This article is written by Mariya Paliwala of 7th semester, student at Mohan Lal Sukhadiya University College of Law, Udaipur (Rajasthan).
Table of Contents
Aadhar Card or UIDAI
Aadhar is basically a 12-digit unique identification number which is issued by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), is a statutory authority regulated by Aadhar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and other subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act 2016. Under this Act UIDAI is responsible for aadhar enrollment and authentication which also includes the operation and management of all the stages of aadhar procedure. The procedure mainly includes developing the policy, procedure and system for issuing Aadhar numbers to individuals and perform authentication and also required to ensure the security of identity information and authentication records of individuals.
The main objective behind creating UIDAI was to generate Unique Identification Number (UIN) which is named as Aadhar. UIDAI has a very well planned Organisational Structure for the smooth and efficient functioning.
Meaning of Aadhar Card
Aadhar card is an identification card which consists of a 12-digit unique identification number generated and issued by UIDAI after undergoing due authentication process which deals with the looking of demographic information including name, address, place of birth, date of birth, etc, and Biometric information which involves digital fingerprints, two iris scan and a facial photograph. Mainly fingerprint and iris data are taken for authentication. Aadhar card is issued only to an India citizen, who is a resident of India so that the system can:
- Be strong enough to eliminate fake, fabricated and duplicate identity cards.
- It is the cost-efficient way for verification and authentication of identity of people.
Usage of Aadhar Card
- Identity card
There wasn’t any exclusive reason behind Aadhar card. This can be used for various reasons. Unlike, voter ID card, whose purpose is to permit the ID card holder to enjoy his political rights by taking part in electoral process. So aadhar card is a versatile card which can be used for all the governmental functions.
- Avail Subsidies
If in case any person is eligible to avail any kind of subsidies or benefits by the government then he/she may grab it through aadhar. For instance, the government has introduced a scheme wherein the citizens with poor economic background will be entitled for subsidies on LPG connection. All they needed to do is link their Aadhar number with their bank account, their amount of subsidy would directly come into the linked account.
- Easily available
Aadhar card is a document which is issued by the government. It is easily available online in the name of e-aadhar, an easy print out can be taken. It reduces the risk of the document being misplaced/stolen.
- Use of Aadhar in Government Scheme
Aadhar is the most important document which can be used to avail maximum of the government schemes and processes such as:
- LPG Subsidy
- Disbursing Provident Fund
- Jan Dhan Yojna
- Digital Life Certificate
- Opening bank accounts
- Acquisition of passport

Features of Aadhar Card
- Notion of Transparency
The notion of the government behind introduction of Aadhar was to increase the efficiency, good governance, transparency and to fulfill efficiently the targeted delivery of subsidies, services and benefits. Consolidated Fund of India is responsible to incur all such type of expenditure to every citizen of India through the unique identification number.
- Authenticate Digital identity
Another function of aadhar is to provide verified and authentic digital identity to the citizens of India.
- Secure confidentiality of identity
As all the verification and authentication work is done on the basis of biometrics, the security and confidentiality of identity is ensured.
Brief History
Back on the 28th of January 2009, UIDAI was established on the issuance of notice by the Planning Commission. Nandan Nilekani, the co-founder of Infosys was appointed as the head of the project by the then UPA government. Moreover, he was made the chairman of UIDAI, which is equivalent to the position of a cabinet minister. Nilekani launched the logo and the brand name “aadhar” in 2010, he was also of the view that he will be a supporter of the legislation which will be passed to favour data held by UIDAI. Further, UIDAI selected 15 agencies to provide training to all those people who will be involved in enrolment procedure. In January, 2012, UIDAI took a step forward and launched the online verification system for aadhar number. With the coming up of this innovation any telecom companies, banks, and government can find out that a person is a Indian resident or not by a single click.
Moreover, in 2017 the then Prime Minister Manmohan Singh launched an aadhar-linked direct benefit transfer scheme. The project was to introduce in 51 districts in 2013 and then it slowly made its root through out India.
Aadhar Services
Aadhar card is the most important document which helps to recognise the identity and the address of a person. Moreover, just providing Aadhar number to the Indian residents is not the only task of UIDAI. It also provides both offline and online services to the card holders to solve their queries and problems.
Aadhar Enrolment
Enrolment activities are carried by the Office of the Registrar General of India (RGI), which is established by UIDAI at every district and union territory. The activities pertaining to enrolment are exclusively done by RGI. Residents except from the state of Assam and Meghalaya, all the other states and UTs are ought to register at Aadhar enrolment centre/ aadhar enrolment camps/ permanent offices.

Aadhar enrolment can be done by adhering to the following steps:
- visiting the nearest enrolment centre,
- filling the enrolment form,
- getting demographic and biometric data captured,
- submitting identity proof and address proof,
- collect and acknowledge the receipt of enrolment ID.
