In this article, Jisnu Dutta who is currently pursuing M.A. IN BUSINESS LAWS, from NUJS, Kolkata, discusses Corporate governance of insurance companies in India. Process, compliance, best practices and relevant law.
Corporate governance of insurance companies in India. Process, compliance, best practices and relevant law
- The general business structures of the companies allow the managers to run the business under the guidance of the board members who in turn is answerable to shareholders of the company. Managers look into day to day business where as board will oversee manager’s job periodically with reference to set agreed goal and policy guidelines.
- The share holders have right to select director which ensures that most powerful directors are also answerable to the shareholder. However, in Indian scenario a typical organizational structure is often observed when the major share holder also act as a board member and manager.
- A company runs on the basis of perpetual succession to satisfy each and every stakeholder. The illustrative list of such stakeholder shall include customer, supplier, employee, manager, share holder, Government. Each and every party or stakeholder has one thing in common, that they have economic interest in a company.
- To satisfy their economic interest all the stakeholder gets into any or different kind of contractual or economic linkage with a company as permitted under the law. This economic interest could be fulfilled lawfully or unlawfully and also can be fulfilled in a biased way so to impair the due benefit of other deserving stakeholder.
Corporate governance is the process to prohibit fulfillment of economic interest unlawfully or unethically or in a biased manner towards any particular stakeholder.
- Ethical satisfaction of different economic interests is guided by either by set rules which encompass broad act (Example : income tax act in relation to Govt), company culture and practice (Example :Rewarding effective employee) or specific contracts (Example: Purchase agreement in relation to customer) in first part together with existence of supervisory body confirming the company action is in line with the Act ,culture or contract in second part and transparency providing the scope to review by any stakeholder in the third part.
- Corporate governance is the continuous process of maximizing shareholders equity ensuring fairness to all other stakeholders including employee, supplier, distributer, customer, banker, Government, project effected people etc. Corporate governance is a precondition for long-term success of an organization. This not only encompass the for profit companies but also include benevolent institution like nonprofit trust, educational institute like universities, administrative bodies of game or cultural activity
- Corporate governance is more important in the financial sector because financial companies act as intermediaries between investor and borrower. Failure of these companies to govern their business in a morally expected way would have long lasting impact on economy forcing it to contract. Insurance sector is a subclass in financial sector. The insurance sector in India is regulated by IRDAI (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India).
Insurance provides necessary safeguard towards unforeseen adverse future events. Insurance business uses the concept of risk pooling and probability of occurrence of loss event. Insurance is a legally binding agreement between insurer and insured that transfers part or full of risk from a policyholder to an insurance provider in return of premium paid by policy holder.
- Corporate governance in insurance sector is guided by the corporate governance guideline issued by IRDAI. IRDAI issued comprehensive Corporate Governance Guidelines on 18.05.2016 which will be applicable on insurance companies from FY 2016-17.
- The revised guidelines cover the broadly covers Corporate Governance practices, appointment of MD/ CEO and other Key Management Persons (KMPs) and the appointment of statutory auditors of insurers. The guidelines also contemplate to oversee the compliance position in regard to the adherence of corporate governance guidelines.
- Those Corporate Governance requirements of companies which were listed in the Stock Exchanges wad guided by the requisite compliance to Clause 49 of Listing Agreement of the Stock Exchanges. The Indian insurance companies are not listed in stock exchanges till date but IRDAI advised insurers to familiarize themselves with Corporate Governance structures and requirements appropriate for listed entities.
The IRDAI guideline squarely put the responsibility of good governance upon the board of insurance company where as IRDA will also oversee the maintenance of the stipulations in this regard. These guidelines are additional to the related provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 and any other laws or regulations framed there under. Where the requirements of these guidelines are in conflict with other rules or guideline as per statute the stricter guideline shall be followed.
The guidelines address various requirements broadly covering the following major structural elements:
- Overall Governance structure
- Constitution of Board of Directors
- Broad tasks of BOD.
