This article is written by Leela Madhuri pursuing Diploma in Intellectual Property, Media, and Entertainment Laws from LawSikho.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Trademarks started to perform a dynamic role in economic growth, and they have since become a key part of the current world of global trade and market-based economies. India being a mixed marketplace, has many industries that function under the free market concept. The struggle in the market system is risky. For any initiative to succeed in the open market, they have to produce brand recognition and brand value. The modest way through which this has to be completed is through trademarks. Trademarks are assumed as the position of intellectual property across the world. There are several organizations, both worldwide and countrywide, that work to protect intellectual properties such as trademarks.
In India, the violation of a trademark is a reasonable crime which means that the infringer may also face criminal charges along with civil charges. With the help of these trademarks, both the manufactures and the consumers can be benefitted. Because trademarks make it easier for consumers to rapidly recognize the source of a given good. And in the meantime, the manufacturers can also get big benefits from the consumers. This article explains what is secondary liability and who has secondary liability in case of trademark infringement.
What is a trademark?
A trademark is a word, symbol, or phrase, used to recognize a specific producer or vendor’s goods and differentiate them from the products of others. For instance, there are different types of shoes. So to recognize them they have specified trademark names like Addidas, Nike, etc. To fulfill their unique purpose from the consumers who wish to make their choice between different goods of the same kind on the market, trademarks must be legally protected. Otherwise, competitors could use identical signs for the same or similar goods or signs so similar that the consumer would be confused as to the origin of the goods. Instead of reading the fine print on a can of cola, consumers can look for the Coca-Cola trademark. By creating goods easier to recognize, trademarks also give producers the motivation to invest in the quality of their goods. A trademark can be protected based on either use or registration. With using one can know that a certain trademark belongs to a specified company or person and with the help of registration one can easily know that the trademark is booked or already registered. Both methods have developed historically, but today trademark protection systems generally combine both elements.
In general, any person who intends to use a trademark or to have it used by third parties can apply for its registration. That person can be either a natural person or a legal entity, even a holding company. The trademark owner does not have any right to stop third parties who are not his competitors from mentioning his trademark by acts such as the listing of the mark in a collection of trademarks or dictionaries or using it in newspaper articles or books or other publications. The ownership of a trademark can change for different reasons and in different ways. And also sometimes, the rights to a trademark can be lost through abandonment, improper licensing or assignment, or genericity. A trademark is abandoned when its use has been discontinued and determined not to resume its use. and Trademark rights can also be lost through improper licensing or assignment. The Trademarks Act, 1999 is the law that protects trademarks in India. The Act arranges the rules dealing with registration, protection, and penalties against infringement about trademarks. The trademark violation suits will be seen in the courts and will be given strict penalties. There will be either given injunctions or claim the damages for violation.
What does trademark infringement mean?
Trademark infringement means using the trademark illegally which happens in confusion, or mistakes about the source of the goods or services. This infringement may mislead the reputation of the products by using them as duplicates. For example, a consumer who wants to consume shoes from Adidas goes to the store and mistakenly buys Abibes which is a duplicate version of Adidas then, Adidas can file a suit against Abibes as his trademark is being infringed which makes him get damage. At present, Bata India Limited, a brand that has become extremely popular amongst the masses, has over the years, brought many suits against rival brands and other organizations.
To know more about trademark infringement please visit
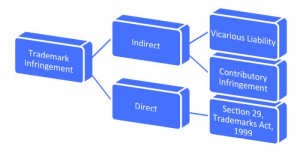
A trademark owner who believes its mark is being infringed may file a civil action in either state court or federal court for trademark infringement, depending on the circumstances. Without registering a trademark, the owner can not bring any infringement proceedings even after filing a suit. When looking into trademark infringement, one must know that there are two types of infringement; Direct infringement and indirect infringement. There is also some defense in the trademark infringements like fair use. If anyone was accidentally filed a lawsuit as a trademark infringer they have few steps to avoid it. Such as considering general liability insurance, registration of the trademark, etc.
One of the famous cases for trademark infringement is “The Coca Cola Company v. Bisleri International Pvt. Ltd”.
