license under the original Trade markets Act 1999. (The exchange of the former Trademark Act 1958) is concerned only to the ‘permitted use’ and ‘registered use ‘ because the former Act was expanded to reach the range of the word ‘permitted use only. The trademark should be accomplished to authorize the outsiders without need to enroll the license as the ‘registered user’. The demand is to note with a Government Agency, Which is the trademark Office has been eliminated to with the failure to enroll should not permit a license invalid (Anon, 2010). In the course of recent years, the law of government trademark licensing has adjusted radically in the reaction of the new commercial factors of supplying the trades and administrations. Because the slow adjustment is to move towards the licensing.
It slowly accepted in point of commercial development in the law. It refuses that the license trade markets has turned into a commercial practicing hub. However, in the meantime, the law has given to satisfaction of specific conditions, viz. ‘quality control’ or ‘association in course of exchange’, which should be confirmed to as the trademark holder chooses to go into a permit game plan. Also, it is recommended that a trademark proprietor ought to maintain a strategic distance from a restrictive permit since it might be perused as a task. Likewise, despite the fact that the arrangement of keeping records of enlisted clients of the trademark is not any more predominant, enrollment keeps on conveying extra points of interest for a trademark proprietor under the present plan of the Act. Moreover, area 53 of the Indian Trademark Act, 1999 makes a motivating force for enlistment by denying the unregistered licensees of the privilege made by the excellence of Section 52.
Assignment and Licensing of Trademarks in India
The thought of responsibility for a development and its security is not new to humankind. To make a clear distinction of clear process for the prevention of crime over individual attempted goals will do have a low quality of merchandise creation process in the infringer reassessed. Taking a trademark process well known that would help in developing a trust in merchandise and have potential customer process. Taking a point of recheck and their implied need for maker directly reflects individual personal stake.
In the medieval times two essential sorts of imprints could be found:-
- Merchants Mark
- Production Mark
Using these process for Mark demonstration of these production needs and their origin are made as per specifications. It is more of additionally etched process in boats and other given specifically for their technique for trademarks for their occurrence for ship destruction for a proof ad there conceivable. Other individuals working together or in societies began declaring it as a blemish on their merchandise. This made the producer in charge of the nature of the merchandise that was being created and helped them to hold their clients[1].
What is trademark authorizing?
- Trademark permitting is the point at which you as a trademark proprietor approve an outsider to utilize your check in course of exchange thought of sovereignty over the offers of items or administrations authorized under the trademark[2].
- By and large, there is “established trademark permitting” done under which the licensee can make items utilizing the trademark authorized. Different types of permitting incorporate marketing, diversifying and so forth. So trademark[3] permitting is the point at which a trademark proprietor permits others to utilize the check without exchanging of possession.
Why would it be a good idea for one to permit a trademark?
It’s the most ideal path in which you can extend your business in locales you haven’t, as of now. All the more imperatively, it is monetarily truly gainful for both the licensor and the licensee. To be more particular, from the licensor’s perspective, it is that compelling business methodology that will just outcome in your officially all around perceived trademark to end up distinctly much more rumored. Like specified before, it is likewise a decent approach to extend your trademark’s topographical reach, enhance mark deceivability and other like things.
From the licensee’s perspective, it allows you to partner yourself with a very much perceived trademark; in this manner giving you a high ground on your rivals. Similarly as on account of physical property, for example, arrive, each proprietor of a Brand or Trademark has the privilege to offer, permit, exchange, and so forth its particular image or trademark as per legitimate strategies. Taking a view on varied factors of branding and trademark will make an impact with that of rights and its methods and task. As per Indian process, the trademarks Act,1999 would have authorization based on it. Simply put, if there should be an occurrence of a task of a trademark, there is an adjustment in the responsibility for enlisted mark and in the event of permitting; the privilege in the exchange stamp keeps on resting with the first proprietor yet just far few confined rights to utilize the brand/check are given to the outsider.
Business Objectives
- Entities can negotiate lump some prices for the transferring of assignment of their respective trade mark for which is ethically a new arena of business in the current society. The business objectives further extends to allowing entities from other part of the world to render service or manufacture goods under the owner’s trademark by duly establishing a relationship through a trademark licence agreement.
- Having a trade mark also benefits by teaming up with respective partners , increasing the capacity of producing , services and marketing without the requirement to expanding ones own company. This opens up new route for delivery or partitioning in the market. By getting the Trade mark licensed, the Company enters into a new area of business which is not used by any entities in the market of the specific geographical area.
- Every entities can have their selections based on what appears to be challenging and more appealing for them in terms of the concerned business the party intends to participate. In case if there disputes, insurgency, acquisition or insolvency of the Company, the owners can take decision to converge a few or can be abandoned by the owners of the Company.
