In this article, Jisnu Dutta who is currently pursuing M.A. IN BUSINESS LAWS, from NUJS, Kolkata, discusses Compliance, best practices, and structuring of a company which holds IP of a business group.
Related concepts
Holding Company
- A holding company is to hold subsidiary companies and generally not to directly participate in manufacturing or production of goods or delivering services by its own. It controls the subsidiary companies by appointing board of directors and aims to act as overall administrator. Holding company can also hold asset on its own, though it’s rare and mostly it administers the company affairs of subsidiary companies.
- Holding company holds more than 50% paid up capital of subsidiary company. A 100% holding company will have all the shares of subsidiary companies. TATA Investment Corporation and Bajaj Holding & Investments are the example of holding Company. In the case study of Apple, Apple Inc,US is the holding company.
Definition of IP
- Intellectual property (IP) are the new creations which were not existing before and would have some application irrespective of whether commercially prudent or not. IP may be developed in the field of inventions, literary work, symbols, names, images, and designs which would have commercial value. If appropriate legal monopoly is created in and around the intellectual property, then it would become a source of continuous wealth.
- IP is divided into two categories. Patents, trademarks, industrial designs, geographic indications of source relate to business sector and Copyright for literary and artistic works relate to domain of art .Both have practical applications. IP law envisages to protect the legal right of original contributor for a defined period of time and prevents unauthorized copying.
- Effective Protection of intellectual property is central to the success of technology driven businesses.
- Intellectual property is a type of intangible property from accounting view point which have finite approved period of legal monopoly. For example, patent holder in India has exclusive right to make, use and sell of patented product for 20 years.
IP holding Company
A holding company which was primarily created for owning group IP other than holding subsidiary company or companies is called IP holding Company. In consolidated balance sheet of IP holding company, one can see the valuation of IP provided in intangible asset which may be directly indicated or may be written in accompanying notes.An IP holding company may directly sell the commercial rights of IP to interested parties or may further incorporate a special subsidiary to manage It.In the second case it sells the whole economic right of IP to subsidiary company through cost sharing agreement and the subsidiary company further redistribute the economic right to interested parties.
Advantage of IP Holding Company
- When main business activity is accomplished by the activity of subsidiary company, an IP holding company ensures the IP rights are financially protected from being sued by third party, supplier, employer or any other aggrieved party who have business relation with subsidiary. A non trading Holding company cannot be sued in business disputes even though subsidiary company can be sued and made insolvent.
- Economic rights of IP can be sold to third party while retaining the legal right centrally by the IP holding company.
- IP can be centrally managed and protected by a holding company more effectively by monitoring the products or services delivered by competitors, arranging periodic IP audit and suing the parties trying to infringe its IP rights.
- IP based holding company structure can create a sophisticated hi tech business image which helps to get easy finance from market, banks, venture capitalist or private equity investors.
- Creating IP holding company provides opportunity to minimize tax liability through cost sharing agreement.
Disadvantage of IP Holding Company
In case of patent infringement the company which have economic rights of IP can not sue the illegal user.The legal IP holder or original holding company has the right to sue. This was determined in the case of Poly America, L.P. v GSE Lining Technology, Inc. (2004). Therefore subsidiary companies who have economic right over IP are not protected from loss by infringement of IP.
IP Audit
IP holding company shall require to protect their IP right as well as to manage the conversion of new IP development activities to successful registration of IP. Accordingly a systematic review of IP assets owned, their market utilization and need for developing additional IP is done. This is commonly known as IP audit. The IP audit also provide for comprehensive advice on IP management by IP holding Company.
The audit covers all aspects of IP like patents, copyright, trademarks and designs which are well known and also the informal IP areas which includes trade secrets & technical know-how.The IP audit will also disclose the infringement prone areas to mitigate future business risks. IP audit can also be done while entering into licensee agreement or right sharing agreement or cost sharing agreement.
IP audit may be done once in a year. Since these businesses are highly dependent on proper utilization of IP rights and continuous development of IP, they require appropriate management attention. It is also desirable to act on the finding of IP audit and to strategize further.
Tranfer Pricing
One important point which is pivotal to the idea of IP holding company is transfer pricing and cost sharing agreement.This needs to be discussed at length.
