This article is written by Shreya Tripathi of Banasthali Vidyapith, Jaipur. In this article she discusses Breach of Contract, remedies related to it and types of damages.
Breach of Contract
When any contracting parties or two different people who want to deal for any business transaction whether, for car selling or purchase of a house etc., it can be any reason, then both the parties sit together with documents and explain their point of view to each other with specified terms and conditions.
Let’s take an example. Mr ‘X’ wants to purchase a car and the dealer wants to sell the car. The buyer wants to know in how many days will he receive the car or how he has to make payment. Also in further slot how much amount he needs to pay and at the same time dealer also wants to know how he will receive the payment amount and whether in a lump sum or in installments. So, as we see both the parties have discussed there points and will be obliged to follow the conditions.
Here, the dealer and the buyer, both have some of the rights and obligations attached. The buyer has the right to receive the car and ownership right over the car and is obliged to make payment at the specified time. The seller has the right to receive the amount made for the purchase of the car and he is obliged to transfer the possession of the car to the buyer.
This important element makes the agreement a valid contract and, the receiving item by both the parties is known as Consideration.
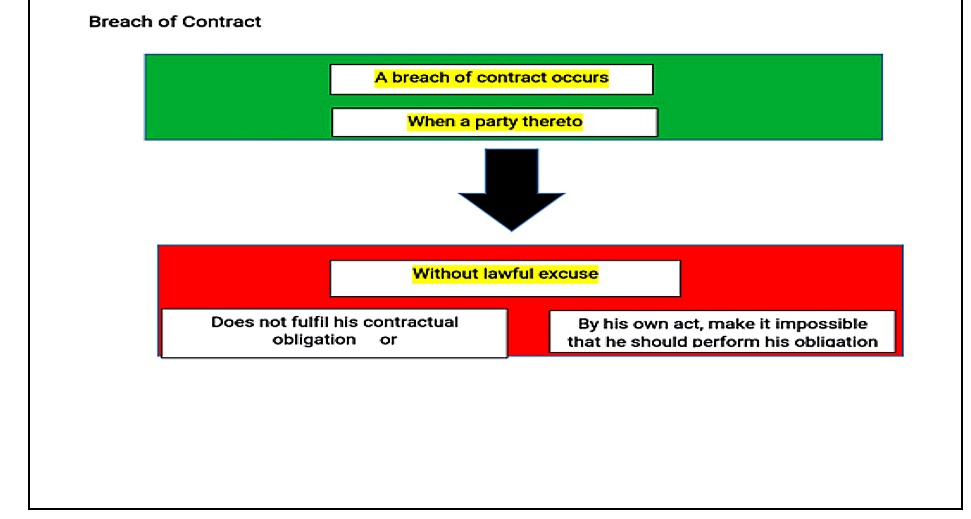
What is Breach of Contract?
Let us “Breach of Contract” with this example. The date was fixed by both the parties for performing that is on 12th June 2019, the seller will give or make the whole payment and the dealer will pass the car to seller person but suddenly on 7th June 2019, the seller deny from doing the payment before the date of performance. This is known as Breach of Contract. Breach of Contract has 2 kinds of breach-
- Anticipatory breach
- Actual breach
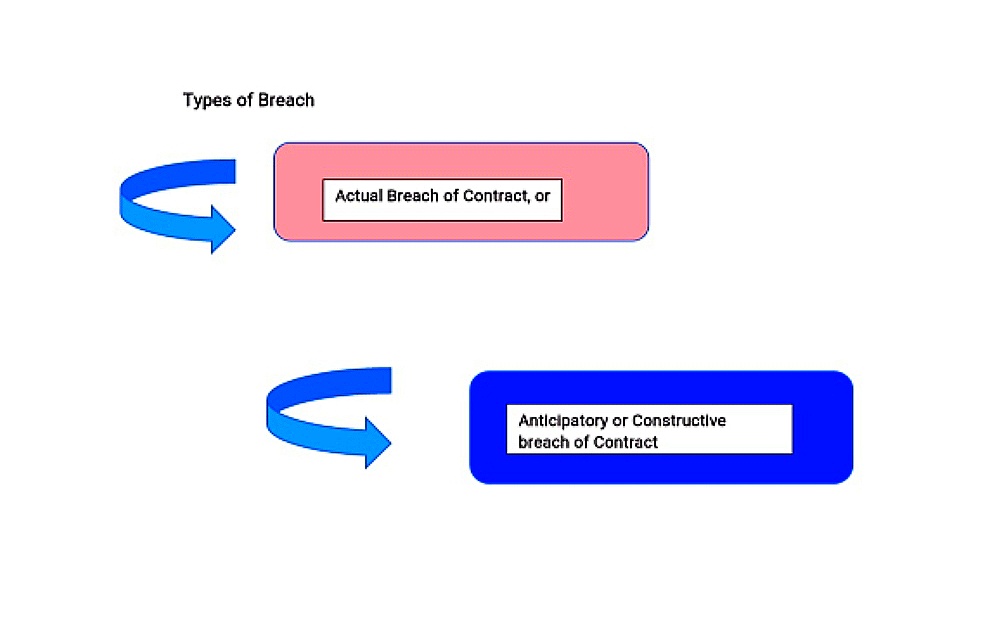
Where the party breaks, cancels or terminates the contract before the due date, it is known as Anticipatory Breach under Section 39 of the Indian Contract Act. When the breach of contract is performed on the fixed due date it will be known as Actual Breach.
