This article is written by Aayushman Jauhari, pursuing a Certificate Course in Introduction to Legal Drafting: Contracts, Petitions, Opinions & Articles from LawSikho.com.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Are you wondering about what is a Licensing Agreement? Why are Licensing Agreements used? What are the adverse effects of not executing a Licensing Agreement? And, how can one make a Licensing Agreement? Then this article is the one-stop answer to all your questions.
What is a licensing agreement?
The term “License” is defined under Section 52 of the Indian Easement Act, 1882 as “Where one person grants to another, or to a definite number of other persons, a right to do, or continue to do, in or upon the immovable property of the grantor, something which would, in the absence of such right, be unlawful and such right does not amount to an easement or an interest in the property, the right is called a license.”
And the term “Agreement” is defined under Section 2(e) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 as “Every promise and every set of promises, forming consideration for each other is an agreement.” And an agreement enforceable by law is a contract.
Thus, a Licensing Agreement is a written contract between two parties (Licensor and Licensee), where one party (Licensor) gives permission or license to use its property/intellectual property/brand name or trademark/patent technology to the other party(licensee) under a specific set of terms and conditions.

Elements of a standard licensing agreement
- Recitals– These are the group of clauses which usually starts with “whereas” and are placed before the main text of the agreement. They provide a general idea about the agreement such as who are the parties and the purpose of execution of the agreement.
- Name of Parties– It includes the name and the place of residence of the parties. In case of a company, it also includes the act under which the company is registered.
- Tenure– It specifies the term for which the license is granted by the licensor to the licensee. Sometimes, it also includes the procedure to extend or terminate the agreement.
- Scope of Usage- It specifies the extent to which the licensee can use the license. It lays down the restrictions on the use of licensed property, which generally include the restrictions on geographical use, channel of trade, making modifications in the licensed property etc.
- Licensed Fee- It is the amount of fee charged by the licensor for allowing the licensee to use or exploit the licensed property. It also includes the payment scheme and mode of payment of licensed fee.
- Force Majeure- It is an unforeseeable and uncontrollable situation that prevents the parties from fulfilling their obligations under the agreement. Thus, this clause lays down the definition of force majeure event and its effect on the liabilities and obligations of the parties under the agreement.
- Indemnification– This clause imposes a duty on the licensee to make good the loss suffered by the licensor, due to the acts of the licensee, during the tenure of the agreement.
- Accounting, reports and audits- It lays down certain reporting and record-keeping procedures which the licensee has to follow to ensure proper records are maintained for a periodic royalty payment.
- Governing laws and dispute resolution– It specifies the laws which governs the licensing agreement and lays down the provisions for resolving the disputes (relating to the agreement) that may arise between the parties during the tenure of the agreement.
Checklist items for a licensing agreement
The proof-reader should check the following points and must ensure that:
- The name of the parties, their residential or registered office address and the act under which they are registered (in case parties are the companies) is mentioned.
- Tenure of the agreement is mentioned clearly.
- Whether the licensor owns the licensed property or not? And if he isn’t the owner but a license holder of the licensed property, does he have the right to further sublicense it?
- The licensed property is described accurately and exhaustively.
- All the terms that are intended to have a special meaning are defined and are used throughout the agreement, in the form in which they are defined.
- Mode of payment of licensed fee is mentioned.
- The formula for calculating licensed fee is correct.
- Provisions for indemnification are exhaustive to make good the loss suffered by the licensor.
- The definition of Force Majeure event is broad and exhaustive.
- The agreement is serving the intended purpose for which it is drafted.
- Provisions of this agreement are not violating any of the laws governing the agreement.
- The agreement has provisions to deal with any future changes in the laws governing this agreement.
