Written by Colin Fernandes, pursuing Diploma in Entrepreneurship Administration and Business Laws offered by Lawsikho as part of his coursework. Colin is currently working as Tax Manager in an MNC.
What is a Hawala Transaction?
Hawala is an illegal foreign exchange market where trading of currency happens outside the parallel (black) controlled financial channels i.e. currency is purchased and sold by dealers who are not “authorized dealers” (“authorized person” means an authorized dealer, money changer, off-shore banking unit or any other person for the time being authorized under sub-section (1) of section 10 to deal in foreign exchange or foreign securities;) at rates different than the rate mandated by the Reserve Bank of India.
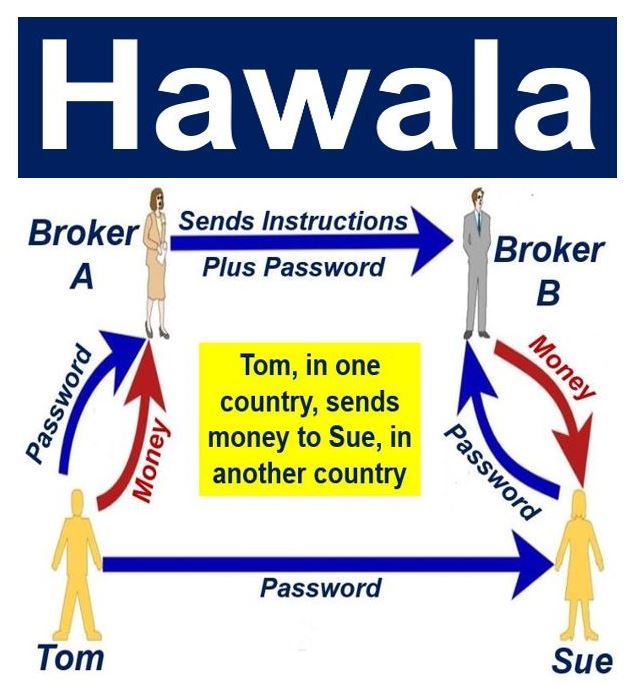
How do Hawala transactions work?
Article 10 of the FEMA act states that “The Reserve Bank may, on an application made to it in this behalf, authorize any person to be known as authorized person to deal in foreign exchange or in foreign securities, as an authorized dealer, money changer or off-shore banking unit or in any other manner as it deems fit. This means that if any person wants to act as a dealer in foreign exchange, he has to be registered with the RBI.
Hawala is used by a number of the Indian diaspora in African & Middle East countries to send money home. This is because it is cheaper than the formal remittance services, and many migrants (some of them illegal) do not have access to banks.
Let’s take an example, say if “Mr. A” a NRI working in UAE wants to send 1,000 AED to his family member in Mumbai. If he sent this money through Authorized dealer, he receives rupees at prevailing exchange rate (regulated b Reserve Bank of India) of INR 19/AED. The exchange rate for the same in uncontrolled (black) is INR 22/AED.