Transfer price is the notional price for the goods and service exchanged between different units/establishments of the same entity. This is not easy to determine transfer price for tangible assets exchanged within a boundary of a country and most difficult for intangible asset like IP when they are exchanged between subsidiaries situated in distant countries.
This type of transaction is measured by three ways. Transaction based method, Cost sharing method and profit based method. Transaction based method states to determine the cost by comparing the price of similar arm length transaction between unrelated knowledgeable and willing parties.
In Cost sharing method patent holder receives portion of development cost of patent in accordance with anticipated future benefit by the subsidiaries. An agreement for cost sharing is signed between patent holding parent company and its subsidiary company.
There is tax advantage associated with cost sharing agreement. In a cost-sharing agreement, the legal holder of patent allows a subsidiary company to use the commercial or business rights in exchange of sharing of cost or royalty.
In the first case, cost, ie in share cost, the subsidiary company agrees to pay fraction of development cost determined by relative benefit of present and future earnings.
Lets assume a hypothetical case involving one parent holding company and its single subsidiary company .The holding company does the business in US where the tax rates are 35% and earns a profit 50 Million dollar where as the subsidiary situated in a low tax country where tax rates are 15% does the business in rest of the world and earns a profit of 100 million dollar. Also lets assume that the earnings just mentioned were perpetuities. Development cost of IP is $30 Million and interest rates are 10%.
So present value of subsidiary company’s earnings will be 100/0.1=$1000m.IP holding Company’s income will be =50/.1=$500m.
As per earning estimation the subsidiary has to pay 1000/1500=2/3 of development cost=$20m
In absence of cost sharing agreement the subsidiary has to pay the total $1000m .
The impact of worldwide tax benefits of cost-sharing agreement can be as follows
The subsidiary’s $20 m payment to the holding company will result in an additional 0.35 x $20m = $7m in tax payment by the parent in the United States. This will be offset by a 0.15 x $20m = $3m tax reduction for the subsidiary company operating in low tax country yielding $4m = $7m — $3m incidence of total tax payments .
If we compare that to what would have happened in absence of cost-sharing .The subsidiary had to pay in present value terms which is $1000m to the parent, which will be attributable to the earnings of patent. The parent has to pay tax @ 35% on $1000m = $350 m which would be offset by the subsidiary’s reduced tax bill of 0.1 x $1000m = $100m. Accordingly the company’s incidence on taxes would increase by $350m — $100m = $250m.
Thereby the firm can reduce its tax payments by $ 246m ($4m vs $250m) by adopting a cost-sharing scheme.
The third method provides that inter company fees or royalties can be allocated as per the profitability ratio. That is, in a combined profit if, subsidiary company has greater share it will pay higher fees.
IP laws in India
India has been a member of World Trade Organization (WTO) since 1995. As a WTO member nation, India incorporated IP related acts to prevent infringement of IP rights. India also signed international IP treaties such as Paris Convention, Berne Convention and Patent Cooperation Treaty. As per Paris Convention any person from a signatory state can also apply for intellectual property (a patent or trade mark) in other signatory states, and he will have same enforcement rights as may be exercised by a national of that country.
Under Berne Convention, India recognizes copyright of authors from other member states exactly equal footing as the copyright of Indian nationals.
India’s patent law recognizes the principle of ‘first to file’. As per this method, if more than one people apply for a patent on same invention, the first person to file the application shall be awarded the patent.
Enforcing IP rights in India can be enforced by civil courts or through criminal prosecution.
IP Legislation in India
- The Patent Act, 1970 as amended by the amendment Acts of 1999 and 2002 and 2005.
- The Copyright Act, 1957 as amended.
- The Trade Marks Act, 1999
- The Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout Design Act, 2000
- The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and protection) Act, 1999
- The Protection of Plants & Varieties and Farmers Rights Act, 2001
Important tax laws in India
A company incorporated as per the laws of India shall be considered as an Indian resident for tax purposes. A company which is wholly managed and controlled from India, even it is incorporated outside India shall be considered as resident in India for taxation purposes.
Income of an Indian company (which would include foreign company’s Indian subsidiary) is taxed in India at a rate of 30% and surcharge and educational cess thereon.