Anticipatory means that you are foreseeing it. That means you know that you cannot perform but when before the contract becomes due. Now, in this case this if the promisor breaches the contract it will become an actual breach. We know that we will not be in a situation to do something on a future day or we might think that he has agreed to do the contract at a very low price and at that price possibility may incur a loss. So, he goes to the promissory and says that he will not be able to start the contract on the due date and he communicates the refusal before the due date.
Remedies against the guilty party
- Rescission- The very first remedy for breach of contract is Rescission. When one party breaks the contract then other parties can treat it as revocation, so the party will be liable to pay compensation for damages to suffering party.
- Suit for Damages- The compensation for the damages occurred by the aggrieved party will be in monetary form. The object is to recover the loss of aggrieved party rather than punishing the defaulted party in breach of contract.
- Suit for Specific performance- Under this case specific performance means seeking an order from the Court that the promising part of the contract should be carried on further. In certain cases where the damages caused due to the breach of contract cannot be measured in terms of monetary value, then Specific performance should be given by the Court of law.
- Suit for Quantum Meruit- If one party is preventing or defending other party form completing his obligation under the contract form by both the parties, the aggrieved party may claim for the payment by the part of a contract which he already performed.
For example, a contractor who has started the work and later he has to stop the work because the other party to the contract breach it, here contractor will be liable to receive compensation in the form of Quantum Meruit.
Damages of Contract
Damages, in a simple language, refers to a form of compensation due to a breach of contract. As explained by Fuller and Perdue, damages may seek protection for an exception, restitution and reliance interest.
Let’s say ‘Y’ has to supply 10 bags to mangoes to ‘Z’ for Rs. 10 per bag now, ‘Y’ cancel the contract and said ‘Y’ don’t have bags to deliver but ‘Y’ has contracted with someone else to deliver the bags of mangoes and he purchased the bags from the market but the price has reached peak now ‘Y’ will get purchase at a high price and he suffered the loss of Rs. 5 on every bag of mango. This amount of loss is called Damages.
What is Liquidating Damages?
Liquidating damages are ascertained in the contract while framing the contract, we have to ascertain the situation where the contract is breached and if the contract is breached what will be the expected estimated loss to either party has to be calculated. If this loss is estimated in itself before the performance date, what is the likely loss to either party and when this estimated is put into the contract itself it is called as Liquidating Damages. So, the party now become liable for liquidated damages.
Ordinary damages
The actual loss which the aggrieved party has suffered in the normal ordinary course of business.
Illustration– I have given the example above of bags of mangoes Rs. 5 is the actual loss per bag if ‘Y’ is suffering this loss will be called Ordinary loss because this is the actual loss ‘Y’ is suffering this is not the estimated loss. So, this difference between the two.
So, which one of these will be incurred when the situation of breach will arise? Liquidated damages are decided by both parties, it is ascertained, estimated and put into the contract by both parties.
However, ordinary damages are actual damages that the aggrieved party has incurred because of the breach of contract. The court will award Ordinary damages to the aggrieved party because in liquidating damages it is the estimated loss and court cannot go ahead the estimated loss, the court will always see what is the actual loss the party is suffering from and the actual loss is Ordinary loss which will award the damages to him. The Court is not much worried about liquidating damages he is more concerned about actual damages.