- The Owner can also retain such ownership of the trade mark or can lease it to somebody else so that the owner could continue in doing the business under the said trade mark without abandoning its business in the Public Domain. The owner can still acquire revenues having the same trademark license. In the current world, Partnership licensing is beyond the horizon of merely lending a logo into establishing a true partnering of business relationship which gives a lot of drive and success to the key business of the Company. For example when Paper pulp manufacturer and a Temporary ceasing Contractor teamed up to develop false ceiling tiles which was not a simple Licensing but was an established business tie up of developing a product which was truly a great success for both the parties.
- Sometimes the mark is fringed by another entity with an object to tampering the brand name, quality and compromising the reputation of the Company. In several instances, many local vendors use others brand to promote their sale of goods. The infringers can basically convince the owners of potential business in a tie up and get into business. For most of the Companies, registering a trademark is mere a recognition than a source of revenue. Company shows keen interest in increasing the Customer recognition of the product that the revenue or sales as a part of promotion or advertisement. While another Entity partners the brand, the promotional or the advertisement costs are shared.
Financial and Commercial considerations of a Trademark
- The Royalties or the payments can be paid or received in a form of a lump amount wherein at the time when the rights of the license is granted upon another entity. This can either be a fully paid agreement or can be periodically paid until the period over the term of the License. Under the royalties, the most common kind of consideration provided by the Entities by some kind of upfront fee or based on the success in sales.
Royalty has to be dealt with in the following ways,
- We need to ascertain when the Royalties are required to be paid,
- What kind of penalties are to be imposed for failing to pay on time,
- Any issues of holding international taxes where there were a requirement to pay out the monies in the Country of established business,
- Any accrued interest on the outstanding payments or due to kind of payment.
Typically if we look into various Trade Mark Licensing agreement , the Royalty calculation would depend on a number of other factor which would include a relative bargaining skill of the Licensor and licensee, Its potential to acquire profit and how well the TM could be known in the marketplace that deals with that particular kind of product or service. The Competitive situation of the market is quite challenging and the Royalties would surely depend on the extent of its success through the market. The base calculation of Royalties whether it is from the gross sale or the net sale, all other associated costs of the overheads , profit margins , the calculation depends
The base calculation of Royalties whether it is from the gross sale or the net sale, all other associated costs of the overheads, profit margins, the calculation depends on a pre-determined rate at which the owner feels would be appropriate within a range of his profit margins. In short, Royalties is a rewarding gesture from the Owner in connection with his performance and appreciation of the parties involved in the business mutually supporting to enhance business.
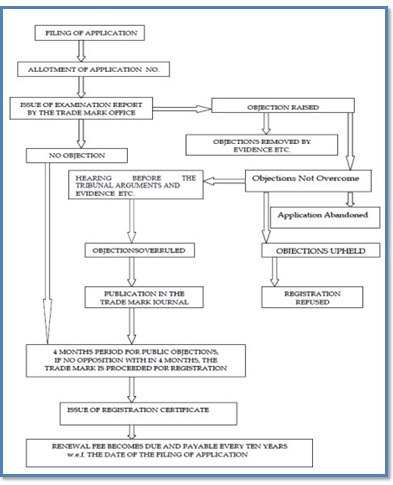
Procedure of Registration of Trademark in India
The process required for the enrollment of the trademark in India is shown in the figure,
Assignment of Trademarks in India
The assignment of a trademark takes place when the ownership of such trademark is transferred from one entity to another, which may either be along with or without the goodwill of the trademarked business and which has to be recorded in the register of trademarks.
Following is the process of assignment of trademark in India:
- Complete Assignment of trademark from one entity to another: The owner transfers all his rights held in the trademark to the other entity.
- Assignment of trademark with respect to only certain goods and services: Here, the ownership of trademark is limited to only certain products or services. For example, “A” is the owner of a brand and uses his trademark for selling computers, television sets, and air-conditioners. “A” assigns “B” the rights in the brand with respect to only the Air-conditioners, and whereby “A” retains the rights in the brand with respect to computers and television sets.
- Assignment with the goodwill: Here, the absolute ownership over the rights and value of a trademark associated with the product is transferred from one entity to another. For example,”A” is the owner of a brand and uses his trademark for selling computers. “A” sells his brand to “B” whereby “B” retains all such rights vested in the brand and can use the brand trademarks for selling computers as well as other electronic products of his choice.
- Assignment without the goodwill: The assignment without goodwill is also known as “gross assignment”. Here, the assignment refers to restrictions of rights of the buyer whereby it limits the new owner of using the brand on products that the original owner is already For example, “A” is the owner of a brand and uses his trademark for selling computers. “A” sells his brand to “B” such that “B” will have no rights to use the brand trademark for selling his computer products. However, “B” can use the brand trademark in the chain of businesses other than a computer.