Tax on foreign company shall be imposed at the rate of 40% on its business income earned in India. India has entered into a tax treaty with the Government of other countries for granting tax relief or avoidance of double taxation. IT Act in Section 90(2) provides that in case of taxpayers to whom such tax treaty applies, the provisions of the IT Act would be applied with modification to the extent they are more beneficial to the tax payer.
Fees for technical services (“FTS”) are taxable in India when they arise from sources within India. FTS and Royalties paid by a resident to a non-resident are also taxable in India. However, when such royalties/FTS are remitted with respect to a profession or business carried on by such resident outside India or for earning income from any source outside India, then such FTS and royalties are not taxable in India.
Further, even payments of royalties or FTS made by one non-resident to another non-resident are brought within the Indian tax net, if such royalties/FTS are payable with respect to any business or profession carried on by such nonresident in India or for earning any income from a source in India.
A case study on IP-based restructuring of Apple Inc, US
Apple is producer of discretionary digital gadgets including ipod, ipad and apple watch. Recently it has drawn much of media attention for its tax avoidance strategy and related disputes to government bodies. Apples engineer and technical staff are known to create premium gadget which has worldwide market.
Innovative technical ideas behind its technical gadgets are the source of Apple’s high demand among the customer .Intellectual property (IP) rights of apple is central to its value creation process which creates ideas, join together and implement those ideas in prototype design. Intellectual property rights are movable and can be transferred across national borders and oceans to different continents and foreign countries. This type of transfer in case of fixed asset or property is not possible.
Apple is a well recognized US success story, as its IP was created through Research and development in US. Apple also have presence in global markets other than US. So Apple Inc is a multinational company operating in different continents .The taxability of MNC is decided primarily based on the tax residency of the company. Tax residency in simple form says in which country the MNC’s income is taxable.
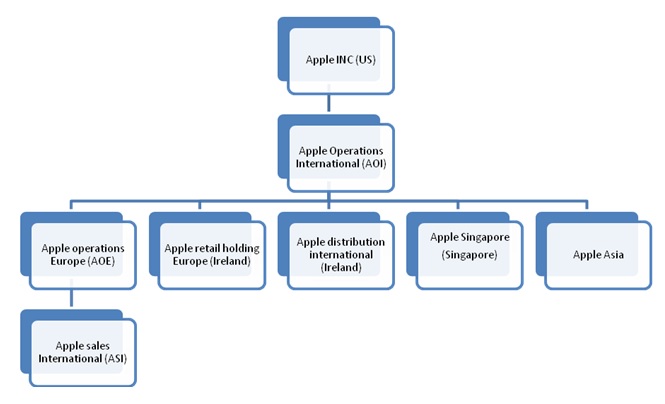
US tax law says the country where company’s registration took place shall be considered as company’s tax residence. Apple has successfully found one country which had contrary view on US definition of tax residency. Ireland considers a company as tax residence of Ireland if it is managed and controlled from Ireland. Taking the opportunity of these two contrary positions taken by Apples home country and one foreign country apple have created three subsidiary company Apple Operations International (AOI), Apple Sales International (ASI), Apple Operations Europe (AOE) all registered in Ireland. Therefore for taxation purpose these three companies which are responsible for the global business outside the US are neither considered citizen of US nor considered the citizen of Ireland .Apple Inc is sole owner of AOI which directly or indirectly owns most of the offshore subsidiaries of apple. Second company is Apple Sales International (ASI) which has the economic rights to Apple’s valuable intellectual property in Europe, Asia, India, Middle East and Africa. Apple’s third subsidiary is Apple Operations Europe (AOE) which had about 400 employees ( in 2012 ) engaged in manufacturing a type of computers for sale in Europe. ASI made necessary Contract with third party manufacturers in China to make Apple products .ASI then sold these products to Apple Distribution International.
A pictorial of Apple’s structure is given below
Apple’s Irish subsidiaries own the economic/marketing rights of intellectual property for goods sold outside the US. Apple Inc. (the U.S.comapny) is the sole owner of the legal rights to Apple’s intellectual property.
The dividends from companies such as AOE, ASI and distribution companies flow to Apple operation international in Ireland where it was not taxed. Apple Inc get back some of revenue from AOI through cost sharing agreements in exchange of marketing right of IP in favor of the Ireland subsidiary. Pricing of cost sharing agreement depends on adopted transfer pricing mechanism.
