This article is written by Vibha Aggarwal, pursuing a Certificate Course in Real Estate Laws from LawSikho.com. Here she discusses ” How are Development Authorities Constituted and what do they do”

Development Authorities: Formation, Role & Challenges
The process of urbanization and migration of people from rural areas to urban areas for better living opportunities has resulted in serious problems of housing, infrastructure, and health. This unplanned urbanization pushes poor people to live in urban slums in very unhealthy living conditions. Thus, tremendous pressure is exerted on urban infrastructure due to unplanned growth.
In India, Development Authorities have come into existence, out of the need to tackle growing housing problems and poor infrastructure. It was envisaged that the development authorities will help to plan, implement & co-ordinate development activities in a structured way. After the constitution of urban development authorities, the actual implementation of urban projects and master plans has started.
Several urban development authorities have been established by various state governments to provide housing, infrastructure, and amenities to its ever-growing population.
The first to come up was the Delhi Development Authority (DDA) in 1957, for the Delhi metropolitan area. Similarly, the Haryana Urban Development Authority – HUDA in 1977 and the Maharashtra Housing and Area Development Authority (MHADA) in 1976 was established to accelerate the process of planned development.
Delhi Development Authority (DDA)
The Development Authority in Delhi – DDA known as Delhi Development Authority was constituted in 1957 under the provisions of the Delhi Development Act. The primary objective of DDA is to promote and secure the development in Delhi.
Under section 6 of the Delhi Development Act, 1957, DDA has provided a charter with the following objectives:
- To formulate a Master Plan for the development of Delhi and work accordingly;
- To possess, manage and dispose of land and other property;
- To carry out building, engineering, mining, and other operations
Over a period of time DDA has not only undertaken housing projects but has also developed commercial complexes, sports facilities, public transportation systems, parks & playgrounds.
The Authority believes in “Green Delhi” and works with the objective to protect the environment by retaining green belts and forests. Realizing the importance of Delhi`s place in national development, DDA along with other state authorities is playing a vital role in the development of the National Capital Region (NCR)
DDA Housing Scheme
During 2016-17 about 53,950 dwelling units were under construction in various zones with prefab technology (Source: DDA Annual Report 2016-17).
Table 1 – Details of housing as on 1.4.2016
|
Description |
HIG |
MIG |
LIG |
EWS/JANTA |
Total |
|
Houses in progress as on 1.4.2016 |
4,747 |
9,121 |
16,612 |
23,470 |
53950 |
|
Houses completed during 2016-17 |
– |
– |
3,108 |
3,108 |
|
|
New houses started during 2016-17 |
– |
11,767 |
2,580 |
14,347 |
|
|
Houses in progress as on 31.3.2017 |
4,747 |
9,121 |
28,379 |
22,942 |
65,189 |
Source: DDA Annual Report 2016-17
The above table 1 shows that 11,767 LIG and 2,580 EWS new houses were taken for construction for urban poor during the year 2016-17 (Source: DDA Annual Report 2016-17)
DDA had launched housing scheme 2019, for 18000 flats across for all four categories – EWS, LIG, MIG and HIG (source: Housing.com)
Proposed Zonal Development of Delhi by DDA as per Master Plan, 2021
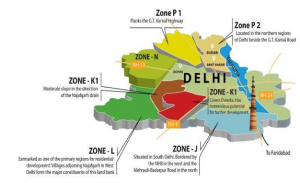
Source: 99 acres
Since 2007, the Master Plan of Delhi came into force with a view to accommodate 23 lakhs individuals by the year 2021.
Haryana Urban Development Authority – HUDA
The Haryana Urban Development Authority –HUDA is a statutory body constituted under the Haryana Urban Development Authority Act, 1977.
HUDA was constituted with a mandate to provide:
- Affordable housing to all sections of the society;
- To promote and secure the development of urban areas in a planned way by acquiring undeveloped land.
HUDA undertakes various development activities and has developed or facilitated the development of housing projects, public infrastructure, industrial & commercial places, recreational zones. Also, it has played a role in providing civic amenities like water supply & drainage systems.
It also provides developed land to Haryana Housing Board & other institutions to achieve its basic aim of providing housing to all sections of society with special focus on the economically weaker section of the society.
HUDA (HSVP) Upcoming Plot Schemes 2018-2019, 2019-2020 Gurgaon
Early this year, the Haryana Shehari Vikas Pradhikaran (HSVP), earlier known as HUDA, launched a new housing scheme for distribution of about 6200 residential plots in urban areas in all across the Haryana. (Source: educationbhaskar)
Also, HSVP constructed low-cost houses (around 9992 houses) for slum dwellers rehabilitation, who have encroached HUDA land (Source HSVP: Information at Glance- as on 31.03.2019)
Work undertaken by HUDA
No. of Sectors floated
|
Residential |
234 |
|
Commercial |
13 |
|
Industrial |
41 |
|
Institutional |
9 |
|
TOTAL |
297 |
(Source HSVP: Information at Glance- as on 31.03.2019)
No. of Plots Allotted
|
Residential |
282369 |
|
Commercial |
43042 |
|
Industrial |
10414 |
|
Institutional |
3761 |
|
TOTAL |
339586 |
(Source HSVP: Information at Glance- as on 31.03.2019)
Land Developed under Parks 877 acres up to 31.3.2019
|
Water supply line |
4799 km |
|
Sewerage line |
3907 km |
|
Stormwater drains |
3153 km |
|
Roads |
9570 km |
(Source HSVP: Information at Glance- as on 31.03.2019)
Maharashtra Housing And Area Development Authority – MHADA
Maharashtra Housing and Area Development Authority (MHADA), was constituted by the Maharashtra Housing and Area Development Act, 1976, with the aim to improve the living standard of the poorest section of the society.