Who has the secondary liability in case of trademark infringement?
The concept of secondary liability is a common point of the law of torts, which rises when a party considerably provides, agrees, encourages, or is otherwise responsible for directly infringing acts passed out by another party. In simple words, It refers to the responsibility of liability on a defendant even though that defendant did not directly commit the tort at issue. Secondary liability is similarly known as vicarious liability. Secondary liability is frequently updated on economic productivity grounds. Secondary liability is classified into two types: vicarious liability and contributory liability. Both secondary liability concepts in trademark law need a fundamental act of direct infringement.
For vicarious liability under trademark law, there must be an appropriate connection between the defendant and the assumed infringer. For creating a vicarious trademark liability, a solid connection needs to be proved. The principal-agent relationship happens if the defendant and the direct infringer have an apparent partnership that they have the authority to fix one another in contact with third parties. In the case of Gregory vs Piper, the master authorized his servant to place rubbish to block the plaintiff from using a particular way. He instructed his servant that the rubbish should not touch the wall of the plaintiff. And the servant did accordingly. But the rubbish touched the plaintiff’s wall and the plaintiff sued the defendant for trespass. The defendant (master) was held liable.
Under the policy of contributory liability, parties other than the direct wrongdoer may be held jointly liable if they acted in performance with or provided aid or encouragement to the direct tortfeasor. This means that there must be evidence that the contributory wrongdoer’s actions aided the tortious act. The contributory tortfeasor (wrongdoer) must firmly assist the performance of a wrongful act. For instance, A as an aid helps B to beat C. Here A does not come into the clash but helps B. So, A is also liable for being a contributive liability. Thus, the influential wrongdoer must identify that the direct tortfeasor’s behavior started a breach of duty.
Courts have known the convenience of both common-law theories of secondary liability. Inwood Laboratories, Inc. v. Ives Laboratories, Inc. in this case, the Court discoursed that although the pharmacists could be held liable for mislabeling the drugs, there was no evidence that petitioners collaborated with the pharmacists or suggested the pharmacists mislabel the drugs, thus, the appellate court’s conclusion that petitioners violated section 32 of the Trademark Act of 1946 was reversed.
The important case in secondary trademark liability jurisprudence. And in Kalem Co. v. Harper Brothers, the Supreme Court declared the request of secondary liability doctrines to copyright infringement. Until now, despite their common origin and shared language, copyright and trademark theories of secondary liability increasingly cover different activities.
Conclusion
The concept of secondary liability in trademark arises from the common law of tort where the burden of liability is on the defendant even though the defendant did not directly commit the tort. It is acceptable on economic and moral grounds. In many cases about trademark infringement vicarious liability is compulsory whose understanding comes from the tort law. For vicarious trademark infringement, a principal-agent relationship needs to be established. The financial benefit is also an important aspect that must be direct. In the case of contributory trademark infringement actual or assigned knowledge is required to be established based on the concept that one who knowingly participates or furthers a tortious act is jointly and severally liable.
Every business must require these trademark infringement laws. Because, then every person can take out their innovative skills, without these infringement laws one will depend on others skills lazily. Then the innovation will collapse. Creation is the basic thing to create wonders. It is best to hire business professional services functioning in the legal space to ensure protection against such innovative agreement issues. Also, there are some severe penalties for this trademark infringement. Because it is a big crime to use other’s trademarks. With the help of the common law of the tort, one can be punished for his wrongful acts where others suffer physically or monetarily. As one puts a huge amount of time and effort into creating a brand, it’s very essential to do everything possible to keep it secure. Following some basic rules and strong backing from a legal professional can put an end to all your legal compliance troubles.
Reference
- https://www.uspto.gov/page/about-trademark-infringement
- https://www.carrferrell.com/uploads/files/SecondaryLiabilityInTrademark.pdf
- https://journals.cdrs.columbia.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/14/2015/01/1-37.4-DINWOODIE.pdf
- http://www.legalserviceindia.com/legal/article-3951-case-analysis-on-the-coca-cola-company-vs-bisleri-international-pvt-ltd.html
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skills.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals, and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack











 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