Types of licensing agreement
If licensed property is an intellectual property then based on the degree of exclusivity of the licensed property, licensing agreements are of following 4 types:
Exclusive Licensing Agreement– This type of agreement creates a unique-relation between the licensor and the licensee. In such agreements, no one, except the named licensee, is allowed to exploit or use the licensed property during the term of the agreement. The unique feature of this type of agreement is that even the licensor is excluded to use or exploit the licensed property during the term of the agreement. Copyright, trademark and patent licenses are the best examples of an exclusive license agreement. For example, suppose an automobile company X invents a car that runs on hydrogen fuel and gets the car patented, under the patent laws. Once the company X gets patent rights on the car, thereafter no other individual or company, not even the government who has granted the patent license, can make, sell and distribute the patent car during the term of the patent license.
Non-exclusive Licensing Agreement– In this type of agreement licensor can grant license of the licensed property to any number of licensees and can also use the licensed property during the tenure of the agreement. For example, suppose a pharmaceutical company X discovered medicine for coronavirus and gets its patent. Now the company wants to sell that patent medicine in the entire world to earn profit by saving people from losing their lives. Then, in such case, the company will enter into the non-exclusive license agreement where it can grant a license to sell its corona medicine to any number of individuals, who are interested in selling that medicine.
Co-exclusive Licensing Agreement– This type of agreement allows more than one licensee to use and exploit the licensed property, but this time the number of licensees is limited and their number is fixed at the time of entering into the agreement. For example, X is a watch company that grants licenses to companies A, B and C only to sell its patent watches on their online platforms. In this example, since the number of licensees are fixed and are limited to 3, it is a good example of a co-exclusive license agreement.
Sole Licensing Agreement– This type of agreement is very similar to an exclusive licensing agreement but the only difference is that here licensor has the right to use the licensed property during the tenure of the agreement. For example, suppose Mr X is a wholesaler of rice, who has a warehouse in Ghaziabad. The warehouse is large enough that at most about 50% of its space is utilized by Mr X for storing his rice. In order to have optimum usage of warehouse space and to earn some profit, Mr X entered into a licensing agreement with Mr Y who is the wholesaler of pulses. Through this agreement, Mr X (licensor) grants the license to Mr Y (licensee) to use the warehouse (licensed property) in exchange of Rs. 25,000/- as consideration. However, it is specifically mentioned that the licensor has the right to use the licensed property during the term of the agreement.
Since in this example only licensor and licensee are only allowed to use the licensed property, the agreement executed is a sole licensing agreement.
Issues covered by the licensing agreement
- Copyright- A copyright is a legal right that is granted to an author or the creator of an original work. It includes the right to reproduce the copyrighted work, to prepare derivative work based on the copyrighted work, to publicly perform and display the copyrighted work and to publicly perform the copyrighted work using digital audio transmission.
- Thus, a copyright license agreement is executed to grant any of the above-mentioned rights of copyright upon the copyrighted work to the licensee for a specific period in exchange of royalty amount.
- Patent- This type of agreement is executed to allow the licensee to make, use or sell the patent invention or design of the licensor in exchange of licensed fee.
- Know-how- This type of agreement is executed to supplement a patent license agreement. It lays down the procedure of how knowledge and skill, which are required for proper utilization of patent technology, will be transferred.
- Trademark and Service mark– This type of agreement is executed to allow the licensee to use the trademark or service mark owned by the licensor as per the terms and conditions of the agreement.
- Trade secret– It is a unique type of intellectual property that is not registered under any law but still provides protection to those secret data or information that has some economic value for the business enterprise. Trade secret licenses are executed to ensure that secret information which is shared with the licensing partners remains confidential. These agreements specify which information is confidential and how such information is used by the licensing partners.
Largest areas of concern of licensing agreement
- Calculation of licensed fee– Since Licensing agreement is all about making money from licensee by allowing him to use the licensed property, deriving a balanced and profitable formula for calculation of licensed fee is always a matter of concern.
- Quality Control– Licensing agreements should specify the licensor’s expected quality of products and services and should also specify the methods of quality control. This is of utmost importance because even a single quality control failure can do massive damage to the brand.