MHADA constructs & allots affordable houses to all income groups of the society. Even though Mumbai is known for its skyrocketing high price, MHADA is able to provide homes comparatively at a low price. It also provides houses to Mill Workers who lost their jobs and homes in midst of the 1980’s during the great mill strike.
MHADA is also involved in repairs & reconstruction of old & dilapidated buildings. In true sense, it works to uplift the living standard of all sections of society not only by way of providing affordable homes but also participating in slum improvement activities.
The most important feature of MHADA is the system of allotment of the houses through its computerized housing lottery system.
Even though MHADA tries its best to provide affordable homes, most of the times its home units are unaffordable to the majority of the population of economically weaker sections as pointed out in the study undertaken by PRAJA, an organization working in Mumbai.
Some of its findings are given below:
Table 1 – Ideal cost of an Affordable House
|
Monthly household income (Rs.) |
Annual household income (Rs.) |
Ideal cost of the affordable house (Rs.) |
|
20,000 |
2,40,000 |
9,60,000 (4 x annual income) |
|
40,000 |
4,80,000 |
19,20,000 (4 x annual income) |
Source: Report by Praja.org on the state of affordable houses in Mumbai
Table 2 – Cost of MHADA dwelling in Mumbai as of 2014
|
Income Group |
Monthly household income limit for various income groups (Rs.) |
% of household in income range |
Ideal cost of an affordable house (Rs.) |
Average price of MHADA dwelling (Rs.) |
|
Economically weak |
Less than or equal to 16,000 |
38.8% |
Less or equal to 7.68 lakhs |
14.77 lakhs |
|
Low-income |
16,001-40,000 |
31.1% |
7.68 – 19.2 lakhs |
19.3 lakhs |
|
Middle – income |
40,001- 70,000 |
9.8% |
19.2 – 33.6 lakhs |
39 lakhs |
|
High – income |
More than or equal to 70,001 |
20.3% |
Not defined |
76 lakhs |
Source: Report by Praja.org on the state of affordable houses in Mumbai
As can be seen from Table 2 above, MHADA dwelling is unaffordable for nearly 80% of Mumbai’s households which belong to the economically weak, low income and middle-income categories.
City and Industrial Development Corporation of Maharashtra – CIDCO
City and Industrial Development Corporation of Maharashtra Ltd. – CIDCO was incorporated on 17th March 1970, under the Companies Act, 1956. The State Government via Resolution (GRNO. IDL/5770/IND –I) issued a notification stating CIDCO as the New Town Development Authority (NTDA). It was a subsidiary of the State Industrial and Investment Corporation of Maharashtra Ltd. (SICOM).
From October 1971, CIDCO was an authority for development in Navi Mumbai. CIDCO undertook to prepare and publish a development plan as required by town planning. CIDCO identified 14 nodes to facilitate development to form Small Township and gave it the identity of a new city.
CIDCO Mass Housing Scheme
CIDCO Mass Housing Scheme was launched in December 2018 in the state of Maharashtra to benefit the economically weaker sections and lower-income group. These section under this scheme will get benefit the same as Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojna.
Under this scheme, total 89,771 houses are to be built – 53,483 for the economically weaker section and 36,288 for the lower-income group will be constructed within a period of 5 years (approx)
(Source www.pmil.in)
Development Authorities: Issues & Challenges
Since their inception, development authorities have undergone various changes to cater to the dynamic needs of growing cities. Post liberalization of economy (after 1992) saw increased demand for industrialization, commercial activities, and infrastructure. Through efficient planning & better utilization of available resources, they have been able to play greater role in urban development by implementing various development projects such as housing, roads, flyovers, metro rail, etc. Also, the focus is on the green initiative to provide a clean & healthy environment to its population.
As India is fast developing the economy, rapid development is essential to fuel the growth engine. To do this, smart planning and quick implementation of development activities are of prime importance.
Unfortunately, multiple agencies are involved in the development of the same area, city, and region. Lack of clear division of responsibilities often leads to a multiplicity of the role and over-lapping functions resulting in wastage of time and resources, thus duplication of work & long delay in project implementation.
Various agencies involved in city development are as follows:
- Development Authority.
- Municipal Corporation /Municipality.
- Town Planning Agency.
- State industrial corporations.
- State housing & urban development agencies.
Involvement of multiple agencies often leads to poor coordination. The multiplicity of authority and lack of coordination results in poor decision making & delay in the implementation of development plans. This poses a big challenge before development authorities in fulfilling their objectives in the most effective and efficient way.
Conclusion
Development Authorities have played an important role since the days of socialist economy wherein state had to play major role in providing basic public infrastructure, housing, and industrial development. Liberalization of the Indian economy in the 1990s required, rapid development in public infrastructure and basic amenities to fuel economic growth.
To fulfil the aspirations of a growing population and provide futuristic public infrastructure, development authorities need to focus on the following points:
- Put more emphasis on institutional & human resource development through training and capacity building programs.
- Create an effective platform for networking and sharing knowledge with stakeholders.
- Devise a sound mechanism for communication & coordination with agencies involved in development activities.
- Explore every possibility of public-private partnerships for efficient planning & implementation of projects.
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skill.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack










 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