Using the case process of Trademarks Act 1999, there is a restriction of these process as per the registered process and their confusion amid various other clear public users and other clear deliverables.
Such restrictions are
- Giving an account of these assignments and their results would have rights in a more desperate work have effective goods and services. It further has a clear need for association as per deeds.
- Taking the approach of these Assignments and their results would have different effective process in a larger Spectrum.
Licensing of a Trademarks in India
- The licensing of a trademark allows the licensee to use the trademark, albeit the trademark itself is not assigned to the other entity, that is to say, the ownership has not been transferred but the mere use of the trademark is permitted to be used by the licensee.
- Licensing of trademark has a plethora of benefits for both entities. Here, the licensor may enjoy his rights to the trademark by generating royalties for its use, whereby the licensee is able to broaden his market chain operations by using the said trademark for building reputation and brand value.
In layman words, a licensor has the right to license his rights over the trademark as he may be pleased with, such as by restricting the rights of the licensee in the trademark with respect to products or services. The licensor may restrict the time and area within which said trademark can be used by the licensee with respect to the product and services.
Agreements for Transmission
Trademark assignments are generally executed by way of trademark assignment agreements under which the transmission of transfer takes place from one entity to another[1].
The following points are to be ensured while drafting such agreements for the assignment and licensing of trademarks in India,
- That the rights of the trademark brand do not tend to cause harm due to obligations prescribed in such agreement.
- The provision with regard to the assignment is with or without the goodwill of the business should be properly negotiated and explicitly mentioned in the agreement.
- The agreement must be drafted in accordance with the purpose of the transaction in question.
- The rights and duties of the licensee must be distinctively pre-determined and defined.
- The license agreement should be registered with the trademark Registrar, although it is not compulsory but in a legal perspective, it is most advisable.
It is more of the licensed for their agreement for Trademark Act 1999, relieved which do provide registration for the license agreement. Using the process of the Trademark Assignment will do make an impact in rights and duties for their distinctively determined and further relieved.
Conclusion
Understanding the process of assignment and licensing of trademarks in India is a paramount issue. The process of marketing and strategic management would surely open a plethora of broadening horizons in this domain, for the licensor and licensee likewise. It all depends upon the development of a brand, and the use of the brand, which collectively form a factor to boost marketing in various sectors.
Having an agreement which set an example for creating IPR and do allow intellectual property transfer of these commercial returns. It is further ensured that various deliverable monetary gain will have utilization as per the Agreements and have purchase value using the benefit of right made up and also provide legal and equitable rights for law and other important Issues. Further acceleration of these IPR would do study the IP rights more rigorously and have companies own valuable needs more carefully understandable and have IPR made out of scope and address the needs of the resource.
It further defines and also provides clear obligations for not able to disclose and create clause to address the issue with the jurisdiction of Alternative Agreement clause for these issues legal contract for their compliance exist laws.
It is, however, worth to note that the ability of a Company to Sell or buy is very much required to sustain in the market. Although the Trademark does not take much of space, too much of IP can actually be a burden to the Company due to the funds required to maintain the registering fees, for its proper defense if there is any third party claim or for manufacturing and sale for a final production. , or creating and marketing a final product. For a Company to sell an unused IP, this can usher the Company’s financial position and could generate revenues and decrease the overall Costs. Selling unused or surplus intellectual property can have an immediate positive effect on a company’s finances, generating revenue and decreasing costs. When the Company plans to enhance its business, Company looks forward in purchasing trademark to support their business motive, creating an identity for themselves and ensure that this is properly marketed.
This was all about Assignment and Licensing of Trademarks in India. Please comment below and let us know what are your views on Assignment and Licensing of Trademarks in India. Do not forget to share.
Bibliography
Ng, D. L. a. P. W., 2010. Intersect between Intellectual Property Law and Competition Law. Journal of Management.
Anon, 2010. REGULATION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY IN THE LEGISLATIVE CONTEXT WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO. Journal of Management.
Anupam Goyal, 2003. “Recognizing the property rights regime for indigenous knowledge of biodiversity in face of TRIPS Agreement”. National Capital Law Journal, 6(9), pp. 129-153.
Dutta, R., 2008. Critical Analysis: Reflection of IP in Competition Law of India.
kumar, B. a., 2006. law of trademarks in India. 2nd ed. Delhi: center for law.
L, W. B., 2000. law relating to patents, trademarks, copyright, designs and geographical indications. 2nd ed. Delhi: universal law publishing co pvt .
S.Chakravarthy, 2005. Evolution of Competition Policy and Law in India. New Delhi: Academic Foundation.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack









 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


