This article has been written by Bhaskar Tryambakrao Behere, pursuing a Certificate Course in Labour, Employment and Industrial Laws for HR Managers from LawSikho.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952 (short title: EPF & MP Act, 1952) was enacted by Parliament of India. The act provides a future to workers after retirement or for dependents, after the death of a worker. In order to secure the right to work, right to education and in case of unemployment, old-age, illness & disablement and uncertainty, to provide assistance, the act has been enacted per Article 41. In other words EPF is a retirement plan for workers. Presently, under this act following three schemes are in force:
- Employees’ Provident Fund Scheme, 1952
- Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976
- Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (replacing the Employees’ Family Pension Scheme, 1971)
Applicability of EPF & MP Act, 1952
EPF & MP Act, 1952 extends to the whole of India subject to the provisions contained in section 16. It applies to
- Every factory where 20 or more persons are employed;
- Every other establishment where 20 or more persons are employed or class of such establishments which the Central Govt. may notify;
- Any other establishment notified by the Central Government even if less than 20 persons are employed.
Under Section 1(4), if the employer and majority of employees agree that the provisions of the act should be applicable to their establishment they can make an application to the Central Provident Fund Commissioner (CPFC).
This act shall continue to be applied to establishment to which act applies even though at any time number of persons employed falls below twenty,
Under Section 2(f), any person employed for wages for any type of work (manual or otherwise) including a person engaged through a contractor, who is drawing wages less than 15000/- is eligible for becoming a member of EPF. Employees working for establishment, whether part time, on a fixed term contract, or as a trainee, are covered under the term of employee.
Person engaged as an Apprentice under Apprentices Act, 1961 is excluded from becoming a member.
Regardless at the time of joining an employee’s wages are more than 15000/-, is eligible to contribute to EPF under existing UAN, if the person was contributing to EPF during previous employment.
Employees’ Provident Fund Scheme, 1952
EPF is the main scheme of EPF & MP Act, 1952. As discussed above it applies to every employed person who is drawing wages less than 15000/- per month. EPF members are required to pay contributions to EPFO and employers need to pay equal contributions for EPF members. Employer is responsible for depositing both employee’s and employer’s contributions to EPFO. In the case of contract employees, the contractor is responsible for deducting and depositing PF contributions. If a contractor fails to comply, the principal employer is responsible to comply.
Under Section 2(b), basic wages includes all remuneration paid or payable by cash. Exclusions are: any food concession, any dearness allowance, house-rent allowance, overtime allowance, bonus commission or any other similar allowance payable to the employee in respect of his employment or of work done in such employment, any presents made by the employer.
Under section 6, contribution of PF to be deducted at the rate of 12 percent of basic wages plus dearness allowance and retaining allowance (if any) payable to employee and employer need to make equal contribution in this respect. For deducting PF, the maximum limit of PF wages is fifteen thousand per month. Employer’s contribution would be divided into two parts – 3.67% goes to provident fund and 8.33% goes to pension fund.
Additionally employers need to contribute EDLI charges and EPF administration charges at the rate of 0.5 percent of PF wages respectively. Minimum Rs. 500/- is payable as EPF administration charges.
Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976
EDLI scheme applies to all employers who provide EPF provisions for their employees under the EPF & MP Act, 1952. EDLI scheme was launched in 1976 to provide insurance coverage to private sector employees. Employers need to contribute to the EDLI scheme. Contribution for EDLI is at the rate of 0.5 percent of basic wages. Employees doesn’t required to pay any contribution for this scheme.
In the event of death in service of an insured person, registered nominee receives lump-sum payment under this scheme. If a nominee is not registered, legal heirs can apply for the claim of EDLI benefits.
Calculation of EDLI Benefits
Average salary of a deceased person for the last 12 months would be considered for calculating EDLI benefits. Thirty times of average salary plus fifty percent of average balance in EPF account of deceased person.