Further, the following highlights must be acknowledged by before the enrolment:
- The aadhar enrolment is free of cost.
- A person going for the enrolment must take his identity and address proof.
- Apart from PAN card or any other government document, electricity and water bills are also accepted and considered as a valid identity proof. Wide range of identity are accepted and also given in the list of supporting documents.
- In case a person does not possess above common proofs, then the Certificate of Identity having photo issued by Gazetted Officer/Tehsildar on letterhead is also accepted as proof of identity. There must be a certificate of Address which contain photo issued by MP or MLA or Gazetted Officer. In case of rural areas, Tehsildar on letterhead or by Sarpanch or its equivalent authority, is accepted as valid proof of address.
Aadhar Update
There are various methods to update aadhar which are as follows:
- Online update
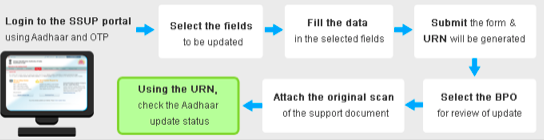
- By visiting the enrolment centre
In case of a change in the demographic details, the person may move to the permanent office and approach the operator for the change. The person needs to carry with him the 2 identity proofs which consist of it’s permanent address.
Document Verification is done by the operator keeping the following highlights in mind:
- Verification is done in those fields which require documentary evidence.
- Verification is normally done by the verifier who is appointed by UIDAI or Registrars present at enrolment centre or update centre.
- The verification procedure followed must also include DDSVP Committee Recommendations followed in the process of enrolment.
Form Filling and Acknowledgement

Form filling and acknowledgement is done by the operator on update client as requested by the resident. Handles spelling, language issues, transliteration, etc. Biometric sign off will be provided by the operator after the update request.
After this the resident gets an acknowledgement receipt with Update Request Number (URN) which can be easily tracked.
Aadhar Card Scan
Aadhar card scan can be done with the help of QR code by using a scanner.
Step by step process to scan QR code given in aadhar:
Step 1. UIDAI Secure QR Code – Windows Client
The person applying must download the UIDAI Smart QR Code Reader. Then double click the installer. After that click on Install button. On the successful installation, a prompt will pop up. Then open the UIDAI Smart QR Code Reader 4.0 for use.
Step 2. Handhold Scanner Device
The device is used for scanning the Secure QR code available on Aadhaar Letter/e-Aadhaar for displaying the demographic details including photograph of the Resident.
Step 3. Scan the QR Code using Scanner Device
- type mobile number and email in the boxes given to verify.
Linking Bank Account with Aadhar
There are various ways in which bank account can be linked with aadhar:
Through net banking
Step 1. Firstly login to www.onlinesbi.com
Step 2. Enter your user ID and password.
Step 3. Under the option “My Account”, click on the “Update Aadhaar with Bank accounts(CIF)”.
Step 4. Then enter profile password for Aadhaar Registration.
Step 5. A page will open where you will be asked to enter your Aadhaar number twice.
Step 6: Select “submit” button after entering your Aadhaar number.
Step 7: On successful linking of your Aadhaar with PAN a message will be displayed on your monitor screen.
Linking in a bank
In order to prevent the deactivation of the account, the Account holders can get their account linked with Aadhaar. Here is how it can be done easily:
- Fill the bank account Aadhaar linking application form. In order to find the Aadhar linking form visit your bank’s official website. If it is not available on the website, please visit a bank branch near you.
- Mention the bank account details and Aadhaar number.
- Attach a self-attested photocopy of Aadhaar card with the form.
- Submit the form and the Aadhaar copy at the counter.
- You will be asked to furnish your original Aadhaar card for verification.
- Your application will be accepted and it may take a few days to link your bank account with Aadhaar card.
- Once it is linked, you will get a notification on your registered mobile number.
The main objective behind linking the Aadhar with the bank account is that all the benefits and subsidies under government programs can be easily transferred to the bank account holder without any hurdle and with efficiency.
Linking Aadhar with PAN card
Step 1. Register at the income tax e filing portal, in case you are not already registered.
Step 2. The e-Filing portal must be logged in, under the Income Tax Department by entering the login ID, password and date of birth.