Mr. A contacts a Hawala operator in UAE and gives AED 1,000 to him. The UAE Hawala operator’s counterparty in India, pays INR 22/AED to the family members of NRI in Mumbai. The transaction between Hawala dealer in AED and his counterparty India are not done through authorized dealers and there is no official record of this transaction.
Are Hawala Transactions legal within the meaning of FEMA Act?
Article 3 of the FEMA Act, 1999 states that no person shall—
(a) deal in or transfer any foreign exchange or foreign security to any person not being an authorized person;
(b) make any payment to or for the credit of any person resident outside India in any manner; (c) receive otherwise through an authorized person, any payment by order or on behalf of any person resident outside India in any manner;
(d) enter into any financial transaction in India as consideration for or in association with acquisition or creation or transfer of a right to acquire, any asset outside India by any person.
As the Hawala dealers do not comply with the above article, the transactions carried out by them are illegal.
Why do Hawala transaction exists?
There are many reasons behind the existence of a Hawala system. One of the reason is converting the Indian rupee into a foreign currency. Indian Rupee is not fully convertible i.e Indian rupee cannot be exchanged (above a limit) without the prior approval of the Reserve Bank of India and Government of India (also other departments like Income Tax, etc.). There are restrictions also imposed under Article 4,5,6 and 7 of the FEMA Act.
Due to the existence of Hawala system, it allows India rupee to be fully convertible. Let say that any person in India wants to convert his black money held in India to US Dollars. This is possible due to the existence of the Hawala system. The Money leaves the country without the knowledge of the regulators ie. RBI, Income Tax, etc. which has an impact on the country’s economy
What is the penalty imposed under the FEMA Act for Hawala transactions?
Article 4 (section 13 to 15), of the FEMA act, imposes penalty on persons violating the Act. Penalties include:
- Penalty up to thrice the sum involved / upto INR 2 lacs (if the amount is not quantifiable)
- Confiscation of currency, security or any other money or property in respect of which the violation has taken place
- Civil imprisonment in case of non-payment of the penalty
How does Hawala impact India?
Hawala supports illegal activities in India namely:
- Black Money: As Hawala is an unregulated transaction, it is the most widely used route black money earned in India offshore.
- Corruption: Hawala permits routing black money in and out of India and is widely used to pay bribes.
- Terror financing: Hawala is mainly used by terrorist organizations to remit money in and out of India
Hawala cases for reference
Some of the famous Hawala cases of India:
- Hasan Ali Khan: The Hawala Kingpin
In March 2007, Hasan Ali’s properties were raided by India’s Enforcement Directorate (ED) and Income Tax officials based on allegations of hawala transactions.
(Source:https://www.indiatoday.in/india/north/story/who-is-hassan-ali-khan-129620-2011- 03-03)Current status: As of October 2013,[10] Hasan Ali is in jail since his bail petitions have been rejected several times by various courts[11] including the Bombay High Court[12] and the Supreme Court of India.
2. Jain Hawala Diary case:
The Hawala scandal, also called the Jain Diaries case or the hawala scam was an Indian political and financial scandal involving payments allegedly sent by politicians (black money) through four hawala brokers, namely the Jain brothers.
(Source: https://www.indiatoday.in/magazine/cover-story/story/19960215-jain-hawala-scandal-excerpt-of-s.k.-jains-final-statement-to-the-cbi-834355-1996-02-15)
Current status: More than two decades after it triggered a political landslide, a city court has discharged SK Jain, his employee JK Jain and others from charges of Foreign Exchange Regulation Act violations in the infamous Jain hawala case.
3. Mumbai Hawala King arrested for Rs. 2,000 crore laundering:
Mohammad Farooq, one of Mumbai’s biggest Hawala operator was arrested by enforcement agencies in connection with Rs. 2000 crore money laundering case involving his Stelkon Infratel Pvt ltd and network of 160 shell companies from a one room office in Zaveri bazaar.
Current status: In July 2018, ED files charge sheet against Mumbai hawala dealer in Rs. 2,000-crore scam
Measures to curb Hawala: Is it possible?
During recent years, Government of India has introduced various measures to control the Hawala transactions. Below are few measures introduced:
- Constitution of the Special Investigating Team on Black money: Setup in 2014 to suggest methods to curb & investigate cases of black money in the economy
- Introduction of Black money (Undisclosed Foreign Income & Assets) and Imposition of Tax Act, 2015: It aims to curb black money, or undisclosed foreign assets and income and imposes tax and penalty on such income
- Multi Agency group: Setup by Ministry of Finance in 2016 to probe the Panama leaks involving Indian nationals
- Crackdown by closing shell companies: 5.43 lakh companies were closed for not carrying out normal business activities & submitting their statutory filing
- Indian Currency notes demonetization: On 8 November 2016, the Government of India announced the demonetization of all ₹500 and ₹1000 banknotes of the Mahatma Gandhi Series. It also announced the issuance of new ₹500 and ₹2000 banknotes in exchange for the demonetized banknotes.[2] The government claimed that the action would curtail the shadow economy and reduce the use of illicit and counterfeit cash to fund illegal activity and terrorism
- Making PAN number mandatory for cash transactions exceeding INR 50,000 in a day
- Easing in processing of foreign currency transactions and reducing restrictions on convertibility of Indian rupee by RBI.
In spite of the government introducing various measures to curb the Hawala transactions, it is difficult to completely eliminate Hawala transactions. Few reasons are listed below
- Indian rupee is not fully convertible. Indian rupee above a certain limited cannot be easily exchanged to a foreign currency. Individuals / companies who require foreign currency use Hawala mode in order to buy them
- Corruption still exists. Kickbacks are normally paid through the medium of Hawala transactions.
- Introduction of Bitcoin (cryptocurrency). With the massive changes in the world of technology, digital currencies are being introduced. As these are not regulated by the central banks it is another mode which is leading to increase in Hawala transactions.
Conclusion
Hawala is an existing parallel illegal exchange market. Hawala mode is used by exchanging currencies without the involvement of the central bank. Individuals who require a higher exchange rate, do not have access to bank accounts, receiving kickbacks (illegal) use Hawala transactions. FEMA act only allows exchange of foreign currencies by authorized dealers and so Hawala transactions are illegal within the FEMA Act. It imposes penalties on people involving in Hawala transactions. Hawala supports the parallel black money market which hampers the growth in the country. There have been many cases in India involving Hawala transactions. However, in spite of the Government imposing measures to abolish the Hawala transactions, it is still existing with huge amounts involved.
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skills.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack










 Allow notifications
Allow notifications



Great Post . It’s really informative post. Keep sharing and posting like this.
Nice post. we are providing money exchange in chennai.
Hawala is an illegal money transfer from one country to another country in an illegal manner. Thank you for this information.