This article is written by Shivangi Agrawal who is pursuing a Certificate Course in Advanced Criminal Litigation & Trial Advocacy from LawSikho. This article is aimed to understand two common types of corporate frauds: payroll fraud and procurement fraud. Further, the article has dealt about the theoretical aspect of fraud investigation and prevention often used in the Forensic auditing and fraud examination process.
Payroll fraud
Meaning
Payroll fraud, a type of accounting fraud occurs when employees or employers fraudulently manipulate the payroll system to falsely receive payment or compensation that they haven’t earned or in case of employers, to withhold the payment of rightfully earned wages or taxes due on those wages.
Types of payroll fraud
Timesheet/Timecard Fraud
It is a most common type of payroll fraud can occur in a number of ways:
- Falsification by employees of their timesheet submissions to get paid for the hours they don’t actually work, known as padding work-hours;
- Arranging other persons or co-workers to (appear) work at their place when they’re not working, known as buddy punching;
- Adding of the name on some individual in the payroll who has actually never worked in the premises and thus, receiving the payment/wages on false pretext. This type of fraud goes undetected for long periods in big institutions who are not able to handle every single worker. This is known as Ghost employment or fictional employment;
- False entry by payroll clerk manually to employee’s timesheet showing increased hours of work in collusion with payroll administrator.
Commission Schemes
When the commission is adjusted on the number of items (units) employees sell instead of adjusting on credits, commission frauds are most common. This can be done by adjusting the number of sales made by an individual and thus, manipulating the overall commission.
Worker’s Compensation/ Insurance Scheme Fraud
This happens when workers/employees fake injuries, accidents to claim false compensation on insurance claims. Employees in these cases, are often found to have colluded to depict “slip and fall” accidents or show injuries elsewhere (in homes, etc.) to have inflicted during working hours at working premises. The companies that are self-insured are the victims while others find their premiums rising gradually.
Employee Misclassification
The above-mentioned types are where the employer is the victim and the employee steals the money. This is the opposite, where an employee is the victim and the employer steals money. These happen when employers or companies in order to avoid paying employment taxes, overtime, insurance or workers’ compensation classify workers falsely as independent contractors.
Case Studies
- This case dates back to 2016. Jaslyn Chen Xiaohong was accused of $1.2 million of cheating, forgery and theft in her duty to manage the payroll of her employer and subsidiary companies. She used ‘Chen Xiaohong’ , the last name of her, submitted the payment instruction letter to the Company with her bank details and got money accounted for herself. She avoided using her initials to escape detection.
- The 2017 case relates to embezzlement of $3,00,000 conducted by former Crown Candy employee McCutchen issuing paychecks to herself, her children and her boyfriend in the name of fictitious employees and former workers. She was responsible for handling the Company’s payroll and finances.
- Paul Randolph Beeks Jr., a Mount Airy Man was charged to 15 months imprisonment for alleging fraud of around $5,26,000. He handled accounting, tax and payroll works at Mount Airy Company. Between 2009 and 2015 made 24 fraudulent transfers to his company allegedly which was actually never authorised. Because of Beek’s fraudulent actions, the Company was debted to state for around $1,22,000 in taxes for 2012.
- Candy Jean Tompkins, employed as payroll administrator, was charged with embezzling $2,45,000 from Broken Arrow Church to pay her credit card bills and purchase concert and theme park tickets from Amazon.com. The fraud was detected by another company hired to take over payroll duties. She was also accused of taking $35,619 from funds she was responsible to deposit on the church’s bank account from tuition payments from parents of children who attended a ministry program.
Procurement fraud
Meaning
The fraud perpetrated by contractors, suppliers external to the organisation or staff, contractors within the organisation during procurement cycle either at beginning, during or last stage of the cycle deliberately, deceptively to make a financial gain for himself or cause a loss to the Company.
The pre-contract stage involves fraud related to processes such as submission of bids, unjustifiable extension of time limits, falsification of bids, documents or leakage of information. Post-contact stage fraud includes charging, concealing or misrepresenting unallowable charges to the buyer, false payment of labour, procuring false invoices or duplicate invoices.
A typical case of procurement fraud is where the procurement manager awards the contract to the vendor (who may provide services such as logistics, transportation, raw materials, etc.) in price well-above the market rate and in turn receives cash, material goods, or other lucrative benefits. The victim in this case is the Company which lose billions for paying unfair amount for the services and goods procured from vendors.
Types of procurement fraud
Collusive Bidding by Contractors
Collusive bidding or bid rigging refers to the process whereby bidders secretly agree to submit high bids allowing pre-selected contractors to win the contracts. This mechanism is usually seen in road construction, paving and waste disposal contracts.
Another similar type of collusion is known as change order abuse whereby a contractor in collusion with a procurement officer submits a low bid to win the contract and thereby increases its price by submitting change order requests after the contract has been awarded.
Deliberately excluding qualified bidders
Contractors and procurement officers in collusion can exclude qualified bidders to direct advantage in favour of a particular person or entity. This can be done through a variety of tactics such as imposing unnecessary pre-qualification criteria known as rigged specifications, unjustified sole source awards, splitting purchases, etc.
Imprest Fund Abuse
Imprest Fund or Operating accounts or petty cash funds are used improperly by employees. The employees submit false requests for reimbursement of expenses which are diverted for their own personal use or expenditures. They can also submit the false requests to both funds and accounts known as double dip technique.
Unjustifiable Sole Source Awards
Sole Source Awards or direct awards or No-bid contracts are such that allow only a single supplier or bidder to fulfil the needs of contractual requirements. This is done to avoid competition with corrupt intention resulting in higher prices and lower quality of goods. This results in huge lase to the contracting organisation.