Special damages
Special damages occur in special circumstances only like ordinary damages have been in the ordinary course of business special damages occur in a special situation only. It is not the loss which occurs in an ordinary situation.
Illustration Let’s say ‘X’ agreed to supply 100 bags of wheat to ‘S’ but due to riots in the city ‘X’ couldn’t supply bags of wheat. Now, this is not an ordinary transaction, this is a special event. So, in this case, the Court will investigate that the special event is directly responsible for the breach of contract. So, the Court appoint an officer to investigate more to find the correct and accurate piece, if the cause of the breach of contract is directly related to it then the Court might award special damages otherwise getting the special damages is not the exclusive right. Like ordinary damages are the right of the aggrieved party whatever loss he has suffered it will get but special damages get in a special situation so it might not get in all the situations. Some of the examples of Special damages are:
- Loss of business opportunities, contract and profits.
- Damage or loss to business reputation.
- Loss of time and other inconveniences.
- Loss from Operating revenues.
- Loss of business product and properties.
For example, in the above illustration if both the party estimated loss and took the difference of Rs. 5 per bags but if he has to suffer the loss of only Rs. 1 per bag then he has to the faceless amount of loss and the particular amount will be recovered under Special damages.
In Cedrick Makara vs. Newmark Realty, Makara claim compensation as he hurt his thumb while leaving the restroom at his workplace, due to injury he was not able to come for 6 months for work. The injury was so bad that he required surgery and jury awarded him a compensation of $ 2 as compensatory damages for pain and suffering and $2,00,000 under special damages for any kind of medical need he might be required in future.
In the case of Bret Michaels vs. CBS, a celebrity sued a company over an accident. At the Tony Award Broadcast in 2009, he was not guided in a correct way on how to exit from the stage due to which he was hit by a set piece in his head and he broke his nose and suffered from a brain haemorrhage. The court has given the decision in favour of Michael but the compensatory and general damage amount was not disclosed in public.
Am I entitled to Special Damages?
Usually, special damages do not occur in a normal situation, failing to request for special damages will occur in losing the right of special damages by the non-breaching party. In order to receive Special damages, some essentials need to be fulfilled.
- Foreseeable- The loss can be easily predicted by the parties at the time of forming a contract.
- Flowing from the Breach- The losses should not be the direct and ultimate consequences of the breach of contract. Some sort of connection should be present between the breach and losses.
- Calculable– Since special damages are not given under the situation of the ordinary contract it is difficult to calculate the loss amount.
For example, the loss incurred due to business reputation to an individual cannot be calculated. It should be calculated during the time of the formation of the contract.
Are Special Damages different in Tort?
Under tort and personal injury also, the claim can be made for special damages. However, in a different condition both damages can be claimed under a contractual term decided by the parties.
For example, special damages claim under personal injury can be easily calculated or determined as it refers to tangible damages and in case of general damages it becomes difficult to determine the pain or suffering faced by an individual. As you can easily observe that below this situation it’s the complete opposite in claim in contract cases. It is important to note down the change because many contract claims include issues also. Thus, the amount of damages recovered by the plaintiff directly depends to attempt that under which head they will file for the violation in contract claim or tort.
Special damages are determined on the market value at the time of the loss arose. But in case of tort claim, the attorney may try to secure the claim by special damages. Such as:
- Replacement of damaged property.
- Medical expenses.
- Loss of wages.
- Cost related to home care or domestic services.
In the case of tort claim under general damages, it has a different meaning. It consists of losses which are hard to determine. Such as:
- Physical injury or disfigurement.
- Mental stress.
- Lower the living standard of life.
- Anxiety.
- Emotional distress like sexual harassment.
Conclusion
In the breach of contract, the suffering party will recover his loss by claiming under compensatory damages, general and special damages in case of Contract and Tort issues. It is very important to note down the difference between General and Special damages under Contract and Tort issues. Special damages are given under special circumstances, it cannot be given in any ordinary situation. In case of tort issues, the general damages cannot be easily determined and in cases of special damage, under personal injury, damages can be easily ascertained by taking into consideration the amount of loss such suffered.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack








 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