For Example:
Member’s average salary is 15,000/- per month and average EPF account balance is 3,00,000/-
(15,000 x 30)+1,50,000 = 6,00,000
Nominee or legal heirs of deceased person is/are eligible to receive maximum up to 6 Lakhs. Also it is provided that EDLI benefits shall not less than 2.5 Lakhs.
Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (Employees’ Family Pension Scheme, 1971 is replaced by EPS, 1995)
Under Section 6, Employers need to make contributions to EPS at the rate of 8.33% of wages payable to employees. Maximum pensionable wages limit is fifteen thousand per month.
Members retire on completion of 58 years of age. Members attaining 58 years of age, rendered service for 10 or more years, will be eligible for superannuation pension. For this purpose, completion of 9 years and 6 month shall be rounded off to 10 years.
Members ceases service before attaining 58 years of age, but rendered service for 10 or more years, is eligible for early pension.
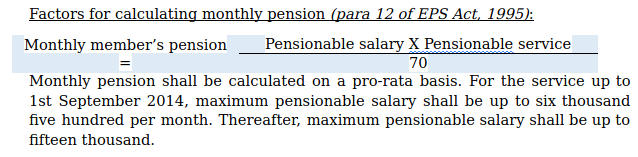
For example:
X had joined ABC Company on 1st September 2007 and retired on 31st August 2020. He rendered 13 years of service. He was drawing a salary 15000 per month before 1st September 2014 and gradually he got increments and on retirement his last drawn salary was 20000 per month.
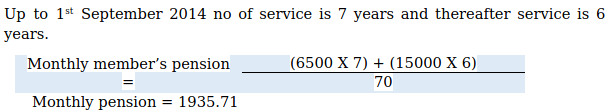
Regardless of pensionable salary, minimum pension shall be one thousand per month. If a member has rendered service for 20 or more years, is eligible for 2 service years as a bonus for calculating pensionable service.
As per section 14 of EPS Act, 1995, if a member has not rendered service for 10 or more years on date of exit or on attaining 58 years of age, is eligible to receive withdrawal benefits as mentioned in Table ‘D’.
In the event of death of a member, during service after completing not less than 10 years of continuous service, nominee/legal heirs of deceased member will be eligible to receive monthly pension.
Universal Account Number (UAN)
Every EPF member is allotted a 12 digit UAN. It will be generated for employees who contribute to EPF by EPFO. Individual employee can be allotted multiple member ids (i.e. PF Number) by different employers. UAN will remain the same for individual members for lifetime even if he changes the job. UAN will act as an umbrella for multiple member ids of an employee. It will be easy to track multiple member ids under single number i.e. UAN.
Members can transfer or withdraw their own claim online easily. Members are able to transfer his/her claim online from one EPF account to another EPF account. Online passbook facility, SMS facility for contribution alerts is provided to every member. With the help of a UAN employee can update his/her KYC, can track PF balance and claim status online. To avail online services members are required to activate UAN. Without activation of UAN members will not be able to track PF balance, claim status and KYC update.
For availing online claim transfer/withdrawal facility Aadhar Number, Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Bank Account details updation with UAN is mandatory.
Provident Fund withdrawal
After retirement EPF members receive a total accumulated fund in EPF account. If a member’s contribution to EPF is less than 10 years, member will not be eligible for monthly pension. In this case, members will receive an accumulated provident fund plus pension fund.
EPF members can get partial withdrawal from EPF accounts in the event of an emergency such as medical emergency, marriage, higher education, house purchase or construction, home loan repayment, renovation of house and purchase of equipment to minimize hardship on account of handicap. Limit of partial withdrawal is depending on the reason. EPF members can apply for advance online using UAN.
- Medical purposes: for medical treatment of self, spouse, children, or parents members can get advance up to 6 times of monthly basic salary or the total employee’s share plus interest whichever is lower. There is no required service year criteria for the withdrawal for medical purposes.