Some of the important points may be noted from the above case study which are as follows,
- IP (intellectual property) is an important factor in achieving good business in technology sector. Holding the IP and managing it is the key in the sophisticated hi tech business activity.
- The holding company keeps the legal right of IP and provides economic right to subsidiary through a cost sharing agreement.
- There exists much difference in tax regulations worldwide. Here we find contrary tax residence definition in US and Irish tax laws.
- Singapore subsidiary of apple probably is incorporated to take tax advantage of low taxing Singapore. So there may be many countries with lower tax rate than home country.
- Manufacturing activity can be profitably done in a country such as china where skilled labor is available at cheaper cost.
- Complete Manufacturing activity can be contracted /outsourced to third party enabling the main company to hold lesser fixed asset and earn extra return on equity. This may also lead to negative cash conversion cycle.
- Separate subsidiary company can conduct operation, sales and distribution in which parent company keeps majority share holding.
- Company can successfully run business by giving prime importance to Research and development work which creates IP.
Restructuring process in IP based business groups
- The first step will be drafting proper licensing agreement between subsidiary company and IP holding Company for economic usage rights of IP. The agreement should specifically provide wheather parent company is delegating full economic right or the right is specific to some geographical area. Further It also shall be clearly mentioned that wheather the subsidiary company purchasing the right can redistribute the right in the specified geographical area. The agreement may also specify who will have the legal responsibility to protect the IP rights in case any infringement to IP is noticed.
- The agreement shall further provide for determination of fees or royalties associated with the use of IP considering relevant regulation of home and foreign country on transfer pricing mechanism and cost sharing agreement.
- The agreement also requires to include the target area on which future IP shall be developed along with the arrangement of sharing associated development cost.
- The subsidiary having economic right over IP is to be established in a low tax country.
Following table gives corporate tax rates at different countries.
Corporate tax rate in low taxing countries
| Country name | Tax Rate | Country name | Tax Rate |
| Bahamas | 0% | Bulgaria | 10% |
| Bahrin | 0% | Paraguay | 10% |
| Cyman Islands | 0% | Quatar | 10% |
| Hungary | 9% | Gibraltar | 10% |
| Bosnia Herzegovina | 10% | Hong Kong | 16.5% |
- However this is very important to keep in mind that there can be several other taxes such as sales tax or service tax other than corporate tax. The low tax country must be economically and politically stable and strong enough to provide necessary protection in case of international infringement into IP rights. The total royalty payment shall be directed to the low tax country. The company may additionally collect the information whether double taxation avoidance treaties have been signed by the countries where subsidiary company will take tax residency.
- The detail process to take tax citizenship must be known to the strategist. Effort shall be made to find pair of countries which take counter view on the tax citizenship. If holding company and subsidiary company is established in such a pair of country, then the tax benefit will be maximum.
- Subsidiary company in possession of economic IP right can further sublet/redistribute the using right to other subsidiary company or third party.
- Manufacturing facility to be located in a country with cheap labour.However the skill set of the labours will also required to be at global level .Further this decision will be taken in consideration with imposable import, export duty. Manufacturing can be optionally fully outsourced to third party.
- Sales activity also could be undertaken from another low tax country because any significant change in legislation in low tax country where the subsidiary having patent right will be instituted may otherwise effect in revenue. The diversification of sales, IP management and manufacturing facility through formation of different subsidiaries at different low tax level countries makes sense. Due to political activism or international pressure from high taxing country, any of the low taxing country may increase tax rate. However it is less likely that all three low-tax countries would increase tax rates. Therefore this strategy reduces the effective tax rate, lowers manufacturing cost and manages the IP in a better way.
However to avoid criticism from taxing department of any of these country subsidiaries must have engaged some employee in their pay role with specific functions. These companies are also required to pay requisite tax in countries of tax residency and act in a socially acceptable way.
This was all on Compliance, best practices and structuring of a company which holds IP of a business group. What are your views on Compliance, best practices and structuring of a company which holds IP of a business group? Comment below and let us know.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack









 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


