In this article, Rishabh of USLLS, GGSIPU discusses the differences between Coins and Tokens in reference to Cryptocurrency.
Currency
Going by the definition, a currency is basically an accepted form of money, which includes notes and coins, issued by the government, which then distributes it in the country’s economy.
The currency distributed then becomes a medium of exchange. A person in possession of a set amount of currency can exchange it for goods and services.
Different countries have different currencies, they have a certain exchange value in other countries, that value is determined by the forces of a market (demand and supply).
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency, as the name suggests are digital currencies which are encrypted (a technical term for “secured”) using various techniques of cryptography. Cryptography involves the use of various techniques of encryption to verify and secure the transactions.
Bitcoin is the most famous of them all, which took the world by storm; although many cryptocurrencies existed prior to bitcoin, it became famous because of its distributed and decentralized nature, i.e., its independence from government and influence from central authorities and organization.
Cryptocurrency has a lot of unique features, such as :
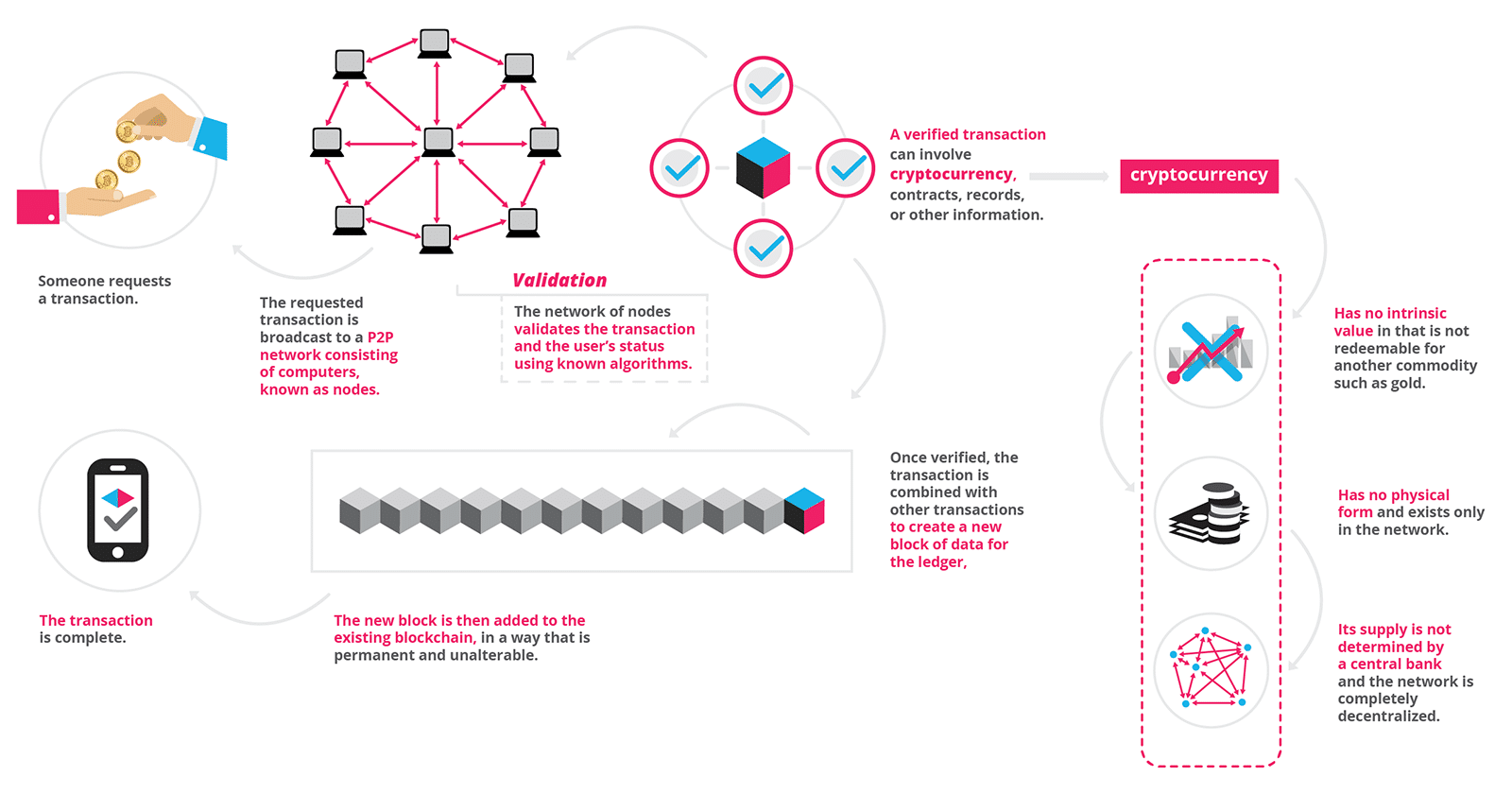
- No intrinsic value: which means it cannot be exchanged for any commodity such as gold.