- Marriage: For the marriage of self, son/daughter, and brother/sister member can avail advance from EPF up to 50 percent of own share. For this purpose members should have completed 7 years of EPF membership.
- Education: For the post matriculation education of self or son/daughter members can avail advance from EPF up to 50 percent of own share. For this purpose members should have completed 7 years of EPF membership.
- Purchase of land or purchase/construction of a house: For purchase of land member is allowed to avail advance up to 24 times of monthly basic salary plus dearness allowance and for purchase or construction of house up to 36 times of monthly basic salary plus dearness allowance, said limits are restricted to the total cost. For this purpose the asset, i.e. land or the house should be in the name of the employee or jointly with the spouse. To avail advance for this reason members should have completed 5 years of EPF membership.
- Home loan repayment: To repay home loan members can avail advance up to 36 times of monthly basic salary plus dearness allowance / total standing credit in EPF account consisting of employer and employee’s contribution with interest / total outstanding on housing loan including interest. The property should be registered in the name of the employee or spouse or jointly with the spouse. For this reason members should have completed 10 years of EPF membership.
- House renovation: for this purpose member can be allowed advance up to 12 times the monthly wages and dearness allowance or own contribution with interest or total cost whichever is the least. The property should be registered in the name of the employee or spouse or jointly held with the spouse. For this reason members should have completed 5 years of membership.
Member can be allowed advance for house renovation twice:
- After 5 years of the completion of the house.
- After the 10 years of the completion of the house.
- Partial withdrawal before retirement: once a member reaches 54 years of age, can withdraw up to 90 percent of fund standing credit in EPF account. Members can partially withdraw EPF up to 90 percent one year before retirement.
- Physically challenged people can be allowed to advance for the purchase of an equipment required to minimize the hardship on account of handicap. Advance for this reason shall not exceed the member’s Basic Wages and DA for six months or his own EPF share with interest thereon or the cost of the equipment, whichever is the least. For this purpose a medical certificate from a competent medical practitioner is required.
Accumulations of a deceased member
In the event of death of a member, under para 70 of the Act, accumulations to be paid to deceased member’s nominee(s), if nomination is present. If no nominations subsists, accumulations shall be paid to every family member of the deceased member.
As per para 2, Family includes, In case of member is-
Male: his wife, his children, whether married or unmarried, his dependant parents and his deceased son’s widow and children.
Female: her husband, her children, whether married or unmarried, her dependant parents, her husband’s dependant parents and her deceased son’s widow and children.
Following members are not eligible for this purpose:
-
- Major sons;
- Major sons of a deceased son;
- Married daughters (If husbands of married daughters are alive);
- Married daughters of a deceased son (If husbands of married daughters of a deceased son are alive).
Under para 70A, if person entitled to receive accumulations of deceased member is charged for committing murder of member, share payable to such person shall be withheld till conclusion of criminal case. If such a person acquitted of the murdering, shall receive share payable to him/her. If such person found guilty and convicted of murdering a member, shall be debarred from receiving pay payable to him/her and share shall be paid to other eligible member.
Forms required for withdrawal in different scenario
PF Forms
|
PF Form |
Description |
|
Form 20 |
Form for withdrawal PF of a minor/deceased member |
|
Form 19 |
Form for claiming PF dues |
|
Application for Advance (Partial PF withdrawal in emergency) |
|
|
Pension withdrawal form |
|
|
Fund Pension Scheme Application Form |
|
|
Form CCF |
Composite Claim Form for withdrawal replaces earlier form 19, Form 10C, Form 31 |
Conclusion
The Act and the schemes provides three types of benefits to EPF members such as Contributory Provident Fund, Pension to employees/family members and Insurance cover to employees.
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skill.
https://t.me/joinchat/J_0YrBa4IBSHdpuTfQO_sA
Follow us on Instagram and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more amazing legal content.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack











 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