- Control Functions to be exercised by board
- Formation of different mandatory committee and their function
- Disclosures requirement
- Outsourcing policy guideline
- Relationship with stakeholders
- Reporting to IRDAI for compliance
- Whistle blowing policy
- Evaluation of Board of Directors including Independent Directors
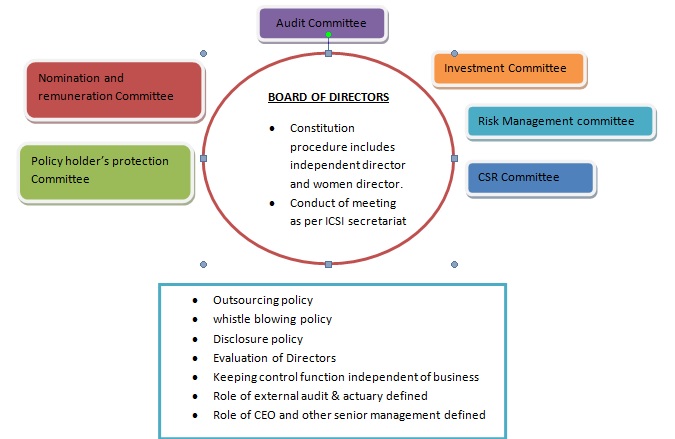
The following pictorial gives overall picture of the corporate governance in action as envisaged by IRDAI policy
Overall Governance structure
Broadly this guideline outlines the required structure of board of director to be adopted by insurance company, the manner by which they will exercise control through the appointment of actuary, auditor, remuneration committee, policy holders protection committee. They will have to adopt whistleblowing policy adequately safeguarding the whistleblower where as board or IRDA can have information regarding irregularities existing inside. The insurer shall submit report to the compliance of guideline to IRDAI.
Constitution of Board of Directors
The Board of Directors of insurance companies/corporations shall have minimum three independent directors. Though, this criterion is relaxed for insurance companies at their initial years. They can have two independent directors in the board in cases they have not crossed five years from the grant of Certificate of Registration to them.
- Any independent director shall have to fulfill the conditions stipulated under Section 149 of the Companies Act, 2013. Independent director shall be issued appointment letter which will lay down the terms and conditions, duties, responsibilities, payable sitting fees, etc. In case the number of independent directors falls below the required minimum as laid down, such vacancy needs to be filled up before the immediate upcoming Board meeting or three months from the date of such vacancy, whichever is later, under intimation to the Authority.
- In case, the Chairman of the Board is a non-executive director, the Chief Executive Officer shall be a whole time director of the Board. As required under Section 149 of the Companies Act, 2013, every insurer shall ensure that there is at least one woman director in the Board .The Board will create standards of ethical behavior which will help the employee to effectively resolve conflict. Board at macro level shall be committing to a corporate philosophy and governance that will also provide for the level of risk adoption properly linked to its investment policy and strategy to mitigation any additional risk.
- The board shall be held responsible for the action of the insurance company though Board can delegate its authority to different committee or executives. The composition of board shall be towards fulfilling different expectation from various stakeholders. The board shall review corporate policies from time to time to ensure the policy takes care of emerging needs and shall be adequately modified to become suitable with passage of time.
The Insurance Act prohibits an insurance intermediary/agent to be the director of an insurance company (except with prior approval of the IRDAI) .A financial intermediary sells policy to policyholder and therefore if put in board he may not be able to take a objective view because of his association with selling of policy and thereby earning commission.
Disclosures requirement by the board
Appropriate procedures and rules shall be maintained by the insurance company in the matter of conduct of board meeting and their committees. In this regard the Secretarial Standards of ICSI as issued from time to time and relevant provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 shall be complied with.
Broad tasks of BOD
The Board in consultation with the Key Management Persons should establish and duly evaluate strategies and policies to address the following broad range of areas.
- Financial projections on the capital requirements, estimated revenue, expenses and projected profitability with the objective to meet the expectations of policyholders and shareholders.
- Full compliance with the Insurance Act and adherence to secondary legislations.
- Broader policy for resolving conflicts of interest between stakeholders.
- Fair treatment of policyholders and employees.
- Establishing adequate business disclosures procedures.
- Establishing channel enabling whistleblower to raise their voice. Adequate protection to whistleblowers.
- Developing a corporate culture that rewards ethical behavior.
Control Functions to be exercised by board
Board should also put on place the following control mechanism,
- Suitable and stringent mechanisms for quantification of agreed risk level, identification of present risk level, identification of additional investment opportunity or ways to mitigate additional risks.
- Board is responsible for compliance and hence processes must be in place for ensuring compliance to not only applicable laws and regulations but also adherence to the policies approved by the board.
- Creation of an internal audit function who will review and assess the effectiveness of policies and ensure company’s adherence to internal control mechanical as well as its disclosures on strategies, policies or procedures to its stake holders.
- Formation of sustainable organizational structure must ensure that the control function remains independent from business operation.
Formation of different mandatory committee and their function
- Board, with the objective to preserve adequate board time, may delegate significant corporate responsibilities to different committees of directors after laying down overall objective, role and responsibilities. Board may form such committees to effectively monitor the company as a whole.