- No physical form: it only exists on a digital network.
- Decentralized network: it is free from any bank’s influence and its supply not decided by a bank.
Why the decentralization of the bitcoin made it so popular?
Decentralization, as discussed, above is the independence from the influence of any government and/or central authorities. Since the government exercises no control over the cryptocurrency market (here the bitcoin’s market) the businessmen don’t have to abide by any trade laws and hence can enjoy super profits. Super profit is basically an amount of profit which is way more than the average profit earned on any trade. Generally, the super profits are earned in a monopoly where the trader is the only seller in that particular market and enjoys access to a huge customer/consumer base.
Bitcoin represents the first decentralized cryptocurrency, which is powered by a public ledger that records and validates all transactions chronologically, called the Blockchain.
As of May 2018, there are more than 1500 cryptocurrencies available over the internet, all but one of which are altcoins. New cryptocurrencies can be created at any time; additionally, there are many older cryptocurrencies which are no longer on the market.
Blockchain
The Blockchain is basically a digital ledger (a ledger is a book in which all the economic transactions are recorded, consisting of debits and credits in separate columns along with monetary balance at the beginning and at the end of the book after the transactions have been made.) where all the transactions are recorded and validated, chronologically/in order of occurrence.
The most unique and essential feature of blockchain is that it allows the distribution of digital data but that same data cannot be copied, making blockchain useful in various other fields other than digital currency.
The diagram goes on to explain the intricacies involved in the transactions involving the bitcoin:
- A transaction is requested;
- The transaction is then run through a series of computers, which are connected via a p2p network (a p2p network or a peer to peer network is created when two or more computers are connected to one another and share the same resources), validating the transaction and user’s status.
- A verified transaction can involve a lot of things like contracts, records, and various other information.
- Once validated, all the transactions are combined to form a new block of information, which is further attached to the existing chain of blocks.
- The new chain so formed is permanent and cannot be changed.
- After all these processes the transaction is said to be complete.
(NOTE: various blocks of information are combined to form a chain of information, hence the name blockchain)
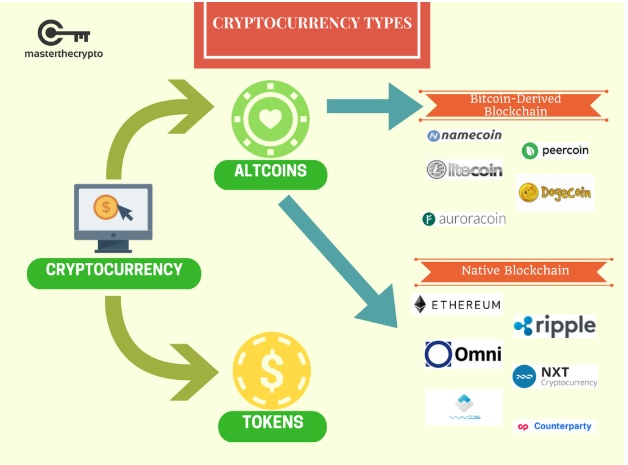
Categorization of Cryptocurrencies
All tokens or coins are regarded as a cryptocurrency, even if most of them do not function as currency or medium of exchange.
The term cryptocurrency is a misnomer (wrong or inaccurate name; not what the name suggests) since it does not have the characteristics of a currency (no store value, not a medium of exchange).
But these characteristics are there within the bitcoin and since the bitcoin was responsible for kickstarting the cryptocurrency space; all the other coins conceived after bitcoin are generally considered as a cryptocurrency.
The most basic categorization of cryptocurrency is:
- Alternative cryptocurrency coins (altcoins)
- Tokens
Altcoins
“Altcoin” is a combination of two words: “alt” and “coin”; alt signifying ‘alternative’ and coin signifying (in essence) ‘cryptocurrency.’Altcoin simply refers to those coins that are an alternative to bitcoin.