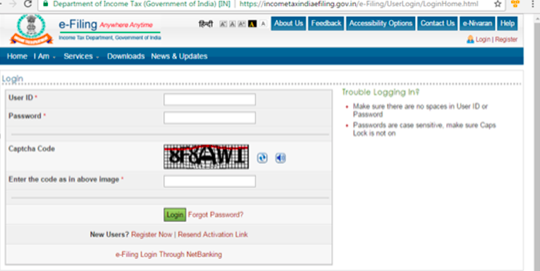
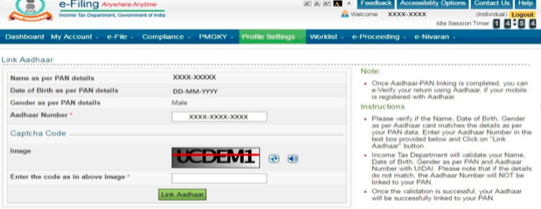
Step 3: When the site is logged in, a pop up window will appear asking you to link your PAN card with Aadhaar card. If you don’t see the popup,then move your cursor to blue tab on the top bar named ‘profile settings’ and click on ‘link aadhaar’.
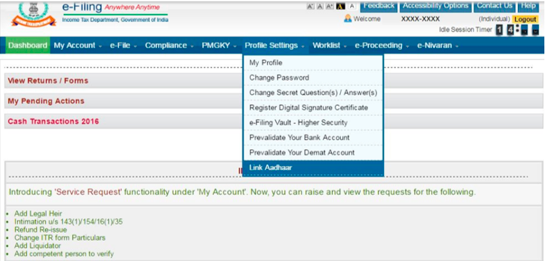
Step 4: Verify the essential details such as name, gender and date of birth, which was already mentioned as per the details submitted during registration on the e-Filing portal.
Step 5: After the details match, enter your Aadhaar number and captcha code and click on the “link now” button.
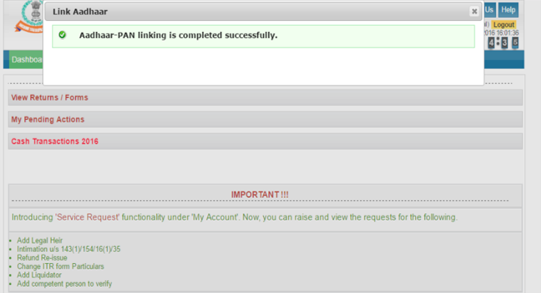
Step 6: You will receive a pop up mail on the successful linking of aadhaar with PAN card.
Aadhar card centre near me
In order to enrol for Aadhaar for yourself or for your family member, you will be required to visit an Aadhaar Enrolment Center. In case your Demographic details (Name, Address, DoB, Gender, Mobile Number, Email)is not up-to-date in your Aadhaar, you can get the same updated by visiting an Aadhaar Enrolment Center. Aadhaar holders children, who have turned as 15 years or others in need of updating Biometrics details including Fingerprints, Iris & Photograph are required to visit an Enrolment center too. Please get valid Address proof documents.
Find for a nearest Enrolment centre by selecting any of the following given mode:
Search By:
Aadhar card Problem
As every coin has two faces, aadhar brings with itself lots of efficiency and transparency but at the same time it carries with it some disadvantages leading to the problems faced by the citizens. Some of the most common problems are stated below:
- Misprints and spelling mistakes.
- Chances of leak of identity and demographic information.
- Biometric authentication is time consuming and not 100% accurate.
- Bank accounts linked with aadhar are likely to get hacked.
- Mis-match of gender and facial photograph.
- Address error.
- Relationship error.
- Name error.
- Lack of Awareness.
Aadhar legislation and Article 21 of the Constitution
Article 21 of the Constitution pertains to the right to life and personal liberty, wherein right to life includes right to privacy also. So with the coming up of Aadhar legislation it was felt by the people that capturing biometric information and recording demographic information is the interference in their privacy, thereby the state is infringing the citizen’s right to life under Article 21 (Part III) of the constitution.
In the case of KS Puttaswamy v. UOI which is also known as ‘Aadhar case’ was first filed by ninety-two year old Justice KS Puttaswamy, the 1st petitioner, who contended that Aadhar legislation must not be enforced on the citizens. On the ground that it was an infringement of the right to privacy of the citizens by the government and lack the legislative backing. In 2017 a judgement delivered by the Supreme Court passed a judgement wherein right to privacy was added to Article 21 of the constitution and passed a legislation called Aadhar Act so as to back the project by UIDAI.
Conclusion
Wherefore, it is well said that the grass always looks greener on the other side. Such procedure to collect data by the government is not only done in India but also in other countries like China. Earlier, when such legislation was absent there were various problems faced in governance like transferring subsidies under government policies, etc. Now, when it is implemented it is hampered because of the lack of awareness, procedural flaws etc.
Students of Lawsikho courses regularly produce writing assignments and work on practical exercises as a part of their coursework and develop themselves in real-life practical skill.
https://t.me/joinchat/J_0YrBa4IBSHdpuTfQO_sA
Follow us on Instagram and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more amazing legal content.
 Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack
Serato DJ Crack 2025Serato DJ PRO Crack









 Allow notifications
Allow notifications