Case Studies
- The case dates to 2006. Sanjay Bahl, then chief of the UN Commodity procurement section was charged with steering $50 million in contracts to Indian firms in exchange for an apartment below market rates. He was charged with Indian business man Nishan Kohli, to whom Bahl gave favours and advantage by cancelling bids of competing companies. Kohli secured a number of IT contracts for TCIL consecutively.
- CBI in 2020 had sought to prosecute former Defence Secretary and CAG Shashikant Sharma, Air Chief Marshal Jasbir Singh Panesar and other officials in the 3600 crores VVIP chopper scandal procurement-process during the UPA-II government. Recent report by French media on the Rafale deal against Mr. Sushsen Kumar Gupta and Dassault collusion are also going to attract the same provisions.
- Commonwealth Games scam of 2010 where award of contracts were made on a single tender basis and irregular payments were made. Works related to construction of flyovers, stadiums, power plants, sewage plants, parking lots were bypassed and rates of some were overwritten. Items were purchased at abnormally high prices of substandard quality.
- CBI booked senior officials of Hindustan Paper Corporation Limited (HPCL) in 144 crore bamboo purchase scam where money was allegedly paid to Dima Hasao Autonomous Council (DHAC) in Assam. The scam relates to irregular procurement of bamboo by Cachar Paper Mill (CPM) from DHAC. The HPCL officers allegedly renewed contracts before existing contracts expired at a steep increase in procurement prices causing loss of Rs. 46.47 crore to the PSU.
- CBI alleged officials of Air India, German firm SAP AG and global computer company IBM with irregularity in software procurement of Rs. 225 crore in 2011.
- Congress government in 2017 also alleged Rs.20,000 crore scam in procurement of LED bulbs from China and Taiwan. Shashikant Gohil, then Congress spokesperson has accused Energy Efficiency Limited (EESL) for the alleged violation relying on power bills of Navsari Municipality procured through showing no reduction in bills since LED bulbs replaced old bulbs.
- Other case studies include: The Druyun case, the Colonel Moran case, the Mississippi valley case, The K & R case, etc.
Understanding the fraud cycle
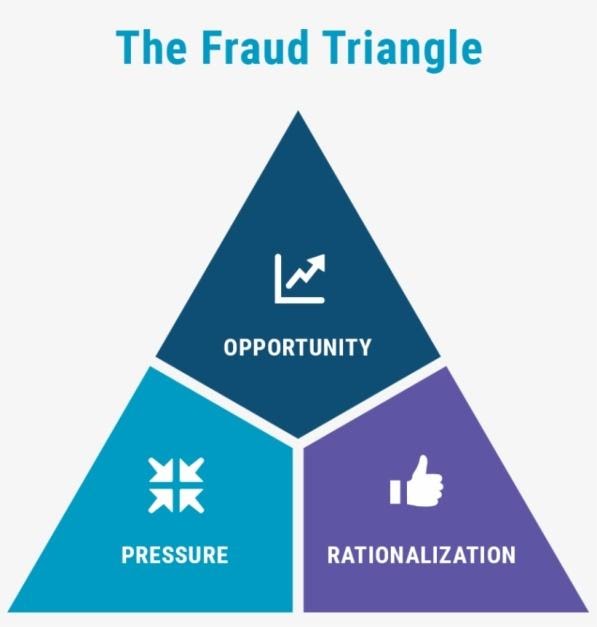
The author has tried to explain this concept by the Fraud Triangle given by Donald Cressey.
He explained the following three components as:
- Opportunity as whenever an individual sees his way clear where he can abuse his position to solve his perceived financial problem or is motivated by ill-will. This section usually accounts for people working for long in the institution who know whereabouts and no one would certainly doubt them.
- Pressure as the motivation behind commitment of such an act due to a number of situations such as medical problems, rising debt, revenue shortage, etc.
- Rationalisation as where the cognitive state of his mind overawes his moral ethics. They are often forced or ones who think that they are underpaid, treated badly, taken advantage of, etc.
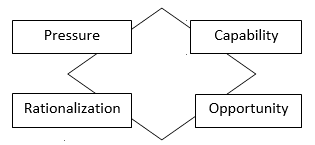
In 2004, Wolfe and Hermanson argued that the fraud triangle could be enhanced to improve both fraud prevention and detection by considering the fourth element- capability. The individual intending to commit fraud must have capability to do so, to control the situation that brings benefits to him and later can turn against him. This was known as Fraud Diamond.
Besides, the Internal Control Concepts like identifying the red flags, continuous monitoring, etc. the forensic experts use this theory to understand the motive behind commission of crime. This has helped them understand the reasons which make an individual to do acts which he knows are wrong or which his conscience resists. In line with these efforts, Fraud Scale was developed by analysis of 212 frauds in the 1980s by Steve Albrecht and his colleagues. They proposed relying on the Pressure and Opportunity of fraud triangle but replacing Rationalisation with Personal integrity and attributes observable for past behaviours. The concept seems to be convincing enough.
Conclusion
Thus, this article has brought out the outline of another aspect of fraud detection and prevention and thus, brings out the increasing role and need of forensic experts in fraud investigation to overcome the increasing frauds and unique methods in the society. The article has not dealt with every detail of the theory but attempts have been made to provide new insight into the fraud prevention techniques to the readers.
References
- Gayton, J., (2004), Naval postgraduate School, California, Case Studies in Government Procurement Fraud, https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a424697.pdf
- If you want to learn, how payroll fraud can be prevented, check here: https://www.softwareadvice.com/resources/payroll-security/
- Forensic Auditing and Fraud Investigation Course by West Virginia University on Coursera.
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skill.
LawSikho has created a telegram group for exchanging legal knowledge, referrals and various opportunities. You can click on this link and join:
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack











 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