Altcoins are basically generated by using the basic programming of the bitcoin while making some changes to coding thereby creating an entirely new coin with its own unique set of features.
Altcoins differ themselves from bitcoin with a range of procedural variations, including different proof-of-work algorithms, this system of an algorithm makes sure that there is no denial of service and other service abuses, different means by which users can sacrifice energy to mine blocks, and application enhancements to increase user anonymity.
The earliest notable altcoin, Namecoin, was based on the Bitcoin code and used the same work algorithm – and like Bitcoin, Namecoin is limited to 21 million coins. Introduced in April 2011, Namecoin primarily diverged from Bitcoin by making user domains less visible, allowing users to register and mine using their own bit domains, which was intended to increase anonymity and censorship resistance
Current leading examples of altcoin include Litecoin, Dogecoin, Ethereum (2nd to Bitcoin in market capitalization as of May 2018), and Ripple. However, Litecoin is seen as the closest competitor to Bitcoin.
Tokens
Going by the definition, a token is a type of cryptocurrency which is usually issued on top of another blockchain. Generally, in any use case(use case is a software engineering term which describes how a user uses a system to accomplish a goal), tokens represent utility or an asset, or sometimes both.
Tokens can represent basically any assets that are fungible(one unit is equivalent to another) and tradeable, i.e., from commodities to loyalty points to even other cryptocurrencies.
(Fact: Tokens cannot exist independently, they need the infrastructure of a coin to exist.)
Basically, a token is a secondary asset for a particular application on a blockchain ecosystem which also has a market value but isn’t a currency as straightforward as Bitcoin or Litecoin.
Creating tokens is a much easier process as you do not have to modify the codes from a particular protocol or create a blockchain from scratch. All you have to do is follow a standard template on the blockchain – such as on the Ethereum or Waves platform – that allows you to create your own tokens. This functionality of creating your own tokens is made possible through the use of smart contracts; programmable computer codes that are self-executing and do not need any third-parties to operate.
Tokens are created and distributed to the public through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), which is a means of crowdfunding, the process of funding a project by raising small amounts of money from a large number of people, through the release of a new cryptocurrency or token to fund project development.
An initial coin offering is same as an initial public offering which is in case of stocks, with some distinctions.
(Image Source: https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-blockchain-technology/)
Differences between Coins and Tokens
There are some basic yet essential differences between coins and tokens ;
- Structure: Coins are digital financial assets; they are actual currencies and are capable of being exchanged and used for trading purposes. Tokens are also digital financial assets but rather than being the actual financial assets like the coins they act as a representation of the actual financial assets.
- Infrastructure: Each coin has its own independent blockchain, distinguishing it from any other coin. While the same can not be said for tokens, tokens are built upon and entered into the same blockchain.
- Creation: Most of the coins use the basic framework of a bitcoin along with some additional coding and changes to the framework to introduce new and unique features so as to differentiate it from bitcoin or any other coin whose framework has been used. All the programming and coding is done from the scratch. Purpose of such a creation is to improve upon the existing technology, making it more efficient. While for creating a token no changes to the programming or additional coding is required, all the tokens use the same codes for their entry into a blockchain.
- Ease and Difficulty of Creation: Since, for the creation of cryptocurrency coins there is a need for programming and coding from the scratch; hence, the level of difficulty of creation is higher as compared to tokens, which use the same set of codes and programming for their creation.
- Platform for Operation: Coins are so programmed that it is in their nature to exist independently. Coins can be used for trading as well as a measure of exchange and a unit of measure for digital financial assets. Tokens on the other cannot exist independently and are not the direct financial assets rather mere representation of assets. They are based upon other platforms.
Conclusion
The difference is becoming more and more complex with the launch of various projects involving cryptocurrencies, However, several countries like US and Japan are forming regulations around different types of cryptocurrencies which will make it relatively easy for us to understand the nuances of this budding industry.
Bibliography
- https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-blockchain-technology/
- https://masterthecrypto.com/differences-between-cryptocurrency-coins-and-tokens/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/currency.asp
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7176229/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/altcoin.asp
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proof-of-work_system
- https://coinsutra.com/coin-vs-token-difference-cryptocurrency/
- https://www.techopedia.com/definition/25813/use-case
- https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-cryptocurrencies-and-tokens
- https://www.google.co.in/search?q=super+profits&rlz=1C1CHBF_enIN799IN799&oq=super+profits&aqs=chrome..69i57j0l5.3883j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack









 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