- IRDAI advises all insurers to mandatorily establish Committees for Policyholder Protection, Risk Management, Investment, Audit, Nomination and Remuneration, Corporate Social Responsibility (only for profit earning insurers).
- However, though not mandatory, additionally the board may form Committees such as Asset-Liability Management Committee, Ethics Committee, etc.
Audit Committee (Obligatory)
- In line with direction contained in Section 177 of the Companies Act, 2013 every Insurance company/corporation shall be required to constitute an Audit Committee.
- The function of Audit Committee is to oversee the accounting methods for preparation of financial statements, statement of cash flow and disclosure on annual and quarterly basis. Audit committee will also see the adherence to financial reporting standards by the insurance company and ensure dissemination of correct facts and figures. Audit committee may also set-up requisite procedures and processes to put in place required checks and control mechanisms.
- An independent director of the Board will act as chairperson of Audit Committee. She should have an accounting/finance/audit experience and may be a person with strong financial analysis background.
Investment Committee (Obligatory)
- An Investment Committee shall be set up by the Board of Insurance corporation .The committee shall comprise of the Chief Executive Officer Chief Risk Officer, Chief of Investment, the Actuary of insurer and at least two Non-Executive Directors.
- This Committee shall be responsible for recommending investment policy and strategizing the operational framework for investment operations of insurance company.
- The policy should have its focus on Asset Liability Management (ALM) supported by stringent internal control systems. The investment policy and operational framework shall encompass liquidity aspects as necessary for smooth operations, compliance with prudential regulatory norms applicable on investments, risk management function to ensure matching yield on investments and protection policyholders’ funds.
Risk Management Committee (Obligatory)
- Insurance is understood to be risky business as it assumes and distributes risk. successful running of insurance company is squarely dependent on how well the different risks are managed across the organization.
- Insurers are required to set up a risk management committee to formulate and monitor company’s risk management strategy in pursuit of developing an effective risk management system.
- Chief Risk Officer (CRO) shall guide and supervise risk management function.Different roles in the risk management committee shall be organized in such a way that it could monitor all the risks across all lines of business of the company and the Chief Risk Officer shall have direct access to the Board.
- Instead of focusing only on compliance this risk management committee shall focus on adding value to the business. This function should closely work with the finance function, without losing its independent and objective view required to assess and evaluate capital, finance and other operation related decisions.
Policyholder Protection Committee (Obligatory)
IRDAI is to protect policyholders’ interests as mandated by statute. IRDAI therefore, in turn, stipulates adoption of healthy market practices in terms of sales, marketing, advertisements, promotion, publicity, redressal of customer grievances, consumer awareness and education through promulgation of various secondary legislation. The list of relevant Regulations/Guidelines/Circulars is as appended below:-
- Regulations for Protection of Policyholders’ Interests, 2002
- Insurance Advertisements and Disclosure Regulations, 2002
- Guidelines on Advertisements, Promotion & Publicity of Insurance Companies and Insurance Intermediaries in May 2007.
- Guidelines on Grievance Redressal by Insurance Companies in July 2010 and Handling of Complaints/Grievances of Policyholders, April 2015
- Master Circular in the matter of Insurance Advertisements’August, 2015
- Guidelines on Public Disclosure for insurance companies
- Different Circulars on Handling and Disclosure of the Unclaimed Amounts of policyholder.
- Guidelines on Electronic Mode/online mode of Payments for Claims
Nomination and Remuneration Committee (Obligatory)
- IRDAI specifies to constitute the Nomination and Remuneration Committee in line with the provisions of Section 178 in Companies Act, 2013. Some of the Insurance Companies which have two independent committees one for Nomination and other for Remuneration may merge these two Committees with the Board approval, under intimation to IRDAI. The two companies shall be merged within 180 days from the date of issue of these corporate governance guidelines issued on 18.05.2016.
- The Nomination and Remuneration Committee shall be responsible to go through the declarations of intending applicants before their reappointment/ appointment/election as directors by the shareholders at the General Meetings. In addition to this, the Committee shall also scrutinize the applications of aspirants for appointment as the Key Management Persons.
- In the remuneration part, the Committee is required to determine on behalf of the Board or shareholders to determine remuneration or compensation packages for the CEO, the Executive Directors, Key management Persons of the company in adherence to the insurance company’s policy on remuneration or other relevant documents as deemed fit.
Corporate Social Responsibility Committee (Obligatory)
- Companies Act, 2013 in Section 135 stipulates constitution of a CSR Committee subject to fulfillment of certain conditions as mentioned in the above mentioned section. Similarly, Indian Insurance Companies has to set up a CSR Committee if the insurance company earns a Net Profit of Rs. 5 Crores or excess during last financial year passed.