- Scope of usage– Licensor should decide in advance the scope of usage of licensed property as per its worth and future demand. This decision is crucial because in case of a wrong decision, both the licensor and licensee will suffer and the agreement will fail to achieve its desired purpose.
Consequences of not making a licensing agreement
Executing the licensing agreement helps the parties to develop an understanding of how to use and approach the licensed property. However, without it, parties become directionless. They waste their precious time, money and energy finding access to the appropriate source to achieve their business goals. However, this only leads to frustration and the ultimate conclusion is that parties failed to achieve their desired goals.
How licensing agreement benefits licensor and licensee?
Let’s take an example to answer this question. Suppose you are a toy car manufacturer. If you manufacture a car having a basic design, its sale will likely be less. However, if you manufacture a replica of a luxury car, its sales will definitely be more. Thus, here licensing agreement helps the licensee to get the license or the right to use the patent luxury car design and thus, promote its sales. On the other hand, it helps the licensor to earn profit by allowing the licensee to use its patent design. In this way licensing agreement is used.
End User licensing agreement
End-User Licensing Agreement (EULA) is a contract between a software developer and the user of that software. Since EULA is a contract, it is governed by the provisions of the Indian Contract Act, 1872. The term “End User” in EULA denotes that these agreements are non-transferable. These agreements are made to serve the following purposes:
- To protect the rights of the licensor on the licensed property. For example, EULA is used to restrict the end-user (licensee) from copying the source code of the software and using it for his own benefit or against the developer (licensor).
- To diminish the possibility of using the software (licensed property) without compensating the licensor.
How can a person create a license agreement?
Hiring an advocate is the best way to draft the licensing agreement. But as there is no legal compulsion that only advocates can draft the licensing agreement, individuals or organisations, if they desire, can also draft their own licensing agreements. However, while drafting your own licensing agreement following things should be kept in mind:
- The language used in the agreement should be simple and clear.
- Avoid using short forms.
- The agreement should be as exhaustive as possible covering all the possible circumstances, relating to the licensed property, that may arise in future.
- To avoid confusion, make sure that the language or words used in agreement convey only one meaning to the readers.
- Date of execution, date of expiry, amount of licensed fee and other charges should be mentioned accurately and clearly.
The steps for making the licensing agreement are as follows:
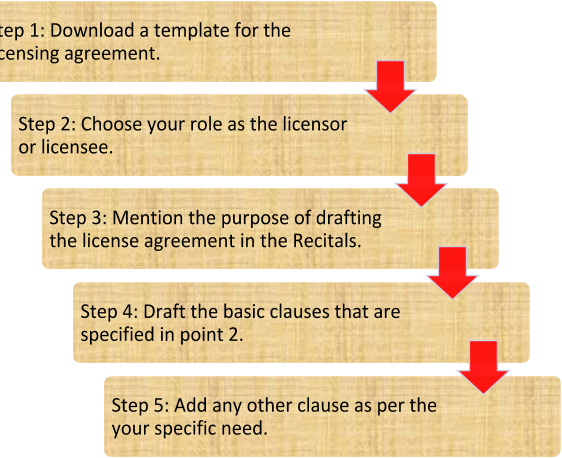

Conclusion
Licensing Agreement has a large scope in Intellectual Property (IP) industry, especially in copyright, patent and trade-marks licenses. It helps in promoting the sales of products and to yield a large return on investment by enabling optimum utilization of licensed property. Thus, a basic knowledge of licensing agreement is important for everyone, especially businessmen, law students and advocates.
Reference
- https://indiankanoon.org/doc/120447987/
- https://indiankanoon.org/doc/1089645/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/l/licensing-agreement.asp
- https://www.taylorwessing.com/synapse/commerical_exclusive_nonexclusive.html
- https://licensing4profits.com/are-you-using-the-right-type-of-licensing-agreement/
- https://blog.ipleaders.in/end-user-license-agreement-key-terms/
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack










 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