- Further the ‘Net Profit’ shall be as shown in the financial statement of the Indian insurance company prepared in accordance with insurance act 1938.Any profit from any foreign branch or dividend from any other Indian company which is already complying section 135 of companies act shall not be included in the net income. Neither the net income is required to be recomputed as per the provisions of companies act.
Disclosure Requirements
The IRDAI (Preparation of Financial Statements and Auditors’ Report of Insurance Companies) Regulations, 2002, have prescribed certain disclosures requirement to be shown in the face of financial statements. Authority is also considering inclusion of additional disclosure requirements to be made by insurers at periodical intervals.
Before finalizing of such additional disclosures, In the meantime, the Board is required to ensure that the following information is prepared as per the relevant standards/formats to the extent available and the impact of any changes therein are also disclosed in the annual accounts:-
- Qualitative and Quantitative information about financial and operating ratios of the insurance company’s such as commission and expenses ratios, incurred claim etc.
- Required solvency margin vis-à-vis the actual solvency position of the insurance company.
- Insurers operating in life insurance business should disclose persistency ratio of policies offered by them
- Financial position including growth rate and current financial performance of the insurance company
- Descriptive commentary on the inside risk management organization.
- Details of claims intimated, claims disposed off and pending claims with details of period the data pertains to.
- Pecuniary relationships or transactions between Non-Executive Directors and the insurance company requires to be disclosed in the Annual Accounts.
- Element wise Disclosure of remuneration package(including incentives or ESOP) of MD & CEO and all other directors and Key Management Persons
- Payments/Advance made to any of the group companies from the Policyholders Funds
- Any other material information which have an impact on the insurer’s financial position.
Outsourcing policy guideline
- All outsourcing arrangements shall be as par the Board approved outsourcing policy & every outsourcing arrangements shall have to be approved by Committee of Key Management Persons.
- The Board or the Risk Management Committee have to be periodically apprised about different outsourcing arrangements entered into by the insurance company along with the confirmation about compliance to existing internal policy while making this outsourcing agreement.
- Company’s core functions shall not be outsourced by any insurance company except in cases where the same is specifically permitted by the IRDAI. Every outsourcing contract shall specific provision ensuring confidentiality of business data, processes and outputs where these data were used .Data shall continue to have ownership with the insurance company /corporation. The outsourced agency is required to hand over the data and all software programs/models etc on termination of the outsourcing arrangement in orderly manner.
- The management of the insurer shall have to monitor and review the performance of agencies to which different noncore jobs have been outsourced .The management is required to review at least once a year and file the report to the Board.
Reporting to IRDAI
- Insurers shall have to examine that how much compliance they are performing with respect to with these guidelines. The insurer have to take immediate action to achieve compliance in cases where already compliance is not made. It is expected that all the necessary compliance structure shall be put in place to ensure total compliance with the guidelines issued. This shall be effective from the financial year 2016-2017. In cases where such compliance is either too difficult to achieve or is not possible for any particular reason, the insurance companies shall have to write to the IRDAI for additional guidance in this regard.
- Company Secretary is required to be designated as the Compliance officer of each insurer whose duty shall be to monitor continuing compliance with these guidelines.
- Annual Report of insurance company shall have a separate certification from the Compliance Officer ( company secretary as mentioned above) in the format given in Annexure 8 of the guideline.
All insurers have to file a report on compliance status in respect to these Corporate Governance guidelines on annual basis. This report is required to be filed within 3 months from the end of financial year, i.e., before 30th June. The report is to be filed as par the format in the Annexure 9 of the guideline.
Whistleblower Policy
Insurers are advised to adopt an effective “whistle blower” policy, where-by employees can raise concerns internally about anticipated irregularities, governance related issues, or any other matter including financial reporting. These may also include a mechanism so that employee can confidentially report to the Chairman of the Board / Committee of the Board / Statutory Auditor.
Evaluation of Board of Directors including Independent Directors
- As stipulated under Schedule IV of Companies Act, 2013, independent directors are required to meet at least once in a financial year to evaluate the performance of non-independent directors. Similarly, Independent Directors shall be evaluated by the non-independent directors of the Board as given in the Schedule.
- The guideline also provides for Role of CEO & other senior functionaries, Role of Appointed Actuaries, External audit and Appointment of Statutory Auditors, Relationship with stakeholders in detail.
- This corporate governance guideline is applicable to all insurers from FY 2016-17 which is expected to induce ethical governance in the business of insurance in India.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack









 Allow notifications
Allow notifications



[…] Image Source […]